






1720 Pop. of the Am. colonies: 450K; Boston 12K; Philadelphia 10K; New York City 7K. Marseille, France becomes the last European city to suffer a major outbreak of the plague, killing 100K. On Jan. 26 the Treaty of the Hague ends the war between the Spain and the Quadruple Alliance (begun 1718), and Spain evacuates Sicily and Sardinia; on May 20 Spain signs an act of adhesion to the Quadruple Alliance in return for recognition by the HRE of the Spanish Bourbons; Don Carlos is acknowledged to the succession of Parma and Tuscany through his mother; 3-y.-o. Infanta Maria-Anne-Victoire is promised in marriage to Louis XIV; the House of Savoy is obliged to exchange Sicily (which it got in 1713) for Sardinia with Austria in return for a promotion from duke to king for Victor Amadeus II, whose 11th cent. House of Savoy has come a long way, baby?; Austria rules Sicily until 1735; Turin (Torino), capital of the duchy of Savoy becomes the capital of the new improved tin can Kingdom of Sardinia (1324-1861), incl. Savoy, Piedmont, and Sardinia, becoming the nucleus of the later kingdom of Italy. On Feb. 29 queen (since Dec. 5, 1718) Ulrika Eleonora of Sweden abdicates in favor of her husband Frederick (Fredrik) I (1676-1751), who on Mar. 25 beccomes king of Sweden (until Mar. 25, 1751) (first king to have been prince consort first), who in 1730 also becomes landgrave of Hesse-Cassel (Hesse-Kassel) (1567-1803); in Feb. Sweden and Prussia sign the Treaty of Stockholm, ending the war between Sweden and Hanover-Prussia, ceding Swedish territory to Hanover and Prussia and restoring the prewar boundaries among Sweden, Saxony, and Poland; on July 14 (July 3 Old Style) Sweden and Denmark sign the Treaty of Fredericksborg, yielding Danish conquests in return for Swedish payment. On July 12 king (since 1674) Sukjong (Sukchong) (b. 1661) dies, and his son Gyeongjong (Kyonjong) (1688-1724) becomes Yi king #20 of Korea (until Oct. 11, 1724). On July 31 Mughal nobleman Nizam-ul-Mulk ("Regulator of the Realm") (1671-1748) becomes ruler #1 of the new state of Hyderabad in modern-day Pakistan (until June 1, 1748), going on to become the "greatest Mohammedan hero of the eighteenth century" (Henry George Briggs). On Aug. 7 (July 27 Old Style) the Battle of Grengam in Sweden sees 86 Russian ships and 11K sailors and soldiers under field marshal Mikhail Mikhailovich Golitsyn (Galitzine) (1675-1730) decisively defeated by the 13-ship 1K-sailor Swedish fleet under vice-adm. Eric Sjoblad, halting Russian naval activities in the Baltic, and becoming the last major naval battle in the Great Northern War (begun 1700). The Pragmatic Sanction is recognized by the estates of Upper and Lower Austria. The cat's away? Marquis Joseph Francois Dupleix (1697-1763) comes to India as an official of the French East India Co. after his shareholder father gets him a seat on the superior council in Pondicherry; in 1730 he rises to supt. of French affairs in Chandernagore, Bengal, then gov.-gen. of all French India in 1742, vexing the British in India for decades by using the decay of the Mogul empire to extend French influence (until 1754) - hahaha, gotcha? The Tibet Revolt (begun 1717) is suppressed by armies from Gansu and Sichuan, the Mongols are driven out of Tibet, and Tibet becomes a Chinese protectorate, with a popular Dalai Lama enthroned, protected by imperial garrisons. Starting in this decade the Kazakh tribes of Kazakhstan fight a war against the invading Jungar (Zhunghar) (Dzungar) ("left hand") hordes of W Mongolia, fighting each other on horseback; by 1760s the Kazakhs drive them off, making a hero of Abulmansur, who becomes Ablai Khan (1711-81). Japanese shogun (since 1716) Tokugawa Yoshimune breaks down and repeals the laws against European books and study. British PM Charles Spender, er, Spencer, 3rd Earl of Sunderland gives Robert Walpole the post of paymaster gen., after which the South Sea Bubble bursts after its stock soars from £128 to over £1K a share, followed by a crashy crash crash, hurting many people in England incl. Sir Isaac Newton, and causing the public to look to him to restore order; on June 11 the Bubble (Royal Exchange and London Assurance Corporation) Act is passed, incorporating the Royal Exchange and London Assurance Corp., and prohibiting the development of joint-stock cos. without a royal charter or act of Parliament; Sunderland's career bursts like a bubble?; "I can calculate the motions of heavenly bodies, but not the madness of people." (Newton) L.V. Izmailov (1686-1738) establishes a Russian Orthodox church and trading agent in Peking. Marine insurance is first established in Britain. The original supply side economics? After a royal decree halves the value of his Banque Royale's notes, causing coined money to disappear from circulation and prices to skyrocket, John Law's Mississippi Co. fails, becoming known as the Mississippi Bubble (Scheme), and many people in France are hurt, causing Law to be dismissed by regent Philippe d'Orleans, leave France secretly, and settle in Venice, where he dies penniless in 1729; meanwhile he pub. a book exposing his fallacious theories of finance, which consider money the cause of public wealth rather than its result, and believe in the power of running the printing presses to produce paper money. Spain occupies Texas (until 1722). Augsburg and Marienthal are founded in Louisiana by Germans immigrants. The city of Karachi on the Arabia Sea is founded as the fortified village of Kolachi; in the mid-19th cent. the British East India Co. arrives, turning it into a major seaport and railroad hub, growing to 400K pop. by 1947, after which the partition of British India causes it to be flooded with millions of Muslim refugees, reaching 14.9M pop. in 2017, becoming the most populous city in Pakistan and #5 in the world, hosting 2M immigrants from Bangladesh, 1M from Afghanistan and 400K Rohingyas from Myanmar, also becoming its industrial and financial center. Sauk and Meskwaki Indians found the village of Saukenuk along the Rock River near its confluence with the Mississippi River on the site of modern-day Moline, Ill., home of John Deere. The Swiss Anabaptist Amish (separate from the Mennonites) begin migrating from Switzerland to Lancaster County, Penn. Illinois (Ill.) ("warriors" in Algonquin) is settled. The first collective settlement begins in New Connecticut (Vermont). Spanish-born Marquis de San Miguel de Aguayo (-1734), gov. of Coahuila (since 1719) organizes Spanish settlements in Texas to counter French encroachment (until 1723). The imperial privileged Alsatian city of Hagenau gets more antsy about its wealthy moneylending Jewish pop., and issues regulations restricting settlement by their children, only one married son per family allowed to settle, and all Jews are restricted to moneylending and dealing in horses, cattle and old clothes (until 1790). French naval officer Gabriel Matthieu Francois D'ceus de Clieu (1687-1774) allegedly smuggles coffee plans from the Jardin Royal des Plantes in Paris to Martinique, sharing his rationed water with the plants, beginning the South Am. cultivation of coffee; in 1727 the Brazilian coffee industry is founded; cultivation is slow until independence in 1822, after which massive areas of rainforest are cleared near Rio de Janeiro and Sao Paulo, making Brazil the largest coffee producer on Earth by 1852 (until ?); in 1737-52 de Clieu becomes gov. of Guadeloupe. After falling behind in their payments, their Turkish landlords evict the Ashkenazi Jews from Jerusalem; 200 families relocate to Hebron, Safed, and Damascus, and don't return for a cent. The Royal (Old) Haymarket (Little) Theatre opens in Westminster, London. The court of the Rhine Palatinate is moved from Heidelberg to Mannheim (until 1777). King George County in Va. between the Potomac and Rappahannock Rivers is formed from Richmond County, and named after George I, later becoming the birthplace of James Madison (b. 1751). The first yacht club is established at Cork Harbor in Ireland. Caffe (Caffè) Florian on St. Mark's Square in Venice is founded, becoming Italy's oldest coffeehouse to survive to modern times. St. Anselm of Canterbury (d. 1109), known for his Ontological Proof of the Existence of God is declared a Doctor of the Roman Catholic Church. The word "roué" (roue) (Fr. "wheel") is coined to describe the dissolute, dissipated, debauched companions of Duke Philippe II of Orleans. Edmund Halley becomes English astronomer royal, and begins an 18-year study of the complete revolution of the Moon through its ascending and descending nodes. Wallpaper becomes fashionable in England. Novels begin to be serialized in newspapers. In this decade black tea (Bohea) (Wu-i) passes green tea in popularity in England, with sugar and milk becoming popular additives early on; by this time maritime Euro trade with China is dominated by the exchange of silver for tea; by 1750 tea is the British nat. drink. Inventions: On June 10 Mrs. Clements of Durham, England becomes the first to market paste-style mustard after finding a way to mill the seed hearts to fine powder. 14-y.-o. Benjamin Franklin (1706-90) invents swimming flippers; he later becomes the only Founding Father in the Am. Swimming Hall of Fame. About this time chili con carne originates in La Villa de San Fernando de Bejar in the Nueva Espana province of Nuevas Filipinas (modern-day San Antonio, Tex.) among mission Indians and mestizos as a way to eat tough meat (goat, jackrabbit etc.), and is disdained by the Anglos until the 1880s. Nonfiction: Arthur Collins, Baronetage of England. William Jacob 's Gravesande (1688-1742), Mathematical Elements of Natural Philosophy, Confirmed by Experiments (Leiden); lays the foundation for physics teaching. Edward Hyde, 1st Earl of Clarendon (1609-74), The History of the Rebellion and Civil War in Ireland (posth.); a companion to "The History of the Rebellion and Civil Wars in England" (1702-4), covering the period after the death of Charles I. Bernard de Montfaucon, L'Antiquite Expliquee (1720-24). Johann Lorenz von Mosheim (1693-1755), Vindiciae Antiquae Christianorum Disciplinae; critique of John Toland. John Trenchard and Thomas Gordon, Cato's Letters; or Essays on Liberty, Civil and Religious, and Other Important Subjects (4 vols.) (1720-3); castigates the "South-Sea Plunderers", the "able guilty Ministers", and "despotick Princes", and argues for freedom of speech; later used by "Real Whigs" in the American colonies to justify independence. Giovanni Battista Vico (1668-1744), De Uno Universo Juris Principis. Music: G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Radamisto (HWV 12) (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Apr. 27); libretto by Nicola Francesco Haym, based on Matteo Noris' "Zenobia" and Domenico Lalli's "L'Amor Tirranico, o Zenobia"; his first opera for the Royal Academy of Music; Harpsichord