



































TLW's Sculptorscope™ (Sculptor Historyscope) |
By T.L. Winslow (TLW), the Historyscoper™ |
© Copyright by T.L. Winslow. All Rights Reserved. |
Original Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2016. Last Update: June 14, 2020. |








Westerners are not only known as history ignoramuses, but double dumbass history ignoramuses when it comes to sculpture and sculptor history. Since I'm the one-and-only Historyscoper (tm), let me quickly bring you up to speed before you dive into my Master Historyscope.
Some like their sex hard, some like it soft, but always wet and juicy, yet to become immortal you have to turn to dry stone and give it up forever, making it okay to go around naked? :)

About 38,000 B.C.E. the Aurignacian Lion Man (Lowenmensch) sculpture in the Hohlenstein-Stadel Cave in Germany is carved from mammoth ivory, becoming the oldest known animal-shaped and anthropomorphic sculpture, and oldest example of figurative art; discovered in 1939.

About 24,000 B.C.E. the Venus (Woman) of Willendorf is carved from limestone in Austria (-25K?); proof of a fertility cult, a matriarchal society, or just prehistoric porno?



About 2600 B.C.E. the pop. in the Indus Valley and Sarasvati regions begins to mushroom due to farming (ends -2000), building a large city by -2500 at Mohenjo-Daro in S Sind, Pakistan, with public bldgs. and sanitation, leaving the sculptures Dancing Girl and Priest-King.





In 1,343 B.C.E. Akhenaten officially moves the Egyptian capital from Thebes to Amarna, although the new city isn't finished for two more years, during which time the famous polychrome painted limestone (or limestone core covered with thin plaster) Bust of Queen Nefertiti is sculpted by Thutmose, and discovered in his workshop in Tell el-Amarna by German archeologists led by Ludwig Borchardt (1863-1938) in 1912, along with a Stela of Akhenaten and His Family; too bad, on Jan. 20, 2013 French Egyptologist Gustave Lefebvre (1879-1957) chooses the stela to go to the Egyptian govt., allowing the bust to go back to Germany, ending up in the Egyptian Museum in Berlin, after which the stela is suspected of being a fake.
About 750 B.C.E. the Greek Dark Ages (begun -1150) end, and the Greek Archaic Period begins (ends -480); having lost their knowledge of the surrounding seas, the Ionian Greeks begin exploring and colonizing Asia Minor and founding cities in Pontus (isolated rocky S coast of the Black Sea); by -650 abstract geometric patterning is replaced by naturalistic art, incl. nude dangly Kouroi (Gr. "male youth") statues.


In 717 B.C.E. Sargon II begins his royal residence of Dur-Sharrukin (modern-day Khorsabad), a planned city in modern-day N Iraq (9 mi. NE of Mosul) (finished in -704), which becomes capital #4 of Assyria; excavated in 1843 by Paul-Emile (Paul-Émile) Botta (1802-70) of France; the entrance to Sargon II's palace throne room features a pair of reliefs of a 16-ft.-high Winged Bull that combines features of a man (head), eagle (wings) and lion (tail); it ends up in the Oriental Inst. of the U. of Chicago.
In 488 B.C.E. the 73rd Olympiad sees tyrant Gelo of Syracuse (d. -48) win a victory in the chariot race, causing sculptor Glaucias of Aegina to make a statue of him, followed by more statues of Olympian athletes incl. Philon of Corcyra, Glaucus of Carystus, and Theagenes of Thasos. In 480 B.C.E. the 75th Olympiad sees Theagenes (Theogenes) of Thasos defeat Euthymus in boxing; later a statue of him is made by sculptor Glaucias of Aegina, which is scourged by a man who had a grudge against the athlete, after which it fell on him and killed him, causing the statue to be tried and convicted of murder and thrown in the sea, then retrieved after the Delphic Oracle declares that the country will be barren until it's back.

About 478 B.C.E. the 1.8m bronze Charioteer (Heniokhos) of Delphi is sculpted to commemorate the V of tyrant Polyzalus of Geta in Sicily in the Pythian Games; discovered in 1896.

In 472 B.C.E. the Doric Temple of Zeus in Olympia, Greece is begun (finished -456), complete with a giant 40-ft.-tall 22-ft.wide seated Statue of Zeus at Olympia (finished -435) by Phidias (Pheidias) (-480 to -430), which is later copied in the Abraham Lincoln Memorial in the U.S.; it is paid for by funds from the Elean defeat of Pisa; the architect is Libon of Elis.

About 460 B.C.E. the lifesize bronze Poseidon (Zeus) of Cape Artemision is sculpted, showing the Greek god hurling his trident or his thunderbolt at the east (Persians).

About 450 B.C. the bronze sculpture The Discobulus (Gr. "discus thrower") is finished by Greek sculptor Myron of Eleutherae, becoming famous and spawning Roman copies, which is good since the original is lost; in 1781 the Discobulus Palombara, a 1st cent. C.E. copy is discovered on the Esquiline Hill in Rome; in 1937 it is acquired for 5M lire by Adolf Hitler, who displays it in the Glyptothek in Munich, Germany until the end of WWII, after which it is returned in 1948; in 1790 another copy is discovered in Hadrian's Villa.

In 440 B.C.E. the Temple of Poseidon in Cape Sounion S of Athens is completed to replace the one destroyed by Xerxes I's Persian troops in -480, replacing a Persian trireme captured at the Battle of Salamis.

About 440 B.C.E. the bronze Doryphoros (Spear-Bearer) statue is cast by Greek sculptor Polykleitos (Polycletus) (Polycleitus) (Gk. "much renowned") of Sicyon/Argos, becoming one of the first examples of contrapposto (the figure rests most of his weight on one foot); the original is lost, and only marble copies survive.

In 438 B.C.E. the Parthenon (begun -447) on the Athenian Acropolis, dedicated to Athena Parthenos is completed; the statue of Athena by Phidias (Pheidias) (-480 to -430) is dedicated; there are few straight lines, all the steps are of different sizes, and the distance between each of the Doric (baseless) columns in the peristyle varies, all to give an illusion of strict balance.

About 436 B.C.E. Greek sculptor Agoracritus (Agorakritos) (born on Paros) becomes the favorite pupil of Phidias, their work later being confused; he sculpts the colossal Nemesis of Rhamnus, starting with a statue of Aphrodite which loses a contest with rival Alcamenes.
In 435 B.C.E. the Statue of Zeus at Elis is completed by the sculptor Phidias (Pheidias) (-480 to -430).

Late in the 5th cent. B.C.E. (-410?) the Etruscan bronze Mars of Todi statue is sculpted.

In the 4th cent. B.C.E. Glycon (Glykon) of Athens sculpts the Farnese Hercules, a copy of a work by Lysippus; found in the ruins of the Baths of Caracalla in Rome in 1599 C.E.



In 377 B.C.E. Greek sculptor Scopas (-395 to -350) of Paros moves to Athens, working there with Praxiteles for 25+ years, building the new Doric Temple of Athena Alea in Tega after the old one burns down in -394, with an ivory statue of Athena made by Endoeus (Endoios), which Augustus later moves to the Forum of Augustus in Rome; Scopas and Praxiteles found the Late Attic School of Sculpture. In 350 B.C.E. the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus is completed as the tomb of King Mausollos of Caria by sculptors Leochares, Praxiteles, Scopas et al. In 350 B.C.E. Scopas (b. -395) dies, leaving Bust of Meleager, Statue of Pothos (Desire) (which is much copied with different props), Statue of Aphrodite (copper), and Bust of Hygieia (daughter of Asclepius).


About 364 B.C.E. possibly legendary Athenian sculptor Praxiteles (Gr. "he who finishes his works"), sculpts a statue of Aphrodite of Knidos (Venus Pudica) (Modest Venus), modeled by Thespian courtesan Phryne (b. -371), becoming the first to sculpt the life-size nude female form, along with the statue of Hermes of Praxiteles (Olympia) and the Infant Dionysus; rediscovered in 1875 C.E. - this stupid knife dispenser is stuck?

About 330 B.C.E. the Red Figure Period of Greek art ends, and the Hellenistic Period of Greek Art (ends -31) begins, spreading with Alexander III the Great's conquests, only to be stopped by the Romans with the defeat of Cleopatra VII at Actium.