Suite No. 5; incl. The Harmonious Blacksmith. Nicola Porpora (1686-1768), Orlando (opera). Art: G.B. Tiepolo, Martyrdom of St. Bartholomew. Jean-Antoine Watteau (1684-1721), Le Enseigne de Gersaint. Plays: Nicolas Lancret (1690-1743), Declaration of Love (fete galante). Charles Shadwell (-1726), The Fair Quaker of Deal, or The Humours of the Navy, Irish Hospitality, or Virtue Rewarded, and Other Plays. Poetry: John Gay (1685-1732), Collected Poems. Novels: Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), The Life, Adventures and Piracies of the Famous Captain Singleton; about an Englishman stolen as a child from his well-to-do family and raised by Gypsies. John Watts (pub.), A Select Collection of Novels in Four Volumes, Written by the Most Celebrated Authors in Several Languages (London); incl. "Upon the Origin of Romances" by Huet. Births: Spanish minister Jose de Galvez y Gallardo, Marques de Sonora (José de Gálvez y Gallardo, Marqués de Sonora) (d. 1787) on Jan. 2 in Macharavialla. English (Cornish) dramatist-actor Samuel Foote (d. 1777) on Jan. 27 in Truro, Cornwall; coins the term "panjandrum" for a pompous, self-important official. Japanese emperor #115 (1735-47) Sakuramachi (Teruhito) (d. 1750) on Feb. 8; eldest son of Nakamikado (1702-37). Swiss entomologist and natural philosopher Charles Bonnet (d. 1793) on Mar. 13 in Geneva. Spanish duke of Parma (1748-65) Philip of Spain (d. 1765) on Mar. 15 in Madrid; 3rd son of Philip V and Elisabeth Farnese; husband of Louise Elisabeth of France, eldest daughter of Louis XV; father of Ferdinand, duke of parma (1751-1802). German marshal Heinrich Wilhelm von Freytag (d. 1798) on Mar. 17 in Estorf. Italian Biblical scholar and archbishop of Florence (1781-1809) Antonio Martini (d. 1809) on Apr. 20 in Prato, Tuscany. English MP (1768-90) and brewer Samuel Whitbread (d. 1796) on Aug. 30 in Cardington, Bedfordshire; father of Samuel Whitbread Jr. (1764-1815). Italian etcher and architect Giambattista (Giovanni) Piranesi (d. 1778) on Oct. 4 in Mogliano Veneto (near Treviso); known for his cool "carceri d'invenzione" (imaginary dungeons). Irish actress Margaret "Peg" Woffington (d. 1760) on Oct. 18 in Dublin; father is a poor bricklayer; as a child she assists a tightrope walker; debuts in Irish theaters at age 10, and in London in 1740. Am. Quaker abolitionist preacher-reformer John Woolman (d. 1772) on Oct. 19 in Mount Holly, N.J. French adm. Count Toussaint-Guillaume Picquet (Piquet) de la Motte (d. 1791) on Nov. 1 in Rennes. Georgian king (1744-98) ("the Little Kakhetian") Erekle (Heraclius) (Erekli) (Irakly) II (d. 1798) on Nov. 7 in Telavi; son of Teimuraz II of Kakheti and Tamar, daughter of Vakhtang VI of Kartli. German jurist Justus Moser (Möser) (d. 1794) on Dec. 14 in Osnabruck. English/Scottish prince ("the Young Pretender") Charles Edward Louis John Casimir Sylvester Severino Maria Stuart (Stewart), Count of Albany (d. 1788) (AKA Bonnie Prince Charlie and Charles III) on Dec. 31 in Rome; son of "Old Pretender" James Francis Edward Stuart (1688-1766); grandson of James II; husband (1772-) of Princess Louise of Stolberg-Gedern (1752-1824). Ottawa Chief Pontiac (Obwandiyag) (d. 1769) in Great Lakes Region, New France. Shawnee Chief Cornstalk (Hokoleskwa) (Hokolesqua) (d. 1777) in Penn. Italian painter Bernardo Bellotto (Canaletto) (d. 1780) (1721 or 1722?) in Venice. English bigamous courtesan Elizabeth Chudleigh, Duchess of Kingston, Countess of Bristol (d. 1788); known for her affairs with courtiers of George II, and being convicted of double-dipping with poor (later rich, but she couldn't wait) Augustus Hervey, 3rd earl of Bristol and rich Evelyn Pierrepont, 2nd duke of Kingston (1776). German self-promoting soldier-adventurer-anecdotist Hieronymus Karl Friedrich, Baron von Munchausen (Munchhausen) (d. 1797) in Bodenwerder, Brunswick-Luneberg. English spinning jenny inventor James Hargreaves (d. 1778) in Oswaldtwistle, Lancashire. Spanish viceroy of Peru (1795-1801) Don Ambrosio Bernardo O'Higgins, 1st Marquis of Osorno (d. 1801) in Summer Hill (near Daingean), County Offaly, Ireland; father of Bernardo O'Higgins (1778-1842); created marquis in 1792. English writer Charlotte Lennox (nee Barbara Charlotte Ramsay) (d. 1804) (b. 1730?) in Gibraltar. Deaths: French sculptor Charles-Antoine Coysevox (b. 1640) on Oct. 10 in Paris. English sea capt. Robert Knox (b. 1641) on June 19 in London. British gov. of Mass. (1702-15) Joseph Dudley (b. 1647) on Apr. 2 in Roxbury, Mass. Am. Puritan minister Samuel Parris (b. 1653) on Feb. 27 in Sudbury, Mass. Italian physician Giovanni Maria Lancisi (b. 1654) on Jan. 20 in Rome. English poet Anne Finch, countess of Winchilsea (b. 1661) on Aug. 5 in Westminster. English poet John Hughes (b. 1677) on Feb. 17.




















1721 On Jan. 28 the Jewish ghetto in Frankfurt, Germany burns down again (first time 1711), and suffers looting by Christians, causing HRE Charles IV to order the town council to punish them and reimburse the Jews, which they do by annuling taxes and fees; in 1729 the last 45 Jewish families living temporarily in Christian houses are forced back into the ghetto. On Mar. 19 Pope (since Nov. 23, 1700) Clement XI (b. 1649) dies, and on May 8 Michelangelo (Michele) dei Conti is elected Pope (#244) Innocent XIII (1655-1724) (until Mar. 7, 1724), going on to impose new frugality standards and end the practice of nepotism among cardinals. What's going on in your head, what's wrong, Or, I walk alone, I walk alone? On Apr. 3 after he English Parliament begins proceedings against the suspects in the South Sea Bubble, the ruling Whig party is blamed, the ministers guilty of taking bribes resign or die, and chancellor of the exchequer John Aislabie (1670-1742) is sent to the Tower for fraud, Robert Walpole (1676-1745), brother-in-law of Lord Townshend replaces him, and his handiness with figures saves the day; James Stanhope dies, and Walpole becomes first lord of the treasury and chancellor of the exchequer, and the first official British First (Prime) Minister (until Feb. 11, 1742, replacing Charles Spencer, 3rd earl of Sunderland as chief of the cabinet (since 1718), where he helps solidify Hanoverian control of the English throne, using bribery to secure a solidly Whig House of Commons, and dominating England until his 1742 retirement - as its Big Whig? In summer China suppresses a revolt in Formosa (Taiwan) led by Zhu Yigui (Chu It-kui) (1689-1721), who is executed on June 28. On July 2 Yale rector Timothy Cutler outrages his protege Cotton Mather (1663-1728) by closing his commencement with the words, "and let all people say, Amen", Mather dubbing him a "treacherous Rector" for using the formula used to close an Anglican service; Cutler resigns and leaves for England, and Cotton is later passed over for the presidency. On Aug. 30 the Great Northern War (begun 1700) between Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Poland, etc. is concluded by the Treaty of Nystadt (Uusikaupunki) between Russia and Sweden, marking the beginning of Swedish military decline; Sweden cedes SE Finland (Karelia) and the Baltic provinces of Estonia (Esthonia), Livonia, and Ingria (Ingermanland), along with a number of Baltic islands to Russia, giving Peter I the Great (1672-1725) his precious outlet (window) to the Baltic Sea, permitting the opening of traffic with the West; Peter I is proclaimed Emperor of All the Russias; Sweden keeps W Finland (until 1809), ending the Great War (begun 1714); Denmark forces the abolition of Sweden's privileges regarding the Sound Tolls and gains the Slesvig lands, but the war takes a big bite out of Denmark, esp. agriculturally; the war causes a 16% pop. loss in Finland and a 10% loss in Sweden. After getting knighted last year, confirmed bachelor Francis Nicholson (1655-1728), becomes British gov. of S.C. (until 1725). Jeremiah Dummer (1681-1739), Mass.-born British agent for Mass. Bay Province since 1710 pub. A Defense of the New England Charters in response to a House of Commons bill seeking to annul the charters of Mass. Bay, N.H., R.I. and Providence Planations, arguing for the colonies' loyalty to the crown, and causing the bill to be defeated, although he loses his job, after which he stays on without pay. The Seneca Iroquois sign the Treaty of Albany, selling the Va. Piedmont to the Virginia Colony. Rama Varma dies, and Ravi Varma III (-1731) becomes king of Cochin in India (until 1731). France declares bankruptcy over the failure of John Law's Mississippi Co. Norwegian Lutheran missionary Hans Egede (1686-1758) sails in the ship The Hope from Norway to Greenland to convert Norse farmers, becoming the first new European in Greenland in 200 years; too bad, the Inuits tell him that there are no Norse there anymore, showing him crumgling stone church walls, causing the mystery of their disappearance to arise, which isn't solved until ? (the Little Ice Age?); he founds Godthab (Good Hope) on Kangeq (Kangek) Island on the W coast, establishing trade with Denmark and beginning missionary work among the Skraelings, er, Inuit, becoming known as "the Apostle of Greenland"; in 1728 Danish-Norwegian gov. Maj. Claus Enevold Paarss (1683-1762) moves Godthab to the mainland, becoming the world's northernmost capital ahead of Reykjavik; in 1979 it is renamed Nuuk ("cape"). After setting out from Quebec last year, French Jesuit priest-traveller Pierre Francois Xavier de Charlevoix (1682-1761) calls a point at the border of modern-day Mo. and Ill. N of St. Louis where the Illinois and Mississippi Rivers meet "the finest confluence in the world". Swiss immigrants to British North Am. introduce rifles. Regular postal service begins between London and New England. The New England Courant newspaper is founded in Boston, Mass. by Ben Franklin's older brother James Franklin (1697-1735) along with his wife Ann and brother Benjamin, introducing yellow journalism to Boston and forming the Hell-Fire Club, getting him imprisoned for four weeks in 1722 for "scandalous libel"; in 1727 the paper is suppressed, and he leaves Boston for Newport, R.I., founding Rhode Island's first printing press, followed in 1727 by the Rhode-Island Almanack AKA Poor Robin, and on Sept. 27, 1732 by the Rhode Island Gazette, which folds on May 24, 1733. Journal Oeconomique is founded in France to promote agrononomy and rational husbandry (until 1772). The first coffeehouse opens in Berlin, Germany. Georg Philipp Telemann becomes dir. of music in Hamburg. Breslau, Silesian-born mathematician-philosopher Christian Wolff (1679-1754) of the U. of Halle, a disciple of Gottfried Leibnitz known for ditching Latin for German gives the lecture "On the Practical Philosophy of the Chinese", citing the moral axioms of Confucius as proof that human reason can attain moral truth by its own efforts without Biblical revelation, pissing-off the religious (mainly Pietist) faculty; on July 12, 1723 Wolff gives another lecture comparing Moses, Christ, Mohammad, and Confucius, which attracts 1K students, pissing-off the Pietists, who convince Frederick William I that Wolff's determinism would ruin military discipline, causing him to be banished to Prussia for atheism and fatalism, where he teaches at the U. of Marburg in Hesse-Cassel until 1740, when Frederick II the Great recalls him and makes him a celeb, getting him promoted to chancellor of the U. of Halle in 1743. Porter, a heavily-hopped beer mixture of dark to light malts is invented in London, England, becoming the first beer to be aged at the brewery and shipped ready-to-drink, and the first that could be made on a large scale; the name comes from the landlord of the Old Blue Last Inn in Shoreditch, London, who orders Harwood Brewery to supply it ready-mixed, and whose customers are mainly market porters; too bad, it initially fails to gain popularity in the Am. colonies. Architecture: John James (1673-1746) begins St. George's Church in Hanover Square, London (finished 1725). The Spanish Steps in Rome are begun (finished 1725). James Gibbs (1682-1754) designs a replacement for St. Martin-in-the-Fields Church in the NE corner of London's Trafalgar Square, and it is completed in 1726, going on to become popular for cloning in British North Am. Inventions: English mathematician John Hadley (1682-1744) builds the first Newtonian reflecting telescope (6 in. mirror). Science: In Apr. Scottish surgeon Charles Maitland (1668-1745) performs the first smallpox inoculation in England with live smallpox virus on 4-y.