About 330 B.C.E. the 7.3' nude dangly Apollo Belvedere statue is sculpted of white marble by Greek sculptor Leochares, showing Apollo after having shot an arrow; a Roman copy is made about 130 C.E., which is discovered in 1489 in Anzio, Italy, and ends up in the hands of Pope Julius II (Giuliano della Rovere); in 1755 German art historian Johann Joachim Wincklemann calls it the best example of the Greek aesthetic ideal, after which it becomes an icon of the Enlightenment; in 1796 Napoleon steals it from the Vatican, which gets it back in 1815 after his fall; about 325 B.C.E. Leochares also sculpts Diana of Versailles (Diana Chasseresse) (Artemis, Goddess of the Hunt), which is is given in 1556 by Pope Paul VI to Henry II of France, who places it in his Jardin de la Reine in Fontainebleau, after which in 1602 Henri IV moves it to the Louvre, after which in 1710 Louis XIV moves it to Versailles; a miniature replica stands on the fireplace mantle in the first class lounge aboard the Titanic when it sinks; Leochares also sculpts ivory-gold statues of Philip II of Macedon, Alexander III the Great, Olympias, Amyntas III, and Eurydice I, exhibited in the Philippeion in the Altis of Olympia, built by Philip II to celebrate his V at the Battle of Chaeronea in -338.




About 300 B.C.E. Greek sculptor Lysippus (Lysippos) (b. -390) (teacher of Chares of Lindos) dies in Sicyon, Greece after having cranked out 1.5K+ bronze sculptures in his well-manned workshop, and seen many replicas circulate on the market; known for a one-to-eight scale for the head and total height of the body, making them appear slender and taller, with exaggerated facial features.

In 293 B.C.E. the 108-ft. (33m) (70 cubits) Colossus of Rhodes (the Greek god Helios, patron god of Rhodes) (finished in -282) is begun by Greek sculptor Chares of Lindos to celebrate the V in -305 over the invading Macedonians under Demetrius I, using iron tie bars with a shiny brass skin that never tarnishes, mounted on a 50-ft.-high white marble pedestal near the Mandraki Harbor entrance, all compliments of materials and weapons left behind; too bad, it is destroyed in an earthquake in 226 B.C.E.; Chares commits suicide before the statue is finished because he grossly underbid the contract, and it is finished by Laches of Lindos?
About 280 B.C.E. Greek sculptor Xenokrates of Sicyon flourishes, becoming the world's first art historian and leaving several vols., making a fan of Pliny the Elder.

In 220 B.C.E. the flaccid, er, reclining Statue of the Dying Gaul is erected by Attalus I in Pergamon about this year to commemorate the big V against them in -241.

About 190 B.C.E. the Winged Victory of Samothrace is carved for the prow of a ship (by Pythokrotos of Lindos?); rediscovered in Apr. 1863 C.E. by French amateur archeologist Charles Champoiseau.

About 150 B.C.E. the strangely Christ-like Laocoon (Laocoön) Group is sculpted by Hagesandros (Agesander), Athenedoros (Athenodorus) and Polydoros (Polydorus) of Rhodes, depicting the brother of Anchises (father of Aeneas), a priest of Poseidon being strangled by sea serpents along with his two young sons Antiphantes and Thymbraeus at the orders of Minerva after he tries to warn the Trojans that the Trojan Horse is a trick, uttering the immortal soundbyte: "Timeo Danaos et dona ferentes" (Beware of Greeks bearing gifts) (I fear Greeks even when they bear gifts); discovered in Rome in 1506 C.E., its anatomical accuracy and depiction of agony wows hard-to-please German critic Gotthold Lessing.

About 100 B.C.E. Greek sculptor Agasias of Ephesus (son of Dositheus) sculpts the life-sized 78-in (199cm) Borghese Gladiator in Ephesus; found in 1610 in Anzio S of Rome in the ruins of a seaside palace of Emperor Nero on the site of ancient Antium.

About 100 B.C.E. the 6.7' (203 cm) statue of Venus de Milo on the Greek volcanic island of Milo (Melos) (most SW island of the Cyclades) is sculpted; discovered in 1820 C.E.

In 52 B.C.E. victorious Roman gen. Pompey (Ganaeus Pompeius Magnus) (-10 to -48) is elected consul, and tries to gain popularity by putting on bigger shows in the arenas, building the first stone theater in Rome, and a public garden inside a square of new public bldgs., incl. the Curia of Pompey, a meeting hall for the Senate featuring a larger-than-life Statue of Pompey the Great in the Forum of Augustus playing Alexander the Great, but retaining Pompey's unique "curly quif" of hair at the center of his forehead?; his rival Julius Caesar is later assassinated under the statue.

In the 1st cent. C.E. the dangly marble Statue of Castor and Pollux (AKA the Dioscuri) is sculpted, ending up in La Granja Palace in San Ildefonso, Segovia, Spain until 1839, followed by the Prado in Madrid.

About 20 C.E. the 2.03m bronze Statue of Augustus of Prima Porta of Roman emperor #1 (-27 to 14) Augustus (-63 to 14) is vowed to him by the Roman Senate, portraying him as divine as he strides into battle barefooted; a white marble copy is made for his wife Livia Dursilla (Julia Augusta), and discovered in her villa Ad Gallinas Albas near the 9th mile marker of the Via Flaminia close to the Prima Porta imperial gate near Rome on Apr. 20, 1863; a gift from her son Tiberius Caesar?; based on the 5th cent. B.C.E. statue "Doryphoros" (Spear Bearer) by Polykleitos, it shows Augustus barefoot like a god, while skipping the old Roman republican style of showing leaders as old and wise and reverting to the classical Greek style of leaders enjoying youth and strength, esp. Alexander the Great; Cupid riding a dolphin helps support the statue, connecting him with Cupid's mother Venus via his adopted father Julius Caesar; his heroic armor (cuirass) depicts the retrieval of the standards of Crassus' army from the Parthians, in which Tiberius played a role as intermediary.

About 54 C.E. the 5-sided 5-layered Great Cameo of France sardonyx cameo is created in Rome, showing the main figures of the Julio-Claudian Dynasty incl. Augustus and Livia, Drusus the Younger and Drusus the Elder, Tiberius, Germanicus, Agrippina the Elder, Claudius and Agrippina the Younger; it ends up in the treasury of the Byzantine Empire, then the treasure of Sainte Chapelle in the 1270s under the title "Triumph of Joseph at the Court of the Pharaoh", after which Louix XVI orders it entered in the Cabinet des Medailles on May 1, 1791; too bad, it is stolen during the 1789-99 French Rev., and recovered in Amsterdam with its gold frame replaced by bronze one, only to be lost again until 1912.


Help stop gingivitis before it starts? On Aug. 25, 79 C.E. Roman historian Pliny the Elder (b. 23) dies in Stabiae, Campania while attemping the rescue by ship of a friend and his family from the Mt. Vesuvius eruption after the wind won't allow his ship to leave the shore (vulcanized?), leaving Natural History (Historia Naturalis) (Historia Naturalis) (37 vols.), which contains all the known science of the day, incl. astronomy (attacking magic), geography, anthropology, zoology, botany, agriculture, pharmacology, metallurgy and mineralogy incl. Roman gold and copper mining, and a history of Greek and Roman painting and sculpture, also info. on the art of soapmaking, learned from the Gallic Celts, who make a mixture of tallow and wood ashes which they call saipo, and use to wash their long wild hair; mentions Escargo as an elite food; in 1469 it becomes the first scientific book to be printed in the West with the Gutenberg printing press: "In vino veritas" (In wine there is truth); "True glory consists in doing what deserves to be written and in writing what deserves to be read"; "Among these things but one thing seems certain: that nothing certain exists, and that nothing is more pitiable or more presumptuous than man."

About 191 C.E. a bust of Roman emperor #18 (177-92) Commodus (Lucius Aurelius Commdus) (161-92) (son of Marcus Aurelius) is sculpted, portraying him wearing a lion skin and carrying a club to emulate Hercules.

About 305 C.E. the porphyry The Four Tetrarchs sculpture is created for the porch of the Philadelphion in Constantinople in a new anti-classical style; in 1204 during the Fourth Crusade the Venetians steal it, and it ends up in St. Mark's Basilica in Venice.


About 970 C.E. the Gero Crucifix (Cross), commissioned by Cologne archbishop (969-76) Gero (900-76) in the Cologne Cathedral becomes the first monumental crucifix in N Europe, and the oldest to survive to modern times, becoming the first great example of the revival of large sculpture since Roman times.


In 1060 the Romanesque Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela in Santigo de Compostela, Galicia, Spain is begun (finished in 1211), featuring the Portico of Glory (Portico da Gloria), commissioned by Ferdinand II of Leon and designed by architect-sculptor Master Mateo (1150-1217), finished in 1188; to the W is the Praza do Obradoiro (Port. "Square of the Workshop").


In 1147 the Cluniac Saint-Lazare d'Autun Cathedral in Autun, Burgundy, France (begun 1120) is finished, containing realistic sculptures by Giselbertus (Ghiselbertus) (Gislebertus) of Autun, incl. "The Last Judgment" and "The Temptation of Eve", which becomes the first large scale nude in Euro art since antiquity, paving the way for the Gothic style.

In 1166 the Brunswick Lion is sculpted for Welf duke Henry the Lion for his Dankwarderode Castle in Braunschweig (Brunswick), becoming the first hollow casting of a figure since antiquity.

In the 1230s the anon. near life-size German Gothic Bamberg Horseman (Bamberger Reiter) stone equestrian statue is sculpted for the new (1237) Bamberg Cathedral in Germany, becoming the symbol of the city of Bamberg, Bavaria, becoming the first of its kind since antiquity.





In 1408-15 Italian Florentine early Renaissance sculptor Donatello (Donato di Niccolo di Betto Bardi) (1386-1466), Clothed Statue of David (marble sculpture) (1408-9); commissioned to be mounted on top of Florence Cathedral, it proves to small to be seen from the ground, and is taken back to the workshop until 1416, when it is mounted in Palazzo della Signoria. In 1408-15 he produces St. John (sculpture). In 1433 he finishes his Nude Statue of David (bronze statue) (begun 1425), the first freestanding nude male sculpture made since antiquity, and first unsupported standing bronze work cast during the Renaissance; a nude dangly statue with David sporting a strange gay hairstyle and bonnet; stands in the center of the Medici Palace courtyard until 1440; not really finished until the 1440s? In 1457-64 he sculpts Judith and Holofernes, becoming one of the first Renaissance sculptures to be conceived in the round.

In 1438 after seeing him in the Council of Ferrara, Pisa-born Italian artist Pisanello (1395-1455) sculpts a Portrait Medal of Byzantine Emperor John VIII Palaeologus, becoming the first-ever portrait medal, great for collectors.

In 1447 Florentine sculptor Luca della Robbia (1399-1482) sculpts The Genoa Madonna, which becomes a favorite for modern Christmas stamps.



In 1483 Florentine painter-sculptor Andrea del Verrocchio (1435-88) finishes the statue Christ and Doubting Thomas (begun 1467) for the Orsanmichele in Florence. On Oct. 10, 1488 he dies in Venice, leaving his masterpiece, Equestrian Statue of Colleoni (-1475) (begun 1478) unfinished (a breakthrough because one of the horse's legs doesn't touch the base).




In 1498 workaholic Italian Florentine sculptor Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (1475-1564) finishes the marble sculpture Pieta (Pietà) in Rome; larger-than-life-sized, it depicts the lifeless Christ in the lap of the mourning Virgin Mary; sculpts himself as Nicodemus; after hearing a group of sightseers erroneously attribute his work to another sculptor, he chisels his name into it, but regrets it later and never signs another work - I'll never be a cicerone? In Jan. 1504 after working day and night since 1501 under dripping water, rarely taking his shoes off, Michelangelo finishes sculpting his dangly 16'4" Carrara marble Statue of David (most famous penis in history?), and unveils it to the Florentines, who adopt it as a symbol of their city and its republican aspirations, and make it the first statue displayed on a plinth since Roman times (they are young, beautiful David with the big slingshot and pouch of smooth stones at the ready, and the Medicis are big bad dumb Goliath?); the hard work doesn't seem to shorten Big Mike's lifespan any? In 1513-15 he sculpts Statue of Moses as part of the tomb of Pope Julius II in the della Rovere family tomb in San Pietro in Vincoli (St. Peter in Chains) Basilica in Rome; he portrays him with horns protruding from his head because of a Bible mistranslation of "rays of light"? (or because it's easier to make?).


In 1507 German sculptor Peter Vischer the Elder (1455-1529) designs the Renaissance-style Shrine of St. Sebaldus in St. Sebaldus Church (Sebalduskirche) in Nuremberg, with a Gothic canopy and a statuette of himself, becoming his masterpiece (finished 1519).


In 1534 Florentine sculptor Baccio (Bartolommeo) Bandinelli (Brandini) (1493-1560), known for insane jealousy of Michelangelo and Benvenuto Cellini finishes the 5.05m marble sculpture Hercules and Cacus (1525-34) in the Piazza della Signoria in Florence; it stands to the right of the entrance of the Palazzo Vecchio.
 "
"

On Apr. 27, 1554 Benvenuto Cellini (1500-71) debuts his bronze sculpture Perseus with the Head of Medusa (1545-54) in the Loggia dei Lanzi in the Piazza della Signoria in Florence, joining Michelangelo's David, Donatello's Judith and Holofernes, and Bandinelli's Hercules and Cacus; the first statue since antiquity where the base incl. a figurative sculpture forming an integral part of the work.





In 1562 after moving to Florence, Italy in 1553, Douai, Flanders-born sculptor Giambologna (Jean Boulogne) (Giovanni Bologna) (1529-1608) sculpts Sampson Slaying a Philistine, followed by The Rape of the Sabine Woman (1574-82), and Hercules Beating the Centaur Nessus (1599); he leaves the sculpture Architettura, a nude woman holding a compass and a square ruler.

In 1618-9 the bronze Manneken Pis (Dutch "Little Pissing Man") Fountain in Brussels is designed by Jerome Duquesnoy the Elder, becoming the symbol of Brussels; in 1965 it is switched with a replica so it can be kept safe in the city museum.









In 1621-2 young Naples-born Italian sculptor-architect Gianlorenzo (Gian Lorenzo) Bernini (1598-1680), sculpts The Rape of Proserpina, followed by Neptune and Triton (1622-3), and Apollo and Daphne (1622-5), showing Peneus' maiden daughter turning into a tree to escape the Cupid-struck Phoebus Apollo. In 1647-52 after inventing the Baroque Style of sculpture to create agitprop for the Counter-Reformation, the mature artist sculpts the white marble The Ecstasy (Transverberation) of Saint Teresa of Avila in the Cornaro Chapel of Santa Maria della Vittoria in Rome. In 1655-7 the old fart sculpts Daniel and the Lion for the Chigi Chapel in the Basilica of Santa Maria del Popolo in Rome, showing him praying while the tamed lion licks his right foot, followed in 1661 by Habakkuk and the Angel, facing the preceding sculpture, in which an angel pulls on his hair to make him take food to Daniel in the lion's den. In 1679 he sculpts his last work Salvator Mundi, a bust of Christ.




In 1634 after arriving in Rome and obtaining patronage from the Borghese and Barberini clans, Bologna-born Italian Baroque sculptor Alessandro Algardi (1598-1654) (rival of Gianlorenzo Bernini along with Francesco Borromini and Pietro da Cortona) gains a commission to sculpt a funeral monument for Pope Leo XI, which he completes in 1644; meanwhile in 1640 he completes a colossal statue of Philip Neri for Santa Maria in Valicella, followed in 1641 by a sculpture of St. Paul's beheading for the church in San Paolo, Bologna, establishing his rep; in 1644 Barberini Pope Urban VIII dies hopelessly in debt, causing his relatives to flee Rome and the Barberini family and their favorite artist Gianlorenzo Bernini to fall out of favor, giving Algardi his big chance, starting with a bronze statue of new pope Innocent X; in 1646-53 he sculpts the marble panel of Pope Leo I and Atilla the Hun (Fuga d'Attila) for St. Peter's Basilica before dying in Rome on June 10, 1654.


In 1653 after Girolami Rainaldi and his son Carlo Rainaldi begin it and begin quarreling, Gianlorenzo Bernini's rival Francesco Borromini (1599-1667) designs Sant'Agnese in Agone (Piazza Navona) Church in Piazza Navona (Agone), Rome, dedicated to St. Agnes, who died there in 304 C.E.; the Aswan granite Fountain of the Rivers (Fontana dei Quattro Fiumi) in front of Pope Innocent X's Palazzo Pamphili and Sant'Agnese in Agone, designed by Bernini features statues of river gods Nile and Ganges, allegedly shielding their eyes from the ugliness of the church, after which Borromini adds a statue of St. Agnes to the facade of his church, pretending to gaze past the fountain?; as the fountain is started during a famine in 1646, the public is vocally against it and on the verge of riot, but when it is unveiled on June 12, 1651 its size and beauty overwhelm them with pride and wonder.