-o. Mary Montagu, daughter of Lady Mary Wortley Montagu (1689-1762), who had contracted smallpox in Dec. 1715 and learned of the procedure while visiting Constantinople and had him do it to her 5-y.-o. son there in Mar. 1718; in Aug. 1722 seven condemned prisoners at Newgate Prison volunteer to become guinea pigs, and all survive and are released; in Dec. 1722 after five orphans of St. James's Parish in London are successfully inoculated, French-born English surgeon Claudius Amyand (1680-1740) inoculates three of the children of Prince George (later George II) and Princess Caroline of Ansbach, and later has Maitland inoculate her eldest son Frederick and one other child; meanwhile a smallpox epidemic in Boston, Mass. in Apr.-Dec. 1721 that infects 5,889 and kills 884 leads Cotton Mather to have his son inoculated, then to preach inoculation, causing a public hue and cry against him even though it works, drawing fire from physician William Douglass and support from physician Zabdiel Boylston, with prejudice against "heathens" in the Ottoman Empire and Bible-thumping arguments playing a role. The first hybrid cabbage is reported - Brussel sprouts right ahead? Nonfiction: Nathaniel Bailey (-1742), Universal Dictionary of the English Language; reissued in 1731 as Dictionarium Brittanicum: A More Compleat Universal Etymological Dictionary Than Any Extant; uses quotations from lit. works; used as the basis of Samuel Johnson's 1755 dictionary. Richard Bradley (1688-1732), A Philosophical Account of the Works of Nature; covers the "mineral, vegetable, and animal parts of the Creation", plus an account of gardening in Britain, getting him appointed Cambridge U.'s first prof. of botany in 1724, going on to pioneer the biological theory of infectious disease while pub. works on greenhouses and the first cookbook in English with recipes using pineapple; in his coverage of humans, he claims that there are "five sorts of men" based on skin color, incl. white Euros with beards, white Native Americans sans beards, men with copper skin, small eyes, and black hair; blacks with straight hair, and blacks with curly hair; later used by Curly, er, Carl Linnaeus?; A General Treatise of Husbandry and Gardening (3 vols.) (1721-4). Cornelius van Bynkershoek (1673-1743), De Foro Legatorum. Matthew Henry, Commentary on the Whole Bible (6 vols.) (Old Tappan, N.J.). Johann Theodor Jablonski, Allgemeines Lexicon; the first short encyclopedia. Johann Lorenz von Mosheim (1693-1755), Observationes sacrae; gets him an appointment as prof. at the U. of Helmstedt. Music: Filippo Amadei (Mattei), Giovanni Bononcini, and G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Muzio Scevola (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Apr. 15); libretto by Paolo Antonio Rolli, based on a work by Silvio Stampiglia (each does one act). Johann Sebastian Bach (1685-1750), Six Concerti (The Brandenburg Concertos), BWV 1046-51; composed for Christian Ludwig, margrave of Brandenburg-Schwedt (1677-1734). G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Floridante (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Dec. 9); libretto by Paolo Antonio Rolli, based on Francesco Silvani's "La Costanza in Trionfo". Art: William Hogarth (1697-1764), The South Sea Scheme; the first of his black-and-white satires. Jean-Antoine Watteau (1684-1721), Pilgrimage to Cythera; his #1 fete-galante painting? Plays: Pierre de Marivaux (1688-1763), Arlequin Poli par l'Amour (comedy). Edward Young (1683-1765), Revenge (Drury Lane, London). Poetry: Thomas Parnell (1679-1718), A Night-Piece on Death (posth.); The Hermit (posth.); A Hymn to Contentment (posth.); pub. in "Poems on Several Occasions", ed. by Alexander Pope. Allan Ramsay (1686-1758), Poems; first major work. Novels: Baron de Montesquieu (1689-1755), Persian Letters (Lettres Persanes); two aristocratic Persian travelers in Europe write letters to each other satirizing French society; a hit, helping fuel the French Enlightenment. Births: British lt.-gen. John Manners, Marquess of Granby (d. 1770) on Jan. 2 in Kelham, Nottinghamshire; educated at Eton College, and Trinity College, Cambridge U. English actor-mgr. Roger Kemble (d. 1802) on Mar. 1 in Hereford; husband (1753-) of Sarah "Sally" Ward (1735-1807); father of John Philip Kemble (1757-1823) and 11 other children, who become the Kemble Family of actors. Scottish architect John Adam (d. 1792) on Mar. 5 in Linktown, Abbotshall (modern-day Kircaldy, Fife); eldest son of William Adam (1689-1748) and Mary Robertson (1699-1761); brother of Robert Adam (1728-92) and James Adam (1732-94); father of William Adam of Blair Adam (1751-1839). Scottish "Roderick Random", "Peregrine Pickle" picaresque novelist Tobias George Smollett (d. 1771) on Mar. 19 in Dalquhurn (Renton), West Dunbartonshire; educated at the U. of Glasgow as a surgeon. Moravian missionary (in the U.S.) David Zeisberger (d. 1808) on Apr. 11 in Zauchtenthal (Suchdol nad Odrou); emigrates to British Am. in 1738. British military leader ("Butcher Cumberland") Prince William Augustus, Duke of Cumberland (d. 1765) on Apr. 26 in Leicester House, Westminster, London; 3rd and youngest son of George II and Caroline of Ansbach; worst Brit of the 18th cent.? Am. Rev. leader Roger Sherman (d. 1793) on Apr. 30 (Apr. 19 Old Style) in Newton, Mass.; moves to Conn. in 1743; only person to sign the Articles of Assoc., DOI, Articles of Confederation, and U.S. Constitution; starts out as a shoemaker, studies law, becomes a superior court judge in 1766, then goes into politics; first mayor of New Haven, Conn.; has 15 children by two wives; first cousin twice removed of Eli Whitney; ancestor of Archibald Cox; Sherman, Conn. is named for him; "A man who never said a foolish thing in his life" (Thomas Jefferson). Italian ballerina #a Barbara "La Barbarina" Campanini (d. 1799) on June 7 in Parma. Am. Rev. War. Gen. (Freemason) Johann von Robaii, Baron de Kalb (d. 1780) on June 19 in Huttendorf (near Erlangen), Bavaria, Germany; becomes a lt. in a German regiment in the French army, rising to brig. gen. by 1761 after fighting in the War of the Austrian Succession and the Seven Years' War. French architectural draftsman and painter Charles-Louis Clerisseau (Clérisseau) (d. 1820) on Aug. 28 in Paris; pupil of Giovanni Paolo Pannini. Swedish vice-adm. and naval architect Fredrik Henrik (Fredric Henric) af Chapman (d. 1808) on Sept. 9 in Gothenburg; son of English naval officer Thomas Chapman, who joined the Swedish royal navy in 1715. Am. Rev. leader Edmund Pendleton (d. 1803) on Sept. 9 in Caroline County, Va. Am. Rev. leader Peyton Randolph (d. 1775) on Sept. 10 in Williamsburg, Va.; pres. #1 of the Continental Congress (1774-5). Am. abolitionist Congregationalist clergyman-theologian Samuel Hopkins (d. 1803) on Sept. 17 in Waterbury, Conn.; nephew of Samuel Hopkins (1693-1755); uncle of Mark Hopkins (1802-87); educated at Yale College; pupil of Jonathan Edwards; kicked out of Housatonic, (Great Barrington), Mass. for his theology in 1769, he becomes a pastor in Newport, R.I. for life. Scottish historian (Whig) (Presbyterian) (historiographer royal, 1764-) William Robertson (d. 1793) on Sept. 19 Borthwick, Midlothian; educated at the U. of Edinburgh. English poet-physician Mark Akenside (d. 1770) on Nov. 9 in Newcastle upon Tyne; educated at the U. of Edinburgh. English "Ode to Evening" lyric poet William Collins (d. 1759) on Dec. 25 in Chichester, Sussex; educated at Winchester College, and Magdalen College, Oxford U. French courtesan (Louis XV's mistress) ("La Reinette") (Little Queen) Jeanne Antoinette Poisson, Marquise de Pompadour (d. 1764) on Dec. 29 in Paris; loves filet of sole topped with truffles. German banker Simon Moritz Bethmann (d. 1782) in Nassau; youngest son of Simon Moritz Bethmann (1687-1725); brother of Johann Philipp Bethmann (1715-93). Italian Neoclassical painter Domenico Corvi (d. 1803) in Viterbo; student of Vincenzo Camuccini (1771-1844) and Francesco Alberi (1765-1836). British fleet adm. Sir Peter Parker, 1st Baronet (d. 1811) in Ireland; knighted in 1772. Deaths: English slave trader Edward Coston (b. 1636) on Oct. 11 in Mortlake, Surrey; in 1895 a statue designed by John Cassidy is erected in Bristol in honor of his philanthropy; on May 8, 2020 it is toppled by Black Lives Matter protesters and thrown in the drink. French Waldensian pastor-soldier Henri Arnaud (b. 1641) on Sept. 8 in Schonenberg. Dutch-born English woodcarver Grinling Gibbons (b. 1648) on Aug. 3 in London; buried in St. Paul's, Covent Garden. Dutch New Amsterdam settler Harmen Jansen Knickerbocker (b. 1648) on Apr. 3 in Albany, N.Y. Am. sweathog Elihu Yale (b. 1649) on July 8 in Wrexham, Denbighshire, Wales; his tombstone is stolen by the secret Skull & Bones society and brought back to Yale U.? English poet-diplomat Matthew Prior (b. 1664) on Sept. 18 in Wimpole, Cambridgeshire; buried in Westminster Abbey. German botanist Rudolf Jakob Camerarius (b. 1665) on Sept. 11 in Tubingen. English natural philosopher John Keill (b. 1671) in Sept. English statesman-gen. James Stanhope, 1st Earl Stanhope (b. 1673) on Feb. 21. Scottish "Robinson Crusoe" mariner Alexander Selkirk (b. 1676); master's mate on the English man-of-war Weymouth. French fete-galante painter Jean-Antoine Watteau (b. 1684) on July 18.