![Tomb of Galileo Galilei [1564-1642] by Giambattista Foggini (1652-1725)](images/fogginigalileotomb.jpg)
In 1675 Florentine Baroque sculptor Giovanni Battista (Giambattista) Foggini (1652-1725) sculpts the marble sculpture The Adoration of the Shepherds; in 1676 he becomes the court sculptor for new grand duke of Tuscany (1670-1723) Cosimo III de' Medici; he goes on to become known for small bronze statues incl. "Chained Captive, Africa" and "Chained Captive, Asia", marble busts of Cosimo III de' Medici (1683 and 1718), Ferdinando de' Medici (1683), and Ferdinando II de' Medici (1690), and Galileo Galilei's Tomb in the Basilica of Santa Croce, Florence.


In 1676 French sculptor Nicolas Coustou (1658-1733) moves from Lyons to Paris, and goes on to work his way up to #1 sculptor along with his brother Guillaume Coustou the Elder (1677-1746) and his son Guillaume Coustou the Younger (1716-77), creating a school that cranks out the marble people; too bad, many of them are destroyed in the 1789 French Rev.


In 1682 after sculpting works in Rome, Florence, Nice, Aix-en-Provence, Toulon, Cuers, La Coitat, Lorgues, and Genoa before ending up back in Marseille, Marseille-born French sculptor Pierre Paul Puget (1620-94) sculpts Milo of Croton, followed by Perseus and Andromeda (1684), and Alexander and Diogenes (1685), all of which end up in the Louvre.








On May 1, 1703 the Russians take Nienshanz Fortress at the mouth of the Neva River, and drive the Swedes from the Neva Delta, then seize Noteburg and rename it Schlusselburg; on May 16 Tsar (1682-1721) Peter I the Great (1672-1725) pissed-off at his Moscow nobles failing to become kulturny and adopt Western culture, officially founds St. Petersburg (modern-day pop. 5.3M) on the banks of the Neva River on territory he just took from Sweden as Russia's "Window on the West" (modern pop. 4.7M), using serfs as expendable slaves; "A giant built it; lacking stones/ "He paved the swamps with human bones" (Mikhail Dmitriev); Peter I builds the Fortress of St. Peter and St. Paul on a small island in the river on May 27, 1703-1740, designed by Swiss Italian architect Domenico Trezzini (1670-1734), who goes on to design Kronstadt (1704) on Kotlin Island 19 mi. W of St. Petersburg, St. Peter and St. Paul Cathedral (1712-33) (world's tallest Orthodox Catholic bell tower), Peter the Great's Summer House (1710-14), the Alexander Nevsky Monastery (1710-13), the Winter Palace (1711-53), and the Twelve Collegia (Colleges) Bldg. Complex (1722-44) (main bldg. of St. Petersburg U.), founding Petrine Baroque, which departs from the Naryshin Baroque of Moscow and follows the Dutch, Danish, and Swedish (Flemish Renassance) styles; in 1709 Peter I begins the Peterhof Palace (Dutch "Piterhof" = Peter's Court), an attempt to ape Louis XIV's Versailles Palace, causing it to become known as "the Russian Versailles", with Domenico Trezzini as the main architect in 1714, succeeded in 1716 by Paris-born Jean-Baptiste Alexandre Le Blond (1679-1719) (Blond, James-Baptiste Blond)?, with his teacher, Versailles landscaper Andre (André) Le Notre (Nostre) (1613-1700) hired to design the gardens; the Grand Cascade of 64 fountains, modelled on Louis XIV's Chateau de Marly features the Samson Fountain (1736), with a 66-ft.-high water jet, which is upgraded in 1800-2 by local Russian Neoclassical sculptor Mikhail Ivanovich Kozlovsky (1753-1802), a gilt bronze statue of Greek god Samson tearing open the jaws of a lion to represent Russia's big V over Sweden in the Great Northern War (1700-21), with the lion representing Sweden's coat of arms, and Samson representing Russia's big V on St. Sampson's Day; in 1747-56 Italian architect Francesco Bartolomeo Rastrelli (1700-71) is hired by Tsarina Elisabeth to design an expansion along with the Winter Palace; Trezzini's architect son Pietro has Peter I the Great as a godfather; this year 8-y.-o. black African slave Abraham (Ibrahim) Petrovich Gannibal (Hannibal) (1696-1781), who claims he was kidnapped from a royal tribal family in Africa is presented by a Russian diplomat as a gift to Peter I the Great, becoming his adopted son, and rising quickly to a 5-language linguist, civil engineer, diplomat, and gen. (Europe's first black intellectual?) - so cute everybody should own one?





In 1710 as part of the rebuilding of Dresden after the 1685 fire, German Baroque sculptor Balthasar Permoser (1651-1732) and German architect Matthaus Daniel Poppelmann (Pöppelmann) (1662-1736) design the Zwinger Palace in Dresden for Augustus II the Strong of Saxony (finished 1728), featuring the Nymphenbad Fountain and the Wallpavilion, with sculptures by Permoser.









In 1725 after winning the Prix de Rome in 1723 and spending a year there studying the works of Bernini et al., Nancy-born French Baroque-Rococo sculptor Lambert-Sigisbert Adam the Elder (l'Aine) (1700-59), son of Jacob-Sigisbert Adam sculpts his first statue of Neptune; in 1732 after a competition is organized by Pope Clement XII, his design for the Baroque Trevi Fountain in Rome (completed in 1762) is unanimously accepted by the committee, which then turns around and selects Florentine architect Alessandro Maria Gaetano Galilei (1691-1737), then after an outcry against Florentines switches to genuine Romans Nicola (Niccolo) Salvi (1697-1751) and his apprentice Luigi Vanvitelli (Lodewijk van Wittel) (1700-73), pissing-off Adam and causing him to return from Rome in 1733; the fountain is finished in 1762 by sculptor Pietro Bracci (1700-73), who sculpts the colossal statue of Oceanus (Neptune) from a plaster model by Cassano Magnago, Lombardy-born sculptor Giovanni Battista Maini (1690-1752). in 1737 Adam follows with The Triumph of Neptune Stilling (Calming) the Waves, which is placed in the Louvre (home of the French Academy, which he is elected to this year); in 1737 he follows with the colossal group The Triumph of Neptune and Amphitrite, which is later (1740) cast in lead for the central fountain in the Bassin de Neptune in Versailles, establishing his rep. and insuring his income; in 1740 he also scallops, er, sculpts Child Being Pinched by a Lobster; Frederick II the Great of Prussia becomes a fan, hiring him to sculpt two works for his Sanssouci Palace incl. "Hunting and Fishing", after which his younger brother Francois Gaspard Adam (1710-61) becomes Freddy's chief sculptor in 1747-60; his sister Anne Adam goes on to become the mother of Claude Michel AKA Clodion, who apprentices in his studio; too bad, the work of Adam and his sculptor brothers Nicolas-Sebastian Adam and Francois Gaspard Balthazar Adam proves too Berniniesque for later critics, who try to forget them.




In 1748 18-y.-o. Paris-born French Neoclassical sculptor Augustin Pajou (1730-1809) wins the Prix de Rome, going on to produce busts of Buffon, Madame du Barry, and Bossuet that end up in the Louvre, and in 1761 at age 30 exhibits Pluton, dieu des Enfers, tenant Cerbere enchaine (Cerbère enchaîné) (Pluto, God of the Underworld Holding the Chained Cerberus), which also ends up in ditto; in 1780 he produces the statue Mercury, God of Commerce; in 1799 he produces the statue Fidelity, the Mother of Constant Love.



In 1753 the 2nd cent. C.E. stone Molossian Guard Dog Statue AKA the Jennings (Duncombe) (Alcibiades) Dog Statue, a copy of a 2nd cent. B.C. bronze statue taken by the Romans after they conquered the Molossian city of Epirus is discovered by English antiquarian Henry Constantine Jennings (1731-1819) in the workshop of Italian sculptor Bartolomeo Cavaceppi (1716-99), causing him to become known as Dog Jennings.

In 1762 86 ft. x 161.3 ft. Trevi Fountain in Palazzo Poli in Trevi, Rome at the junction of three roads (It. "tre vie") of the ancient Aqua Virgo is completed, designed by Nicola Salvi and completed by Pietro Bracci, becoming the largest Baroque fountain in Rome; barrels of water from it are sent across the Tiber River to the Vatican for cents.; people begin throwing coins into it, which are collected and given to charity; the belief is that one day they will be granted a safe return; later featured in several films incl. "Roman Holiday" (1953), "Three Coins in the Fountain" (1954), and "La Dolce Vita" (1960); refurbished in 1998; watch video; watch video.

In 1768 French Rococo sculptor Etienne (Étienne) Maurice Falconet (1716-91) begins The Bronze (Copper) Horseman, a monument to Peter the Great in St. Petersburg (finished 1782), named after the 1833 poem by Alexander Pushkin; its pedestal is the 1,250-tonne Thunder Stone, largest stone ever moved by humans (until ?).


In 1775 York, England-born John Flaxman (1755-1826) is hired by potter Josiah Wedgewood to model reliefs for the company's jasperware and basaltware, going on to produce "The Dancing Hours" (1776-8), "The Apotheosis of Homer" (1778), and "Hercules in the Garden of Hesperides" (1785); in 1780 he begins sculpting grave monuments, incl. Thomas Chatterton (1780), Mrs. Morley in Glouchester Cathedral (1784), and Rev. Thomas and Margaret Ball in Chichester Cathedral (1785).



In 1783 Possagno, Venice-born Italian Neoclassical sculptor Antonio Canova (1757-1822), known for his lifelike marble skin sculpts Theseus Vanquishing the Minotaur, followed by Psyche Revived by Love's Kiss (1787).


In 1788 London-born English sculptor Thomas Banks (1735-1805) sculpts Shakespeare Attended by Painting and Poetry after being commissioned by John Boydell for 500 guineas for his new Shakespeare Gallery in Pall Mall, which opens in May 1789; the pedestal reads: "He was a Man, take him for all in all, I shall not look upon his like again"; moved in 1871 to the garden in Shakespeare's home of New Place, Stratford-upon-Avon.




In 1788 Prussian architect Carl (Karl) Gotthard Langhans (1732-1808) begins the Neoclassical Brandenburg Gate (Brandenburger Tor) (originally the Friedenstor or Peace Gate, dedicated to Eirene, goddess of peace) in Berlin (finished 1791), commissioned by Friedrich Wilhelm II to represent peace, based on the Propylaea in Athens, becoming the first structure in Langhans' "Athens on the River Spree"; it features six Doric columns and five passageways on each side, of which the public is only allowed to use the outermost two; a Quadriga (chariot pulled by four horses) sits atop the gate, sculpted by Berlin-born sculptor Johann Gottfried Schadow (1764-1850); it is built on the site of a a former city gate that marked the start of the road from Berlin to Brandenburg an der Havel, capital of the margaviate of Brandenburg; after the fall of Hitler in 1945, it ends up incorporated into the Berlin Wall by the Commies; Schadow goes on to sculpt portrait statues of Frederick II the Great, Martin Luther, Goethe, Wieland, and Fichte, along with the Prinzessinengruppe, hugging statues of Crown Princess Louise and her sister Frederica.

In 1795 French sculptor Jacques-Edme Dumont (1761-1844), son of sculptor Edme Dumont and father of sculptor Augustin-Alexandre Dumont sculpts a terracotta Statuette of the Mythological Paris.




On Aug. 15, 1806 French Rococo sculptor Claude Michel (Clodion) (1738-1814) and neoclassical architect Jean Francois Therese Chalgrin (1739-1811) begin the 164-ft. Arc de Triomphe in Paris to trumpet Napoleon's overarching you know whats; in 1811 French architect Jean-Nicolas Huyot (1780-1840) takes over for Chalgrin; it is interrupted during the Bourbon Restoration of 1814-30, and finally inaugurated on July 29, 1836. On July 29 the 164' x 148' x 72' (50m x 45m x 22m) Arc de Triomphe (commissioned by Napoleon on Aug. 15, 1806 after the V at the Battle of Austerlitz) on the right bank of the Seine River in Paris is completed at the center of a duodecagonal configuration of 12 radiating avenues.


In 1815 Paris-born French sculptor Etienne-Jules (Étienne-Jules) Ramey (fils) (1796-1852), son of Claude Ramey and pupil of Pierre Cartellier sculpts Ulysses Recognized by His Dog Argos; in 1826 he sculpts Theseus and the Minotaur, which ends up in the Jardin des Tuileries in Paris.




In 1815 the 15-ft. (5m) 20-ton Waterloo Vase is sculpted by London-born English sculptor Sir Richard Westmacott (Jr.) (1775-1856) (student of Antonio Canova) from a single piece of Carrara marble originally hewn in Tuscany for Napoleon to celebrate his coming V in Russia and presented to the Prince Regent (later George IV) by Grand Duke Ferdinand of Tuscany complete with bas-reliefs of George III on his throne and loser Napoleon unhorsed; after the Nat. Gallery can't find a place for it in 1836-1906, it ends up in the garden of Buckingham Palace; after sculpting statues of John Locke, Adm. Horatio Nelson, George III, and the Duke of York, he sculpts a statue of Achilles in 1822 for the Duke of Wellington, based on a sculpture from Monte Cavallo in Rome, which is placed on the Wellington Monument in Hyde Park, London; he goes on to sculpt memorials in Westminster Abbey to William Pitt the Younger, Spencer Perceval, Charles James Fox, and Joseph Addison, and in St. Paul's Cathedral to Sir Ralph Abercromby, Lord Collingwood, Gen. Sir Edward Pakenham, and Gen. Gibbs.
On May 5, 1821 Napoleon Bonaparte (b. 1769) dies in exile on St. Helena Island, some say of arsenic poisoning, others of stomach cancer, like his daddy Carlo (1746-85); the last word on his lips is "Josephine"; his body is not released by the British to the French until May 25; he is buried under a weeping willow, and is later interred in a crypt at the Hotel des Invalides in Paris, his tomb decorated with 12 Personified Victories by Swiss-born French sculptor James (Jean-Jacques) Pradier (1790-1852); the city of New Orleans, La. proudly houses his death mask; the Memoirs of Napoleon Bonaparte become very popular in France and Europe; a postmortem by Australian surgeon Charles MacLaurin (1872-1925) finds that "his reproductive organs were small and apparently atrophied. He is said to have been impotent for some time before he died"; a priest obtains his 1 in. penis, and it turns up in 1971 at a Christie's auction in London, but there are no takers; in 1977 a U.S. urologist buys it for $3.8K - guess what I got, baby?






In 1828 after winning the Grand Prix de Rome in 1812, Dijon-born French sculptor Francois Rude (1784-1855) sculpts Mercury Fastening his Sandals after Killing Argos, which becomes a hit and ends up in the Louvre; in 1831-3 he sculpts Neapolitan Fisher Boy Playing with a Tortoise, which wins him the Legion of Honor along with the job of all the sculptural frieze ornament on the Arc de Triomphe, along with the group Departure of the Volunteers of 1792 (La Marsellaise) (1836), which makes him a star; he goes on to sculpt Statue of Louis XIII at Age 16 (1843), and Jeanne d'Arc Listening to Her Voices; (1845) in 1947 the Musee Rude in Dijon is dedicated.

In 1832 Paris-born French sculptor Jean-Baptiste Roman (1792-1835) sculpts Cato of Utica Reading the Phaedo of Plato on the Death of Socrates Before Committing Himself to Death, which becomes a big hit among French revolutionaries; finished in 1840 by his friend Francois Rude.





In 1843 after graduating from miniatures, French Romantic animal sculptor ("the Michelangelo of the Menagerie") Antoine-Louis Barye (1796-1875) sculpts the bronze Theseus and the Minotaur, followed by Roger and Angelica Mounted on the Hippogriff (1846), Lapith and the Centaur (1848), and Jaguar Devouring a Hare (1850); too bad, he declares bankruptcy in 1848, causing his work to be sold to a foundry, which cranks out inferior copies until the Ferdinand Barbedienne Foundry acquires them in 1876 and begins giving him his due; his son Alfred Barye (1839-82) attempts to carry on his work, with less success.


In 1843 Woodstock, Vt.-born Neoclassical sculptor Hiram Powers (1805-73) sculpts The Greek Slave, the nude chained blonde-blue babe we'd all like to own?; attracts 100K viewers in the U.S. in 1847, and is a hit in 1851 at the Crystal Palace Exhibition, making him a celeb; Elizabeth Barrett Browning writes the sonnet Hiram Powers' Greek Slave about it, after which it gets used in the abolitionist cause.