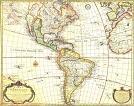
1722 The Golden Age of Piracy (begun 1650) for Britain comes to an end. after only about good 30 years. By this year S.C.'s slave pop. reaches 65% of the total pop. of 18,350, brought about by the profitability of the mortar and pestle technique of removing rice grains from husks. On Jan. 24 Peter I the Great issues an edict that the ruler of Russia shall choose his own successor, and establishes the Table of Ranks; he then joins in the fun and attacks Persia, seizing territories around the Caspian Sea; meanwhile the Ottomans want theirs too, and capture parts of W Persia as far as Hamadan (until 1723). On Mar. 8 (Sun.) Afghan Ghilzai Pashtun leader Mir Mahmud Hotaki (1697-1725) of Kandahar invades Persia and defeats the Persians at the Battle of Gulnabad near Isfahan; on Oct. 23 Isfahan falls after a 6-mo. siege and 80K starved or KIA and sultan (since 1694) Soltan Hosayn (Hosein) (1668-1726) abdicates in favor of Mahmud, declaring him his successor; Safavid rule in Persia collapses, and C and S Persia, and Sistan in W Khurasan are captured; Soltan Hosayn's son Prince Tahmasp flees to Tabriz, declares himself shah in Nov. and establishes a govt., and goes on to gain the support of Sunni Muslims in the Caucasus as well as Qizilbash tribes, regaining control of most of the country by 1729, while the Ottomans and Russians grab their pieces. On Apr. 2 the first of Benjamin Franklin's Addison-Steele-style essays by the fictional prudish middle-aged widowed woman Silence Dogwood appears anon. in his brother James Franklin's periodical the New England Courant. On Apr. 5 (Easter Sun.) after entering the Pacific in Mar. and sailing E to W in a search for Terra Australia, Easter Island (Rapa Nui) (Isla de Pascua) in the mid-South Pacific is discovered by Dutch explorer Adm. Jacob (Jakob) Roggeveen (1659-1729); due to overpop., deforestation, and the introduction of the Polynesian rat, the pop. is down to 2K-3K from 15K a cent. earlier; it is filled with 300 30-ft.-high stone busts (moai) (carved from volcanic rock from dormant Rano Raraku) with red headpieces, mounted on huge platforms; Roggeveen and his three ships sail away, and when Euros return almost 50 years later, the busts had been toppled from the platforms to the ground after tribal wars; 400 more uncompleted busts are found inside the crater, covered with Rongorongo inscriptions; Roggeveen continues on and discovers Bora Bora and Maupiti of the Society Islands and Samoa. On Dec. 20 emperor (since Feb. 5, 1661) Qing Sheng Zu (Kang Xi) (b. 1654) dies, and on Dec. 27 Qing Shi Zong (Shih Tsung) (Yongzheng) (Yinzhen) (1678-1735) becomes Qing (Manchu) emperor #3 (#5) of China, founding the Yung Zheng (Cheng) Dynasty (until Oct. 8, 1735), going on to ban Roman Catholicism in China, issuing the first anti-opium edict in 1729, and reducing slavery in China in 1730 while fighting Mongols in the W and cracking down on corruption and financial mismanagement; in 1733 he establishes the Grand Council (Junjichu) ("Office of Military Secrets"), which starts out in charge of military affairs and evolves into a privy council higher in rank than the grand secretariat. Hungary rejects the Pragmatic Sanction. Satha Ang Chey II becomes king of Cambodia (until 1738). The Australian East India Co. is founded. A British Privy Council memorandum sets out doctrines of discovery and conquest for Canada. Black Bart's ships are finally defeated by HMS Swallow off the African coast after logging 35K mi. in 3 years of plundering shipping lanes, and his men are captured after Bart is killed on Feb. 10 in a battle with a British warship after capturing a record 470 prizes since 1719. George I allows exiled (since 1715) Tory leader Viscount Bolingbroke to return to England, and restores his property in 1725; he settles at Dawley near Uxbridge, and becomes a literary bird, associating with Alexander Pope (1688-1744), Jonathan Swift (1667-1745), et al., and writes a series of letters in The Craftsman attacking PM Robert Walpole and his Robinocracy, later reprinted as A Dissertation on Parties. The Gen. Workhouse (Knatchbull's) Act is passed by the English Parliament, enabling parishes to build workhouses for able-bodied paupers and form poor law unions; too bad, it proves more expensive than outdoor relief. The English Parliament levies a tax on Roman Catholics. The Moravian Sect (Bohemian Brethren) is founded in Saxony by the Bohemian Brethren of the Lutheran Church, disciples of John Huss from Moravia in C Bohemia, and after persecution they found the Herrnhut settlement in Betrthelsdorf, Upper Lusatia on the estates of religious reformer Count Nikolaus Ludwig von Zinzendorf (1700-60). The English Parliament forbids journalists to report debates. The Iroquois-speaking Tuscarora tribe of N.C. and Va. joins the Iroquois Confederacy and moves to N.Y. and Ont. Danish dramatist Ludvig Holberg (1684-1754), prof. at the U. of Copenhagen opens a theater in Copenhagen, staging plays in Danish, which establish it as a lit. language. London bookseller and South Sea Bubble winner Sir Thomas Guy (1644-1724) founds Guy's Hospital in Southwark, London with a £300K donation. The Izhorsky Factory on the Izhora River in St. Petersburg is built by order of Peter I to supply the Russian fleet. Architecture: The Dresden Zwinger (begun 1711) is finished, becoming the city's most famous landmark. Quaker minister Elihu Coleman (1699-1789) builds a spacious house on Nantucket Island S of Cape Cod. Science: German physician Friedrich Hoffmann (1660-1742) discovers that the base of alum is an individual substance. Music: Johann Sebastian Bach (1685-1750), The Well-Tempered Clavier, Vol. 1 (Das Wohltemperierte Klavier); preludes and fugues in all 24 major and minor keys "for the profit and use of musical youth desirous of learning, and especially for the pastime of those already skilled in this study"; vol. 2 is pub. in 1742; becomes one of the top musical works of Western music. Francois Couperin (1668-1733), Les Concerts Royaux; performed for the court of Louis XIV in 1714-15. Reinhard Keiser (1674-1739), Ulysses (opera) (Copenhagen). Nonfiction: Henry St. John, Viscount Bolingbroke (1678-1751), Reflections on Exile. Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), History of Peter the Great; A Journal of the Plague Year. Guillaume Delisle (1675-1726), Map of the Americas; shows Calif. as a peninsula. Johann Mattheson, Critica Musica. Jean-Philippe Rameau (1683-1764), Traite de l'Harmonie (Treatise on Harmony); mathematizes music, describing the modern 12-tone musical scale with major and minor keys; makes him famous as a musical theorist, "the Isaac Newton of Music". R.A. Ferchault de Reaumur, L'Art de Convertir le Fer Forge en Acier. Hyacinthe Rigaud (1659-1743), Grand Tour; travel handbook, making the well-educated (Greek and Latin) young man who goes on a Grand Tour of Paris, Venice, Florence and Rome the thing to be. Plays: Henry Carey (1687-1743), Hanging and Marriage. Susanna Centlivre (1667-1723), The Artifice (comedy); a flop, becoming her last play. Pierre de Marivaux (1688-1763), Surprise de l'Amour. Ambrose Philips (1674-1749), The Briton. Richard Steele (1672-1729), The Conscious Lovers (comedy) (last play); based on Terence's "Andria". Novels: Richard Boyle (1694-1753) (tr.), The Travels and Adventures of Three Princes of Serendip; the ever-lucky princes from Ceylon (Sri Lanka). Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), The Fortunes and Misfortunes of Moll Flanders (picaresque); The History and Remarkable Life of the Truly Honorable Colonel Jack, Another Robinson Crusoe. Births: British dramatist and gen. John "Gentleman Johnny" Burgoyne (d. 1792) on Feb. 24 in Sutton (near London); educated at Westminster School. Am. Baptist minister (founder of Brown U.) Morgan Edwards (d. 1795) on May 9 in Wales; educated at Bristol College. Dutch anatomist-naturalist Pieter (Peter) (Petrus) Camper (d. 1789) on May 11 in Leiden; educated at the U. of Leiden; inventor of the term "extinct" with Geores Cuvier to describe the mammoth. English sculptor Joseph Wilton (d. 1803) on July 16 in London; born to a wealthy family. French salonist Anne-Catherine "Minette" de Ligniville, (d'Autricourt) Madam Helvetius (Helvétius) (d. 1800) on July 23; wife (1751-) of Claude Adrien Helvetius (1715-71); Ben Franklin proposes to her? Am. brewer and Rev. patriot-statesman ("Father of the Am. Rev.") Samuel "Sam" Adams (d. 1803) on Sept. 27 in Boston, Mass.; cousin of John Adams (1735-1826). French Adm. of the West Indies Francois Joseph Paul, Comte de Grasse (d. 1788) in Sept. German painter Johann Heinrich Tischbein (Ger. "table leg") (the Kasseler) (d. 1789) on Oct. 3 in Haina; father of Johann Friedrich August Tischbein (1750-1812) and Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Tischbein (1751-1829). British Battle of Bunker Hill Maj. John Pitcairn (d. 1775) on Dec. 28 in Dysart, Fife, Scotland. Afghan amir (emir) #1 (1747-73) Ahmed (Ahmad) Shah Durrani (d. 1773); son of Abdali (Durrani) chief Sammaun Khan; father of Timur Shah Durrani (1748-93); founder of the Sadozai dynasty of the Abdali tribe. Austrian luthier (stringed instrument maker) Leopold Widhalm (d. 1776). English poet Christopher Smart (d. 1771) in Shipbourne, Kent. Am. Rev. printer William Bradford Jr. (d. 1791) in New York City; son of William Bradford (1663-1752); brother of Philly publisher Andrew Sowles Bradford (1686-1742). Am. indigo planter Eliza Lucas Pinckney (nee Lucas) (d. 1793) in Antigua; daughter of the gov. of Antigua; emigrates to S.C. in 1738; wife (1744-) of Charles Pinckney (-1758). Deaths: Scottish physician Sir Robert Sibbald (b. 1641) in Aug. English soldier-statesman John Churchill, 1st duke of Marlborough (b. 1650) on June 16 in Windsor. Italian composer Carlo Francesco Pollarolo (b. 1653). Chinese Qing emperor #4 (1661-1722) Kangxi (b. 1654) on Dec. 20 in Beijing. German architect Christoph Dientzenhofer (b. 1655) on June 20 in Prague. French historian Comte Henri de Boulainvilliers (b. 1658) on Jan. 23 in Paris. French historical painter Antoine Coypel (b. 1661). English freethinker John Toland (b. 1670) on Mar. 11 in London, England. French painter Claude Gillot (b. 1673). English PM (1618-21) Charles Spencer, 3rd earl of Sunderland (b. 1674) on Apr. 19. Welsh pirate Black Bart (b. 1682) on Feb. 10 off Cape Lopez, Gabon.




1723 On Feb. 15 Louis XV of France attains majority, and puts Dr. Evil, er, regent (since 1715) Duke Philippe II of Orleans (b. 1674) out of business just in time, since he croaks on Dec. 23 after becoming PM - a little arsenic? On Oct. 10 after Peter I the Great conquers territory on the Caspian Sea incl. Baku in his last major military campaign, to insure against future hostilities, the Treaty of Charlottenburg between England and Prussia is signed, promising George I's grandson to the Prussian princess while Prince Frederick is promised to the daughter of the Prince of Wales. On Oct. 10 17-y.-o. runaway Boston printing apprentice Benjamin Franklin comes ashore on Penn's Landing in Philadelphia in a storm, attracted by its promise of "liberty of conscience" and no mandatory tithing; he buys three pennies' worth of bread and roams the streets, one roll under each arm and one in his mouth, going on to become the world's first self-made man (multimillionaire), starting by working for printer Samuel Keimer (1688-1739). On Oct. 31 ultra-reactionary grand duke (since May 23, 1670) Cosimo III de' Medici (b. 1642) dies after a 53-year reign, during which he allowed Tuscany to deteriorate economically to a new low, and is succeeded by his eldest surviving son Gian (Giovanni Battista) Gastone de' Medici (1671-1737), who becomes the 7th and last Medicean grand duke of Tuscany (until July 9, 1737), who tries in vain to reverse his father's policies, abolishing taxes for the poor, ending public executions, and repealing penal laws oppressing Jews; too bad, he has no heirs. On Nov. 12 Joseph Clemens von Wittelsbach (b. 1671) dies, and Clemens August of Bavaria (1700-61), brother of Bavarian elector Maximilian II Emanuel is appointed archbishop-elector of Cologne. On Nov. 18 the city of Ekaterinburg (Yekaterinburg) (named after Peter the Great's wife Yekaterina AKA Tsar Catherine I) on the Iset River E of the Ural Mts. of Russia (modern-day pop. 1.34M/1.49M) is founded, becoming Russia's mining capital, known as "the window to Asia" after Tsar Catherine II builds the Siberian Route (Tea Road) (Moscow Highway) (Great Highway) from Russia to Siberia to China through it. On Dec. 29 the Anglican Georgian-style Old North (Christ) Church in Boston, Mass. (193 Salem St.), designed by William Price, and built with bricks from Medford and designed to copy Sir Christopher Wren's St. Paul's Cathedral in London (whose tall spire dwarfs the other bldgs. in North End) holds its first service, becoming Boston's oldest church bldg. surviving to modern times, made famous as the scene of Paul Revere's Midnight Ride (Apr. 18, 1775); on Oct. 23 Increase Mather (b. 1639) dies, and his son Cotton Mather (1663-1728) becomes minister of Boston's original North Church, which is a different (Puritan) church. Prussia establishes a ministry of war, finance, and domains. The Hungarian Diet finally accepts the Pragmatic Sanction. The Marthas invade Malwa Province, and take the capital Ujjain. British PM Robert Walpole reduces the duty on tea. The Waltham Black Acts make poaching and 49 other pissant offenses a capital offense in England. The princely state of Bhopal in the Vindhya Mts. of C India is founded by an Afghan chieftain who had fought in Aurangzeb's army, becoming the capital of Madhya Pradesh. J.S. Bach is appointed Thomascantor in the Thomaskirche in Leipzig after Telemann turns the post down. The London theatrical seasons of 1723-4 are dominated by spectacle and pantomime plays, and Henry Carey (1687-1743) becomes the unnoficial composer for Drury Lane (until 1733); next year William Hogarth composes a satire on the abandonment of drama for puppets. Alessandro Scarlatti (d. 1725) returns from Rome to Naples for the last time. Architecture: Pedro de Ribeira builds the Toledo Bridge in Spain. Nonfiction: Anon., T'u Shu Chi Ch'eng (1723-36); Chinese encyclopedia. William Buchanan, An Inquiry into the Genealogy and Present State of Ancient Scottish Surnames, with the Origin and Descent of the Highland Clans and Family of Buchanan; dude from Auchmar covers all the Scottish clans, but takes up half the book with his own Buchanan clan. M.A. Capeller, Prodromus Crystallographiae. Joseph-Francois Lafitau (1681-1746), Moeurs des Sauvages Ameriquains Comparees aux Moeurs des Premiers Tempes; study of Iroquois customs. Lodovico Antonio Muratori, Rerum Italicarum Scriptores (28 vols.) (1723-51). Manuel Teles da Silva, 3rd Marquis of Alegrete (1682-1736), Collections of the Documents and Memories of the Royal Academy of Portuguese History; followed by History of the Royal Academy of Portuguese History (1727). Voltaire (1694-1778), La Henriade. Music: J.S. Bach (1685-1750), St. John Passion. G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Ottone, Re di Germania (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Jan. 12); libretto by Nicola Haym based on a libretto by Pallavicini; stars Francesca Cuzzoni as Teofane and Farinelli as Adelberto (only time he performs in a Handel opera); first composed for the Royal Academy of Music; Flavio, Re di Langobardi (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (May 14); libretto by Nicola Francesco Haym, based on Matteo Noris' "Il Flavio Cuniberto". Antonio Vivaldi (1678-1741), The Four Seasons (Le Quattro Stagioni); pub. in 1725; becomes his most famous work. Plays: Elijah Fenton (1683-1730), Mariamne (tragedy). Ambrose Philips (1674-1749), Humphrey, Duke of Gloucester. Alexander Pope (1688-1744) (ed.) Shakespeare's Plays (1723-5); his "regularizing" of metre and other revisions cause Lewis Theobald and other critics to ridicule him; "I have discharg'd the dull duty of an Editor to my best judgment, with more labour than I expect thanks, with a religious abhorrence of all Innovation, and without any indulgence to my private sense or conjecture"; "Players are just such judges of what is right, as Taylors are of what is graceful. And in this view it will be but fair to allow, that most of our Author's faults are less to be ascribed to his wrong judgment as a Poet, than to his right judgment as a Player". John Thurmond, Harlequin Dr. Faustus (pantomime) (Drury Lane, London). Novels: Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), The Highland Rogue; Or, The Memorable Actions of the Celebrated Robert Mac-gregor, Commonly Called Rob-Roy; about Rob Roy (1671-1734), making him a legend, and causing George I to pardon him in 1727 just before he is scheduled to be transported to the colonies. Births: Am. Presbyterian minister (DOI signer) John Witherspoon (d. 1794) on Feb. 5 in Gifford, East Lothian, Scotland; educated at Edinburgh U.; emigrates to the U.S. in 1768; pres. of Princeton U. (1768-94). German physicist Johann Tobias Mayer (d. 1830) on Feb. 17 in Mabach, Wurttemberg; educated at the U. of Gottingen. French historian Louis Pierre Anquetil (d. 1808) on Feb. 21 in Paris; brother of Abraham Hyacinthe Anquetil-Duperron (1731-1805). Scottish-Swedish Neoclassical Somerset House architect Sir William Chambers (d. 1796) on Feb. 23 in Gotheburg, Sweden; rival of Robert Adam (1728-92); sails to Canton, China at age 16, and brings the Chinese Style to Britain. British Adm. Sir Hugh Palliser, 1st Baronet (d. 1796) on Feb. 26 in Kirk Deighton, North Riding of Yorkshire; created baronet in 1773. Danish-Norwegian king (1746-66) Frederick V (d. 1766) on Mar. 31 in Copenhagen; son of Christian VI (1699-1746) and Sophia Magdalen of Brandenburg-Kulmbach; father of Christian VII (1749-1808). Scottish "The Wealth of Nations" laissez-faire economist ("Father