On Jan. 8, 1853 Clark Mills (1810-83), Equestrian Statue of Andrew Jackson; commissioned in May 1847; first equestrian statue made in the U.S.; Jackson's horse Duke is modeled by Mills' horse Olympus, who he trained to post on its haunches; cast from captured British cannon, and unveiled in Lafayette Square in Washington, D.C. on Jan. 8 (Sat.) at the 38th anniv. of the 1815 Battle of New Orleans, attended by 20K, with U.S. Sen. Stephen A. Douglas as the keynote speaker; the base bears the inscription "Our federal union/ It must be preserved"; he places clones in New Orleans, La., Jacksonville, Fla., and Nashville, Tenn. On Feb. 22, 1860 Pres. Buchanan dedicates the Equestrian Statue of Lt. Gen. George Washington in Washington Circle in Washington, D.C., by S.C.-born sculptor Clark Mills (1810-83) authorized by Congress on Jan. 25, 1853; hows Washington leading an advance on the redcoats at the Jan. 3, 1777 Battle of Princeton, with the horse's mane copied from "Napoleon Crossing the Alps" by Jacques-Louis David (1805); cost: $60K.



In 1857-60 Valenciennes, France-born painter-sculptor Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux (1827-75) (student of Francois Rude) sculpts Ugolino and his Sons; taken from Dante's "Inferno"; 13th cent. Count Ugolino della Gherardesca (1220-89) is locked up with his children to starve; influenced by the 1st cent. B.C.E. sculpture "Laocoon and His Sons". In 1868 he sculpts La Danse (The Dance) for the Opera Garnier in Paris, which is widely panned as obscene, causing an anon. vandal to throw black ink over it in Aug. 1869; in 1964 it is moved to the Louvre.


In 1860 after being comissioned by the British govt. in 1858 and stalling by requesting copies of casts of a real lion from Turin, Italy, London-born Sir Edwin Henry Landseer (1802-73), known as a painter of animals sculpts four lions for the base of Nelson's Column in Trafalgar Square, which are installed in 1867; after his death on Oct. 1, 1873, wreaths are hung from them, while a large crowd lines his funeral cortege en route to St. Paul's Cathedral.


In 1865-9 Paris-born French academic sculptor Jean-Joseph Perraud (1819-76) (student of Etienne-Jules Ramey and Augustin-Alexandre Dumont) sculpts Le Drame Lyrique (The Lyrical Drama) for the facade of the Palais Garnier.


In 1866 Viggiu-born Italian sculptor Giosue (Giosuè) Argenti (1819-1901) (student of Pompeo Marchesi) sculpts Modesty, followed by The Sleep of Innocence (Il Sonno dell'Innocenza) (1872), and Perseus Freeing Andromeda (1884).



In 1872 Nantes-born French sculptor Charles-Auguste Lebourg (1829-1906) begins sculpting 50 small cast-iron Wallace Fountains (drinking fountains), financed by English art collector Sir Richard Wallace, 1st Baronet (1818-90), which are sited throughout Paris on the busiest sidewalks and give Paris its character, also in Lisburn.




In 1880 French sculptor Auguste Rodin (1840-1917) produces The Thinker (sculpture); original name "The Poet"; supposed to be a portrait of poet Dante in front of the Gates of Hell pondering his Divine Comedy; starts out as small plaster statue, then is cast full-size in bronze in 1902; in 1922 it is moved to the Hotel Biron in Paris, which becomes the Rodin Museum; in 1880 he also produces the unfinished sculpture The Gates of Hell (La Porte de l'Enfer), which is supposed to be a portal to the Musee des Arts Decoratifs in Paris. In 1882 he produces The Kiss, a sculpture of Paolo and Francesca da Ramini inspired by Dante's "Inferno" (Circle 2, Canto 5); Paolo holds a copy of "Lancelot and Guinevere"; the lovers' lips do not touch because Paolo's brother Giovnni Malatesta (Francesca's hubby) murders them; shows the woman as an active partner, not totally submissive, outraging Victorian society; displayed at the 1889 Paris Exposition Universelle, and at the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago, Ill. in a guarded chamber; many copies are made by Rodin in bronze, terracotta, and plaster; the sculpture supposedly brings the era of classical art to an end; Rodin calls it "complete in itself and artificially set apart from the surrounding world." In 1884-9 he produces the sculpture The Burghers of Calais (Les Bourgeois de Calais), about the humiliating terms of surrender to the English in the 1347 siege of Calais.






On Oct. 24, 1881 new U.S. minister to France (since Mar. 2) Levi Parsons Morton (1824-1920) hammers the first rivet into the Statue of Liberty in Paris, driving it into the big toe of her left foot; Colmar, France-born sculptor Frederic Auguste Bartholdi (1834-1904) got the idea from his friend, French jurist Edouard Rene Lefevre (Édouard René Lefèvre) de Laboulaye (1811-83). On Oct. 28, 1886 (Thur.) the 305' 1" 225-ton (heaviest in the world) "harbor chick" Statue of Liberty (AKA Liberty Enlightening the World), built by Dijon-born Alexandre Gustave Eiffel (Bonickhausen) (1832-1923) and designed by Frederic Auguste Bartholdi (1834-1904) of Alsace (a recycled version of "Egypt Bringing Light to Asia", once planned for the entrance to the Suez Canal, with the Roman goddess Libertas robed as an Egyptian fallaha peasant) is dedicated at Liberty (formerly Bedloe's) Island in New York Harbor "beside the golden door"; the base is an 11-pointed star constructed from the remains of Ft. Wood; the seven spikes in the crown signify the seven seas and continents; the right hand of the 152-ft. steel-reinforced copper-clad Lady Liberty on a 150-ft. pedestal holds a torch aloft, while her left hand carries a book inscribed "July IV MDCCLXXVI"; the sonnet The New Colossus, by Jewish-Am. poet Emma Lazarus (1849-87) is engraved on a tablet inside the pedestal, cementing the purpose as the welcoming of er, white immigrants; "Give me your tired, your poor/ Your huddled masses yearning to breathe free,/ The wretched refuse of your teeming shore,/ Send these, the homeless, tempest-tost to me,/ I lift my lamp beside the golden door!"; on Oct. 29 the first-ever ticker tape parade is held for Lady Liberty in New York City, with workers spontaneously throwing ticker tape out of brokers' windows, while Pres. Grover Cleveland accepts the statue for the U.S.

In 1884 Hamden, Conn.-born sculptor Chauncey Bradley Ives (1810-94) sculpts Undine Rising from the Waters, which becomes a hit with art historians, who like to grace their front covers with it; too bad, after sculpting marble statues of Jonathan Trumbull and Roger Sherman for the Nat. Statuary Hall and finding the market overcrowded, he moves to Rome for life, dying in obscurity.







In 1887 Dublin, Ireland-born Am. sculptor Augustus Saint-Gaudens (1848-1907) sculpts a 12-ft. (3.7m) bronze statue of Abraham Lincoln: The Man (Standing Lincoln) for Lincoln Park in Chicago, Ill.; 10K attend the unveiling incl. Lincoln's grandson Abraham Lincoln II, with the New York Evening Post calling it "the most important achievement American sculpture has yet produced"; Stanford White designs a semicircular platform (exedra) for it. In 1892-3 he sculpts Diana (of the Tower), which ends up on top of the Madison Square Garden in 1893-1925, followed in 1932 by the Philadelphia Museum of Art. On May 31, 1897 he unveils the bronze relief Robert Gould Shaw Memorial (begun 1884) at 24 Beacon St. in Boston Common in Mass., depicting Union Col. Robert Gould Shaw (1837-63) leading the 54th Regiment Mass. Volunteer Infantry (first all-black regiment in New England) down Beacon St. on May 28, 1863 before being KIA in Morris Island, S.C. on July 18, 1863. In 1907 the U.S. Mint discontinues the Coronet design (begun 1838 for the eagle and 1949 for the double eagle) and begins issuing $10 Indian Head Eagle coins and $20 Standing Liberty Double Eagle coins (until 1933), all designed by Dublin, Ireland-born Am. sculptor Augustus Saint-Gaudens (1848-1907), who works from a studio in Cornish, N.H.; Pres. Roosevelt forbids the motto "In God We Trust", considering it in bad taste; Pres. Taft restores it in 1908.



In 1893 the Shaftesbury Memorial Fountain (begun 1885) by London-born English New Sculpture Movement sculptor Sir Alfred Gilbert (1854-1934) in Piccadilly Circus, London is unveiled, crowned with the aluminum statue of Anteros, which he calls "the Angel of Christian Charity", but is popularly known as Eros, becoming the world's first aluminum statue. In 1926-32 he sculpts the Art Nouveau bronze Queen Alexandra Memorial for Marlborough Road in London, commemorating Queen Alexandra of Denmark.


In 1894 Paris-born French post-Impressionist artist Eugene Henri Paul Gaugin (1848-1903) sculpts the ceramic sculpture Oviri, the Tahitian goddess of mourning, shown coddling wolves.






In 1894 English art critic Sir Edmund William Gosse (1849-1928) coins the term "New Sculpture", which seeks to reanimate the form of the classic statue with realism, bridging the 19th cent. neoclassical style and modernism, first seen in the 1877 exhibition of the bronze sculpture An Athlete Wrestling with a Python by Frederic Leighton, 1st Baron Leighton (1830-96), and adopted by his London-born sculptor friend Sir William Hamo Thornycroft (1850-1925), who was elected to the Royal Academy in 1882 and went on to sculpt major monuments in the London area incl. Oliver Cromwell (1899), Alfred the Great (1901), and Alfred Lord Tennyson (1909).




On Jan. 1, 1895 after years as a starving artist living above a Cremerie in Paris, where he gained a lot of friends incl. Gaugin, and founded the Bal des Quat'z Arts artists' ball, Czech artist Alphonse (Alfons Maria) Mucha (1860-1939), presents a poster for Sara Bernhardt's play "Gismonda", becoming an instant star with his sensuous style, launching the French Art Nouveau Movement (ends 1914), centered in a Paris art gallery called guess what run by Siegfried Bing (1838-1905), who opens it in Dec., writes La Culture Artistique en Amerique for the French govt., and goes on to exhibit works by Edouard Vuillard (1868-1940), Pierre Bonnard (1867-1947), Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec (1864-1901), Henry Clemens van de Velde (1863-1957), Louis Comfort Tiffany (1848-1933) et al.; the style becomes a total art style, spreading to architecture, furniture, jewelry, textiles, ceramics, etc., becoming known as Jugendstil in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Germany, and the Baltic states, Modernism in Spain and Russia, and Secessionsstil in Austria and Czech. - remodel your home at better than sale prices?


In 1895 Canton, N.Y.-born Old Am. West artist Frederic Sackrider Remington (1861-1909) saves the best for last with his bronze sculpture The Bucking Broncho (Bronco); in 2014 the Denver Art Museum loses its bet over the outcome of the Denver Broncos-Seattle Seahawks Super Bowl and has to loan the sculpture to the Seattle Art Museum for 3 mo.


On Oct. 23, 1901 (2:00 p.m.) a statue of Confed. Brig. Gen. Albert Pike (1809-91) by Italian-born Am. sculptor Gaetano Trenatnove (1858-1937) is dedicated at 3rd and D Sts., NW in the Judiciary Square neighborhood of Washington, D.C. by Masons to commemorate his work for them, accompanied by a parade of thousands of Masons, becoming the first Confed. officer with a statue in Washington, D.C. (until ?), and one of 18 Civil War monuments in Washington, D.C.






In 1903 Elmwood, Ill.-born sculptor Lorado Zadok Taft (1860-1936) pub. The History of American Sculpture, first-ever; the 1925 rev. version becomes a std. reference until Wayne Craven's "Sculpture in America" (1968); he follows with Modern Tendencies in Sculpture (1921). In 1909 he sculpts Eternal Silence (Statue of Death) (Dexter Graves Monument) (Graceland Cemetery, Chicago, Ill.) (Dexter Graves (-1844), who led a group of 13 settlers from Ohio in 1831 to Chicago), followed by Thatcher Memorial Fountain (1918) (City Park, Denver, Colo.) (wealthy Denver businessman Joseph Addison Thatcher (-1918), showing the State of Colorado surrounded by three groups representing Loyalty, Love, and Learning, followed by Fountain of Time (1920-22) (Midway Plaisance, Chicago, Ill.), followed by The Recording Angel (1923), Fountain of Creation (unfinished) (1923) (U. of Ill. Library) (planned to complement "Fountain of Time"), Lincoln the Lawyer (1929), and The Patriots (1932) (La. State Capitol, Baton Rouge).


In 1907-8 Romanian sculptor-painter Constantin Brancusi (1876-1957) creates the sculpture The Kiss, which is exhibited at the 1913 Armory Show, launching a career of art emphasizing clean geometrical lines that dabbles in primitive exoticism a la Paul Gaugin.


In 1908 Le Cateau-Cambresis, Nord-born French painter-sculptor Henri Emile Benoit Matisse (1869-1954) begins sculpting the four bas-relief sculptures titled The Back Series (1913, 1916, 1930).




In 1910 after trying painting and tapestry, Banyuls-sur-Mer, Roussilllon-born French bronze sculptor Aristide Joseph Bonaventure Maillol (1861-1944) sculpts Flora Nude and Summer (1910-11), beginning his career of being fascinated with the female body the same way the ancient Greeks were; he follows with The Night (1920), Venus Without Arms (1920), Air (plaster) (1938), The River (1938-43), and Kneeling Woman: Monument to Debussy (1950-55) (conceived in 1930 and cast in six numbered proofs).


In 1911-12 Livorno, Tuscany, Italy-born painter-sculptor Amedeo Clemente Modigliani (1884-1920) sculpts the 2 ft. African-inspired limestone sculpture Tete (Tête) (Fr. "Head"), which is exhibited in the 1912 Salon d'Automne; in 2010 it is auctioned by Christie's in Paris for 43.2M Euros.
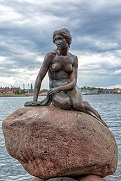


On Aug. 23, 1913 the 4.1' (1.25m) 385 lb. Statue of the Little Mermaid (begun 1919), mounted on a rock by the waterside at the Langelinie promenade in the harbor of Copenhagen, Denmark, based on the Hans Christian Andersen fairy tale is unveiled, sculpted by Edvard Eriksen (1876-1959), whose wife (since 1900) Eline Vilhelmine Eriksen (nee Moeller) (1881-1963) is used as the body model, with ballerina Ellen Price (Ellen Juliette Collin Price de Plane) (1878-1968) modeling for the head, becoming the nat. symbol; on Apr. 24, 1964 vandals steal the head, followed by many more episodes; every time somebody steals something, they replace it using a copy made with the original mold.


In 1916 Strasbourg-born sculptor Jean (Hans) Arp (1886-1966), along with Max Ernst and Alfred Gruenwals set up the Dada Group in Cologne, Germany, turning into a Surrealist by 1925, then founding the anti-Surrealist Abstract-Creation (Abstraction-Création) Group in Paris in 1931.


On Sept. 27, 1917 after a painting career that began in 1859, painting mainly females, Paris-born French artist Edgar Degas (Hilaire Germain Edgar De Gas) (b. 1834) dies in Paris, leaving several sculptures of females, incl. Little Dancer of Fourteen Years, Dancer Moving Forward with Arms Raised, The Spanish Dance, and Seated Woman Wiping Her Left Side.


In 1917 Blainville-Crevon, France-born French Cubist/Dada sculptor-painter Henri Robert Marcel Duchamp (1887-1968) sculpts Fountain, a "ready-to-wear" porcelain urinal signed "R. Mutt"; the most influential art work of the 20th cent.?





The final shrine to White is Right in America? On Feb. 12, 1922 (Pres. Abraham Lincoln's birthday) the $3M Lincoln Memorial in West Potomac Park in Washington, D.C. is dedicated, designed by Watseka, Ill.-born architect Henry Bacon (1866-1924), with the seated statue of Lincoln designed in 1920 by Exeter, N.H.-born sculptor Daniel Chester French (1850-1931), and carved by the Piccirilli Brothers, with interior murals painted by St. Louis, Mo.-born Jules Vallee Guerin (Jules Vallée Guérin) (1866-1946); poet Edwin Markham reads his poem Lincoln, the Man of the People, containing the soundbyte "Into the shape she breathed a flame to light/ That tender, tragic, ever-changing face./ Here was a man to hold against the world,/ A man to match the mountains and the sea"; chief justice William H. Taft dedicates it again on May 30; the bldg. is of marble, granite, and limestone (all white), and there are 36 Doric pillars representing the 36 states in the Union in 1865; the white marble statue of Lincoln is designed by Daniel Chester French, and behind it are the words "In this temple, as in the hearts of the people for whom he saved the Union, the memory of Abraham Lincoln is enshrined forever"; the S wall decorations depict the Emancipation of the Black Race, with subordinate groups representing Civilization and Progress; the N wall represents Reunion and Progress in the Arts and Sciences; other walls contain the Gettysburg Speech and Lincoln's Second Inaugural Address.