of Economics") Adam Smith (d. 1790) on June 16 (June 5 Old Style) in Kircaldy, Fifes. German Halley's Comet astronomer Johann Georg Palitzsch (d. 1788) on June 11 in Prohlis (near Dresden), Saxony. Scottish Englightenment philosopher-historian (friend of David Hume) Adam Ferguson (of Rath) (d. 1815) on June 20 in Logierait, Atholl, Perthshire; educated at the U. of St. Andrews. English "Commentaries on the Laws of England" jurist Sir William Blackstone (d. 1780) on July 10 in London; educated at Charterhouse School, and Pembroke College, Oxford U. English Grand Style portraitist Sir Joshua Reynolds (d. 1792) on July 16 Plympton (near Plymouth), Devon; pupil of Thomas Hudson; pres. #1 of the British Royal Academy of Arts (1768); knighted in 1769. Am. statesman William Livingston (d. 1790) on Nov. 30 in Albany, N.Y.; brother of Philip Livingston (1716-78); educated at Yale College; gov. of N.J. (1776-90); signer of the U.S. Constitution. Welsh poet Gronwy Owen (d. 1769). Am. Rev. 6'2" black (mulatto) martyr Crispus Attucks (d. 1770); from Wopanaak "ahtuk" = deer? German philosopher-encyclopedist (in France) (atheist) Paul-Henri Thiry (Paul Heinrich Dietrich), Baron d'Holbach (d. 1789) in Edesheim, Germany; inherits his French uncle's money, estate and title, and moves to Paris to set up shop. Welsh liberal Congregationalist minister Richard Price (d. 1791) in Tynton, Glamorganshire. French statesman Clement Charles Francois de Laverdy (d. 1793). English architect John Carr (d. 1807) in Horbury, West Riding of Yorkshire. Deaths: Dutch scientist Antony van Leeuwenhoek (b. 1632) on Aug. 30 in Delft. English's chief architect Sir Christopher Wren (b. 1632) on Feb. 25 in London; epitaph: "If you seek his monument, look around you." Am. clergyman Increase Mather (b. 1639) on Aug. 23 in Boston, Mass. Italian grand duke #6 (1670-1723) Cosimo III de' Medici (b. 1642) on Oct. 31 in Pitti Palace, Florence. German-born English portraitist Sir Godfrey Kneller (b. 1646) on Oct. 19 in Twickenham (fever); painted portraits of 10 reigning monarchs. Spanish architect Jose Churriguera (b. 1650). English playwright Thomas D'Urfey (b. 1653) on Feb. 26 in London: "All animals, except man, know that the principal business of life is to enjoy it." Chinese Ming emperor #2 (1661-1723) Qing Sheng Zu (b. 1654). Austrian architect Fischer von Erlach (b. 1656). English bishop William Fleetwood (b. 1656) on Aug. 4 in Tottenham, Middlesex. Italian anatomist Antonio Valsalva (b. 1666) on Feb. 2 in Bologna. English poet-dramatist-actress Susanna Centlivre (b. 1667) on Dec. 1 in London. Romanian prince-musician Dimitrie Cantemir (b. 1673) near Kharkov, Russia (exile). French duke Philippe II of Orleans (b. 1674) on Dec. 23 in Versailles. German poet Johann Christian Gunther (b. 1695).








1724 On Jan. 28 the Russian Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg, Russia is founded by Peter I the Great with advice by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, with members incl. Leonhard Euler (1707-83), Daniel Bernoulli, Nicholas Bernoulli, and Christian Goldbach; called St. Petersburg Academy of Science until 1917, and Soviet Academy of Science in 1925; moves to Moscow in 1934. Philip V abdicates in favor of his 17-y.-o. son, who becomes Luis I of Spain, but he dies of smallpox before the year is up, and Philip V resumes his reign; his 2nd son Ferdinand becomes the prince of Asurias, next in line for the throne; Philip V builds San Ildefonso, the palace of the Granja (modeled on Versailles) to house himself and Elizabeth as the palace of the Bourbons in Spain. On Mar. 7 Pope Innocent XIII dies, and on May 27 Pietro Francesco Orsini is elected Pope (#245) Benedict XIII (1649-1730); he learns to smoke and repeals papal bulls against clerical smoking - didn't I make you feel like you are the only man? In June Russia and Turkey agree to a peaceful partition of Persia's newly-captured NW provinces. On Aug. 23 after Father Rale's War (Lovewell's War) (Gov. Dummer's War, Greylock's War, the Three Years War) (4th Anglo-Abenaki War) (Wabanaki-New England War of 1722-5) begins after English colonists suspect French Jesuit missionary (since 1694) Father Sebastien Rale (Rasle) (Rasles) (b. 1657) of abetting tribal hostilities against British settlements, 200 colonial troops under Capt. Johnson Harmon, Capt. Jeremiah Moulton, and Capt. Richard Bourne from Fort Richmond via Taconic Falls (Winslow), Maine arrive in the Abenaki village of Narantsouak (Norridgewock, Maine) on the Kennebeck River on the border with Acadia, starting the Battle of Norridgewock, massacring 26 Indian warriors incl. Chief Mog along with Father Rale and injuring 14, with the 150 survivors fleeing to St. Francis (where they get a little payback in 1757) and Becancour, Quebec, after which Rale is treated as a Catholic martyr, with a monument erected over his grave in Madison, Maine in 1833; the Abenaki Confederacy (founded in the 1670s) is destroyed by the English. On Nov. 16 famed highwayman Jack Sheppard (b. 1702), who commits a robbery a day in and about London is betrayed by fence Jonathan Wild, arrested and sentenced to death, then escapes with the help of Edgeworth Bess, is rearrested, escapes from Newgate, gets drunk and is arrested a final time, placed under 24-hour guard, then hanged in Tyburn, going on to be celebrated in A Narrative of All the Robberies, Escapes, Etc., of John Sheppard, attributed to Daniel Defoe. In Nov. after receiving a promise of a line of credit to buy equipment and supplies to start his own printing shop, 18-y.-o. Benjamin Franklin sails for London with aspiring poet James Ralph, befriending prominent Quaker merchant Thomas Denham on the voyage; on the way they stop at Block Island, and the sight and smell of the plentiful cod being cooked causes him to give up his flirtation with vegetarianism, picked up after by reading a book by Thomas Tryon (1643-1703) in 1722; after the line of credit falls through, he gets a job at Samuel Palmer's printing house; he then tries to seduce Ralph's girlfriend and they break up. Thomas Pelham-Holles, Duke of Newcastle (1693-1768) is appointed secy. of state for the British ministry's southern dept., with responsibility for supervising the Am. colonies; a petty buffoon, his policy becomes known as "solitary neglect". Lord Newcastle becomes secy. of the committee of the privy council in England, and commandeers control of the Board of Trade (ends 1748). Peter the Great crowns his wife Tsarina Catherine. The Austrian Netherlands agree to the Pragmatic Sanction. Most of the Tulpehocken Delawares migrate to the Ohio Valley. Vermont (Vt.) is settled at Ft. Dummer on the Connecticut River by the English. France issues a decree against the Reformed (Protestant) Church, prohibiting it from holding secret exercises; a price is put on the head of reformer Antoine Court (d. 1760), causing him to flee to Lausanne in 1730 and found a seminary, which he runs for life. After the Portuguese begin fortifying the heights around the Bay of Montevideo in Uruguay, a Spanish force from Buenos Aires led by Spanish soldier Bruno Mauricio de Zabala (1682-1736) forces them back to Colonia, and Zabala founds a fortress that becomes the city of Montevideo (San Felipe y Santiago de Montevideo) on the NE bank of the Rio de la Plata River 68 mi. E of Buenos Aires (modern-day pop. 1.3M/1.9M), continuing the turf war, while the British and Portuguese carry on what they claim to be illicit trade in the Rio de la Plata region; Montevideo goes on to become the center of Spanish control over the Banda Oriental, capital and largest city of Uruguay, and southernmost capital city in the Americas. Gin drinking becomes popular in Great Britain. The Paris Bourse, France's nat. stock market opens. Professorships of modern history and languages are founded at Oxford U. and Cambridge U.; David Gregory (1696-1767) becomes the first Regius Professor of History at Oxford U. (until 1736); Samuel Harris (1682-1733) becomes the first Regius Professor of Modern History at Cambridge U. (until 1733); in 2010 it becomes the Regius Professor of History at Cambridge U, starting with Sir Richard J. Evans (until 2014), then Christopher Clark (until ?). Bavarian elector Maximilian II Emanuel founds a union of all the lines of the Wittelsbach family in hopes of one day getting the HRE title away from the Hapsburgs, which happens in 1742, 16 years after his death when his sonny boy Charles VII Albert finally gets to sit his you know what on the emperor's chair, although only for three years. Longman's Publishing House is founded in England, becoming the oldest to survive to modern times. After receiving a bequest from William III's secy. Sieur D'Allone, English philanthropist Dr. Thomas Bray founds the Associates of Dr. Bray in London educated enslaved blacks in the British North Am. colonies; on Jan. 2, 1760 they elect Ben Franklin to membership, signifying him as a leading philanthropist in New England. The Three Choirs Festival for Gloucester, Hereford and Worcester in England is founded. The Academy of Antient Musick in London elects Italian composer Agostino Steffani as honorary pres. for life, causing him to send them a bunch of musical mss. which end up in the British Museum. Architecture: James Gibbs begins building the Fellows' Bldg. at King's College, Cambridge (finished 1749). Prince Eugene's Belvedere Palace in Vienna is finished by Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt. Leonardo de Figueroa designs the West Entrance to the St. Telmo Palace in Seville, Spain. Inventions: Blasting is first used in Sweden. Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit of Amsterdam discovers the phenomenon of supercooling (undercooling), the ability of a liquid or gas to be lowered below its freezing point, for example when water doesn't freeze in clouds. Am. tavern owner Joseph French near Albany, N.Y. invents French toast; should have called it French's toast? Science: After being freaked-out by the 1692-3 Salem Witch Trials, Puritan New England minister Cotton Mather (1663-1728) advances physical rather than demonic explanations for mental illnesses. Nonfiction: Anon., Letter of Jesus Christ; claims to have been "written by Jesus Christ, and found under a great stone both round and large, at the foot of the cross, 18 miles from Iconium, near a village called Mesopotamia", and "now in the possession of the Lady Cuba's family"; becomes a big hit, circulating into the 20th cent. Herman Boerhaave (1668-1738), Elementa Chemiae (Elements of Chemistry); describes Boerhaave's Syndrome (tearing of the esophagus); tells how in the winter he "exposed beer, wine, vinegar, and brine in large open vessels to the frost; which, thus, congeal'd nearly all the water of these liquors into a soft, spongy kind of ice, and united the strong spirits of the fermented liquors; so that by piercing the ice, they might be pour'd off and separated from the water, which diluted them from freezing... it is probable, that the utmost possible cold in nature would deprive water of all its dissolving power." Anthony Collins (1676-1729), Discourse of the Grounds and Reasons of the Christian Religion. Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), A Tour Through the Whole Island of Great Britain (1724-6) (3 vols.). Bernard de Fontenelle (1657-1757), De l'Origine des Fables (On the Origin of Fables); written in 1691-9. August Hermann Francke (1663-1727), Commentatio de Scopo Librorum Veteris et Novi Testamenti. Capt. Charles Johnson, General History of the Robberies and Murders of the Most Notorious Pyrates; the real author is Daniel Defoe? Philip Miller (1691-1771), The Gardener's and Florist's Dictionary; or A Complete System of Horticulture; by the chief gardener of the Chelsea Physic Garden. Herman Moll (1654-1732), New Description of England and Wales; atlas. John Oldmixon (1673-1742), A Critical History of England (1724-26). Isaac Watts (1674-1748), Logic, or The Right Use of Reason in the Enquiry After Truth With a Variety of Rules to Guard Against Error in the Affairs of Religion and Human Life, as well as in the Sciences; bestseller (20 eds.). Music: William Croft (1678-1727), Musica Sacra; first church music collection printed in the form of a score; incl. Burial Services, which is used at British state funerals. Francois Couperin (1668-1733), Le Parnasse, ou L'Apotheose de Corelli. Francesco Gasparini (1661-1727), Tigrane (opera). G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Giulio Cesare in Egitto (Julius Caesar in Egypt) (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Feb. 20); libretto by Nicola Francesco Haym; stars Senesino as Caesar, and Francesca Cuzzoni as Cleopatra; incl. Al Lampo dell'Armi, L'Empio, Sleale Indegno, L'Angue Offeso Mai Riposa; Tamerlano (Tamerlane) (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Oct. 31); libretto by Nicola Francesco Haym based on Agostin Piovene's "Tamerlano"; stars Francesco Borosini as Sultan Bajazet, Andrea Pacini as Tamerlane, and Francesca Cuzzoni as Bajazet's daughter Asteria; Bajazet is one of the first major tenor roles in opera. Plays: Ludvig Holberg (1684-1754), Henrik and Pernille (comedy). Poetry: Allan Ramsay (1685-1758), The Tea-Table Miscellany: A Collection of Choice Songs, Scots and English (4 vols.) (1724-7); The Ever Green (1724-7); anthology of Scottish verse, incl. The Vision. Novels: Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), Roxana: The Fortunate Mistress (The Fortunate Mistress: Or, A History of the Life and Vast Variety of Fortunes of Mademoiselle de Beleau, Afterwards Called the Countess de Wintselsheim, in Germany, Being the Person known by the Name of the Lady Roxana, in the Time of King Charles II). Births: Am. Baptist preacher and church-state separation advocate Isaac Backus (d. 1806) on Jan. 9 in Yantic, Conn. Courland duke (last) (1769-95) Peter von Biron (d. 1800) on Feb. 15 in Jelgava; son of Ernst Johann von Biron (1690-1772). Am. Rev. leader Brig. Gen. Christopher Gadsden (d. 1805) on Feb. 16 in Charleston, S.C.; grandfather of James Gadsden (1788-1858). British field marshal George Townshend, 1st Marquess Townshend (d. 1807) (AKA Viscount Townshend from 1764-87) on Feb. 28; son of Charles Townshend, 3rd viscount Townshend (1700-64) (Lord Lynn); brother of Charles Townshend (1725-67); 1st cousin of Thomas Townshend, 1st viscount Sydney (1732-1800); educated at St. John's College, Cambridge U. Am. Rev. leader and physician (DOI signer) Lyman Hall (d. 1790) on Apr. 12 in Wallingford, Conn.; educated at Yale U. German "Critique of Pure Reason" philosopher (founder of the Idealist school) Immanuel Kant (d. 1804) on Apr. 22 in Konigsberg, Prussia (Kaliningrad, Russia). Austrian field marshal Dagobert Sigismund, Count von Wurmser (d. 1797) on May 7 in Strasbourg, Alsace. English artist (originator of the idea of the picturesque) Rev. William Gilpin (d. 1804) on June 4 in Cumberland; educated at Queen's College, Oxford U. English civil engineer-physicist ("Father of Civil Engineering") John Smeaton (d. 1792) on June 8 in Austhorpe, Leeds. Swiss (Genevan) physicist Georges-Louis Le Sage (d. 1803) in Geneva; educated at the U. of Geneva. German poet Friedrich Gottlieb Klopstock (d. 1803) on July 2 in Quedlinburg. English historian Lawrence Brockett (d. 1768) on Aug. 13; educated at Trinity College, Cambridge U. English painter George Stubbs (d. 1806) on Aug. 25 in Liverpool; known for his paintings of horses. British gen. Sir Guy Carleton, 1st Baron Dorchester (d. 1808) on Sept. 3 in Strabane, County Tyrone, Ireland. German educator Johann Bernhard "J.B." Basedow (d. 1790) on Sept. 11 Hamburg; educated at the U. of Leipzig. Spanish queen consort of Naples and Sicily (1738-59) and Spain (1759-60) Maria Amalia Christina Franziska Xaveria Flora Walburga of Saxony (d. 1760) on Nov. 24 in Dresden; daughter of Augustus III of Poland (1696-1763) and Maria Josepha (1699-1757) (daughter of HRE Joseph I); wife (1738-60) of Charles III (1716-88); mother of Maria Louisa of Spain (1745-91) (wife of HRE Leopold II), Charles IV (1748-1819), and Ferdinand I (1751-1825). German Palatine elector (1742-99) and Bavarian elector (1777-99) Karl IV Theodor (Charles IV Theodore) (d. 1799) on Dec. 11 in Drogenbos (near Brussels); of the Oberpfalz-Sulzbach line of the House of Wittelsbach (founded 1119). English natural philosopher John Michell (d. 1793) on Dec. 25 in Earking, Nottinghamshire; educated at Queen's College, Cambridge U. Chinese "Dream of the Red Chamber" novelist Cao (T'sao) Xueqin (Zhan) (Chan) (d. 1764) (b. 1715?) in Nanjing; Han Chinese. Irish "Memoirs of Miss Sidney Bidulph" novelist-playwright Frances Sheridan (nee Chamberlaine) (d. 1766) in Dublin; wife (1747-) of Thomas Sheridan (1719-88); mother of Richard Brinsley Sheridan (1751-1816). Japanese wood block artist Suzuki Harunobu (d. 1770) (b. 1725?); pupil of Shighenega; inventor of polychrome block prints. Spanish Calif. gov. (1775-82) (founder of Los Angeles) Felipe de Neve (d. 1784) in Bailen, Jaen Province. Dutch novelist Willem Leevend (d. 1785); collaborator of Rhijnvis Feith (1753-1824). Am. Rev. leader-jurist (DOI signer) ("Father of American Jurisprudence") ("Virginia's Foremost Classical Scholar") George Wythe (d. 1806) in Chesterton (Hampton), Va.; first law prof. in the U.S., and Thomas Jefferson's mentor. Deaths: English philanthropist John Kyrle (b. 1637) on Nov. 7 in Ross-on-Wye. German composer Johann Theile (b. 1646) on June 24. English divine Humphrey Prideaux (b. 1648). Scottish-born Am. colonist William Trent (b. 1653). French Jesuit missionary Sebastian Rale (b. 1657) on Aug. 23 in Norridgewock, Maine (KIA). English writer Delarivier (Mary) Manley (b. 1663): "There's no time like the present." Spanish viceroy of New Spain (1702-11) Francisco Fernandez de la Cueva, 10th duke of Alburquerque (b. 1666) on June 28 in Madrid. English highwayman Jack Sheppard (b. 1702) in Tyburn (hanged). Korean king Kyonjong.