In 1924 New York City-born poor little rich girl Gertrude Vanderbilt Whitney (1875-1942) sculpts the bronze statue The Scout to commemorate Buffalo Bill Cody in Cody, Wyo.; dedicated on July 4; located near Cedar Mountain, which Cody chose as his gravesite, only to be buried against his wishes at Lookout Mountain outside Denver, Colo.





On Oct. 4, 1927 Pres. Coolidge dedicates the Mount Rushmore Memorial, whose 60-ft. (18m) busts of George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, Abaham Lincoln, and Theodore Roosevelt represent the nation's founding, development, and preservation; it takes sculptor Gutzon Borglum (1867-1941) the rest of his life to sculpt the gigantic heads, and when he dies on Mar. 6, 1941 leaving it unfinished, his son James Lincoln Borglum (1912-86), who worked with his father on it for 14 years attempts to complete it, but gives up on Oct. 31, 1941 after funds run out; 5,725-ft. Mt. Rushmore (called "6 Grandfathers" by the Lakota Sioux) is named for New York City atty. Charles E. Rushmore (1857-1931), who opened the Etta Tin Mine on it in 1885, and contributes $5K to the project; the idea came from S.D. state historian Jonah LeRoy "Doane" Robinson (1856-1946), who suggested Needles and tried to contact Lorado Taft first, then was excluded from a commission created in 1929 by Pres. Coolidge to oversee the work; Washington's nose is 20 ft. long; two of the presidents (Jefferson, Lincoln) passed the bar to become lawyers.






In 1930 Castleford, Yorkshire, England-born abstract sculptor Henry Spencer Moore (1898-1986), son of a coal miner debuts Reclining Woman, based on Chac Mool figures from Chichen Itza, followed in 1939 by Reclining Figure (elmwood sculpture), becoming known for his abstract monumental bronze sculptures located around the world, featuring reclining nudes and mother-child motifs, rock-tree-bone motifs, and massive garment folds; in 1953 he debuts King and Queen in Antwerp, followed by Draped Reclining Woman, 1957-8; in 1965 he debuts Reclining Figure at the Lincoln Center.

In 1936 Chicago, Ill. sculptor Sylvia Shaw Judson (1897-1978) produces the 50" (130cm) Bird Girl (bronze sculpture), which is featured on the cover of the 1994 novel "Midnight in the Garden of Good and Evil", making it famous.



In the late 1950s after working as asst. to Henry Moore, New Malden, England-born sculptor Sir Anthony Alfred Caro (1924-2013) achieves internat. success with his assemblages of metal using "found" industrial objects, often sans plinth; in 1960 he creates Twenty Four Hours, his first abstract and first welded sculpture, launching his rise to #1 sculptor in England; in 1974 he creates the abstract sculpture Black Cover Flat in Tel Aviv, Israel; in 1985 he visits Greece, causing him to switch to classical Greek themes incl. After Olympia; in 2000 he helps design the Millennium Bridge in London.


In 1960 Krefeld, Germany-born performance artist Joseph Beuys (1921-86) sculpts Bathtub (Badewann), covering his childhood metal tub with plaster and fat-soaked gauze, commemorating his WWII experience as a Luftwaffe pilot shot down over the Crimea and saved by Tatars by wrapping him in fat; too bad in fall 1973 two women at the Museum Schloss Morsbroich mistakenly clean it.


In 1960 Augusta, Ga.-born Pop Art painter-sculptor Jasper Johns (1930-) creates the sculpture Painted Bronze (Ale Cans), two cans of Balantine XXX ale, painted on a bet about his dealer Leo Castelli; "Somebody told me that Bill de Kooning said that you could give that son-of-a-bitch two beer cans and he could sell them. I thought, what a wonderful idea for a sculpture." (Johns)



In 1966 New York City-born Pop Art painter-sculptor George Segal (1924-2000) debuts his sculptures The Truck and The Laundromat (1966-7), made by casting full-body molds of people with Plaster of Paris and making statues out of them. In 1992 he debuts his sculpture Street Crossing, which is installed in the College Ave. Promenade at Montclair State U. in N.J.


On Aug. 15, 1967 after refusing the $100K commission, Pablo Picasso (1881-1973) dedicates The Chicago Picasso in Daley Plaza in Chicago, Ill., a 50' 147-ton Cubist sculpture, which becomes a landmark and playground jungle-gym.


In 1967 the 67-ft. minimalistic stumpy Christ of the Ozarks statue on Magnetic Mountain outside Eureka Springs, Ark. (begun 1964) is completed by sculptor Emmet Sullivan (1887-1970) (student of Gutzon Borglum) for anti-Semitic white supremacist conservative Christian preacher Gerald Lyman Kenneth "L.K." Smith (1898-1976), founder of the Am. First Party in 1944, a former associate of Huey P. Long, who leads the hardcore anti-Semitic element in the U.S. and claims that Jesus was a blue-eyed blonde and not a "modern hook-nose shopkeeper, money-changer, brothel owner and whiskey peddler", also that the 6M Jews allegedly murdered by the Nazis were secretly illegally immigrated to the U.S. to keep FDR in power - and all those German U-boats missed them?



In 1981 Barcelona-born Spanish Surrealist artist Joan Miro i Ferra (Miró i Ferrà) (1893-1983) unveils his 12m outdoor sculpture The Sun, the Moon and One Star (Miro's Chicago) in Chicago's Loop area across the street from the Chicago Picasso. In 1982 he unveils his 22m concrete outdoor sculpture Doni i Ocell (Woman and Bird) in Barcelona.


In 1990 Dortmund, West Germany-born artist Martin Kippenberger (1953-97) produces the 4' sculpture Fred the Frog Rings the Bell (Feet First) (Prima i Pied), a frog in a loincloth being crucified while holding a mug of beer and an egg.


In 1995 the 24m-high Nacka Fountain in Stockholm, Sweden opens, designed by Uppsala-born Swedish-Am. sculptor Carl Milles (Carl Wilhelm Emil Andersson) (1875-1955) and copied by his asst. Marshall M. Fredericks, with the title "God, Our Father, on the Rainbow", celebrating the founding of the United Nations.


In 1999 Paris-born French sculptor Louise Josephine Bourgeois (1911-2010) sculpts the 30 ft. x 33 ft. bronze, stainless steel, and marble sculpture Maman (Fr. "mother"), a gigantic spider complete with egg sac containing 26 marble eggs for Turbine Hall at Tate Modern Museum, which opens on May 12, 2000 in Southark, London across the Thames River from St. Paul's Cathedral in the former Bankside Power Plant after a $200M renovation by Swiss architects Jacques Herzog (1950-) and Pierre de Meuron (1950-); the old Tate Museum upriver is renamed Tate Britain and continues to display Gainsboroughs and Turners, while the 12-story-high lobby of the Tate Modern features modernist crap, er, art incl. Louise Bourgeois' gigantic steel sculptures I Do, I Undo, and I Redo.




In Apr. 2000 after U.S. Sen. (R-Minn.) (1995-2001) Rodney Dwight "Rod" Grams (1948-2013) introduces a bill on Oct. 21, 1997, the U.S. Treasury issues its first $100M worth of gold-tinted copper-brass-manganese Sacagawea Dollar Coins, circulating them through Wal-Mart stores and in 5K lucky boxes of Cheerios brand breakfast cereal; Lubbock, Tex.-born sculptor Glenna Maxey Goodacre (1939-) uses Shoshone student Randy'L He-Dow (Bannock "close to ground") Teton (1976-) (pr. "HEE-tho") as a model for the Shoshone guide's face; they tarnish easily, and soon turn into collector's items as nobody wants to circulate the suckers that are too small to seem like dollars?


On May 15, 2006 the 33' x 66' x 42' 110-ton Cloud Gate AKA The Bean public sculpture by Bombay, India-born British artist Sir Anish Kapoor (1954-) in AT&T Plaza in Millennium Park, Chicago, Ill. is dedicated, composed of 168 welded stainless steel plates modeled after liquid mercury.


On Mar. 26, 2018 the stainless steel Cloud Column sculpture by British sculptor Sir Anish Kapoor (1954-) is unveiled in Houston, Tex., pissing-off rival Chicago, Ill., which hosts Kapoor's 2006 Cloud Gate (AKA The Bean), which lies on its side and doesn't stand upright like Houston's; meanwhile Houston gained 94,417 residents in 2017, while Chicago lost 13,286, putting Houston track to pass Chicago as the 3rd largest U.S. city in 10 years.