1725 The pop. of black slaves in the British Am. colonies reaches 75K. In 1725-1800 there are 137 newspapers pub. in N.Y. state, incl. 20 in New York City; by 1865 there are 373 newspapers being pub. in 428 eds. in N.Y., incl. 54 in New York City. On Jan. 9 (Dec. 29 Old Style) Peter I the Great asks Danish-Russian explorer Vitus Jonassen Bering (1681-1741) to launch an expedition E from St. Petersburg to explore the N Pacific Ocean, becoming known as the First Kamchatka Expedition, going on to discover the Bering Strait, Gulf of Kamchatka, Avacha Bay, and the Chukchi Sea, proving that Asia and North Am. aren't connected; they return on Feb. 28, 1730 to St. Petersburg via Okhotsk, making Bering a celeb. On Feb. 8 (Jan. 28 Old Style) after aggravating his condition by attempting to rescue some drowning soldiers by wading into the Baltic, tsar (since 1682) Peter I the Great (b. 1672) dies of uremia in the middle of writing his will ("I leave everything to..."), and his illiterate serf wife (not so great) Catherine (Ekaterina Alexeyevna) I (1684-1727) takes the Russian throne as Russian Romanov tsar #6 (until May 17, 1727), taking advantage of all his modernization efforts to begin a push to expand Russia to the Black Sea, creating the Order of Alexander Nevsky on June 1 (May 21 Old Style), conveniently forgetting the way this hero sold-out to the Tartars; Peter's black adopted son Gen. Abram Petrovich Gannibal (d. 1781) is demoted and sent to exile in Siberia, but eventually retires to a modest estate, where he does research on military engineering amongst his white serfs. On Apr. 22 after watching the Persian pop. rise against him, and inviting Persian nobles and princes to a meeting then having them slaughtered, along with 3K Persian royal guards, along with all the Safavid princes except Soltan Hosein and his two sons, then going insane, Mir Mahmud Hotaki (b. 1697) is killed in a palace revolt, and his son Ashraf Ghalzai (1700-20) becomes Hotaki shah of Afghanistan and Persia, marrying a Safavid princess and going on to stop Ottoman and Russian incursions. In Apr. after mapping the W African Kingdom of Whydah, French explorer Reynaud des Marchais, Chevalier des Marchais witnesses the coronation of king Haffon (1695-1727); Whydah is conquered by Dahomey in 1727; he also discovers the Miracle Fruit (Synsepalum Dulcificum), whose berries cause sour foods (lemons, limes etc.) to taste sweet; it takes until 1968 to isolate the active ingredient miraculin. On May 18 George I founds the Most Honourable Military Order of the Bath, based on the medieval ceremony for creating a knight, which involves bathing as a symbol of purification. In May Dutch ship officer Leendert Hasenbosch (b. 1695) is marooned at Clarence Bay on Ascension Island for sodomy, and dies of thirst after failing to find the freshwater spring in Breakneck Valley or Dampier's Drip lower down and drinking urine and turtle blood instead, and leaving a diary after dies at the end of the year. On June 7 after his daughter's engagement to Louis XV is broken off, Philip V of Spain signs the Treaty of Vienna with Austria, guaranteeing the Pragmatic Sanction, and causing Britain, France. and Prussia on Sept. 3 to form the Alliance of Herrenhausen in opposition, signing the Treaty of Hanover. On June 23 the Malt Tax Riots begin among Scottish highlanders in hamilton over a new malt tax, spreading throughout the country, sparking the Shawfield Riots in Glasgow; James I decides to treat them like Jacobites, founding the Black Watch of several cos. of Scottish militia wearing kilts and dark tartans to quash the revolt and curb feuds among Scottish highland clans; in 1729 they are integrated into the British army; the chieftains of the clans are known for the Fiery Cross (AKA bidding stick, budstikke, war arrow, stembod), a partially burned cross dippped in blood and sent via relay runners in order to assemble the clans in time of emergency, which is later adopted by the Ku Klux Klan and jazzed up. On Nov. 25 after French settlers of Ill. led by Pere Beaubois send 22 native chiefs, only to see the ship sink, then try again and send Chief Agapit Chicagou of the Metchigamea and five other chiefs to France, they meet with 15-y.-o. Louis XV in Fontainebleau, and Chicagou has a letter read pledging allegiance to the crown; they later dance three kinds of dances in the Theatre Italien, inspiring Jean-Philippe Rameau to compose the rondeau Les Sauvages for harpsichord. In Dec. (around Xmas) Voltaire escorts actress Adrienne Lecouvreur to the Comedie-Francaise in Paris, and is publicly insulted by Chevalier de Rohan Chabot, who says, "Monsieur de Voltaire - Monsieur Arouet - why don't you decide what your name is?", to which he replies, "My name begins with me, yours ends with you"; after Chabot has him beaten up by six rogues, Voltaire demands a duel, gets put in the Bastille, and is released upon promise of voluntary exile? Monkey, will you marry me? Louis XV of France marries Marie Leszczynska (1703-68), daughter of Stanislaus I of Poland, and she goes on to live in a few small rooms in Versailles while her hubby excludes her from court life and carries on with his parade of can't-take-it-with-you mistresses. The Marathas under Baji Rao I battle the Nizam-ul-Mulk in Hyderabad, while other Maratha forces invade Gujarat, and are routed by a Mughal army led by Sarbuland Khan. Yongjo (1694-1776) becomes Yi king of Korea (until 1776). Canada begins making treaties with the aborigines. Sir Francis Nicholson returns to London, is promoted to lt.-gen., and lobbies to unite the British North Am. colonies in order to provide for their common defense against French and Indians, with a viceroy and a united army; too bad, the Va. legislature opposes it. The word "waffle" first appears in English in Robert Smith's Court Cookery. Ben Franklin switches to the popular pub. house of John Watts in Wild Court near Lincolns-Inn-Fields in London (until 1726), and sells an asbestos purse to Royal Society secy. Sir Hans Sloane for a goodly sum; Watts' printing press is exhibited in the 1876 Centennial Exposition in Philly, then sold to the Smithsonian Inst. in 1901. King George grants an explanatory charter to the Mass. Bay Province. The 1679 French wooden fort at Niagara is rebuilt of stone and named Ft. Niagara, becoming the oldest continuously occupied military site in North Am. to survive to modern times. After asking himself the question "How doth Christ execute the office of a king", Scottish minister John Glas (1695-1773) founds a nonconformost society "separate from the multitude", with 100 members who reject nat. covenants and believe that the true Reformation can't be carried out by political secular weapons but only by the spirit and word of Christ. Charles Radclyffe, 5th Earl of Derwentwater (1693-1746), an illegitimate cousin and personal secy. of Bonnie Prince Charlie founds the first Masonic lodge in Europe in Paris. The New York Gazette is founded on Nov. 8 by Philly-hating William Bradford (until 1744), becoming the first newspaper in New York City and the 4th in British Am. A.D. Philidor gives the first concerts spirituels (public concerts) in Paris. German organ maker Gottfried Silbermann (1683-1753) of Freiberg adopts Bartolommeo Cristofori's pianoforte mechanism. Chantilly soft-paste porcelain begins to be produced in France (until 1800), with tin-oxide glaze, switching to an orthodox glaze in 1760, becoming known for the Chantilly Sprig of cornflower and forget-me-nots. Architecture: The Standetheater opera house in Prague is founded. The Spanish Steps in Rome (begun 1721) are finished. The Octagon Orleans House in England (begun 1720) is finished. St. George's in Hanover Square, London (begun 1712) is finished. Inventions: Scottish goldsmith William Ged (1699-1749) patents stereotyping, using a 1-piece printing plate cast in type metal from a mold (matrix) taken off a page of set type; too bad, he can't push it on the public and ends up dying broke. Science: English astronomer royal #3 James Bradley (1692-1762) observes that the fixed stars describe small ellipses within exactly the duration of the terrestrial year, and that stars from the poles of the ecliptic to the ecliptic describe figures increasingly less circular and more approaching straight lines, suggesting the possibility of observing stellar parallax (discovered in 1838); he also discovers the aberration of light (which he explains by the finite speed of light combined with the motion of the Earth around the Sun), and the phenomenon of nutation, and begins measurement throughout an 18.5-year lunar cycle (until 1748). Sir William Gage, 7th Baronet (1695-1744) introduces the Greengage plum (Prunus domestica italica) (Reine Claude) (a large plum with golden-green skin and flesh) into England from France. Nonfiction: Anon., Compendium of Books Past and Present (Gujin Tushu Jicheng) (5,020 vols.); Qing Dynasty encyclopedia; 66 copies are printed using 250K bronze movable type characters. Guillaume Delisle (1675-1726), Map of Europe. Elijah Fenton (1683-1730) (ed.), The Works of John Milton. John Flamsteed (1646-1719), Historia Coelestis Britannica (3 vols.) (posth.); first ed. in 1712; observations of 3K fixed stars, becoming a key work for British astronomers. Benjamin Franklin (1706-90), A Dissertation on Liberty and Necessity, Pleasure and Pain; a critique of William Wollaston's "The Religion of Nature Delineated"; claims to disprove free will, immortality, and Calvinist salvation-damnation by starting with the theorem: "What He [God] consents to must be good, because He is good; therefore evil does not exist"; he is later embarrassed by it. Johann Joseph Fux (1660-1741), Gradus ad Parnassum (Ascent to Mount Parnassus); dedicated to HRE Charles VI; becomes a standard textbook on counterpoint, used by Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven. Abram Petrovich Gannibal (1695-1781), Geometry and Fortifications. Arai Hakuseki (1657-1725), Autobiography. Francis Hutcheson (1694-1746), An Inquiry into the Original of Our Ideas of Beauty and Virtue; Inquiry Concerning Moral Good and Evil. Marquise de Sevigne (1626-96), Letters (posth.). Giovanni Battista Vico (1668-1744), The New Science (Principii d'una Scienza Nuova Intorno Alla Commune Natura Delle Nazione); his magnum opus; attacks the separateness of body and mind, along with Cartesian analysis and other forms of reductionism in favor of systemic thinking, propounding a cyclical view of history (the divine, heroic, and human phases), founding the modern philosophy of history; "[We] must take seriously Vico's great observation that men make their own history, that what they can know is what they have made, and extend it to geography." (Edward Said) Samuel Wyld, The Practical Surveyor. Music: J.S. Bach (1685-1750), Notenbuch for Anna Magdalena Bach; incl. Bist Du Bei Mir. Henry Carey (1687-1743), Sally in Our Alley. G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Rodelinda, Regina de' Longobardi (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Feb. 13); libretto by Nicola Francesco Haym based on a libretto by Antonio Salvi, based on Pierre Corneille's "Pertharite, Roi des Lombards". Johann Adolf Hasse (1699-1783), Antonio e Cleopatra (Naples); sung by Farinelli and Vittoria Tesi; makes German composer Hasse a celeb in Naples. Reinhard Keiser (1674-1739), Bretislaus oder Die Siegende Bestandigkeit (opera) (Hamburg). Art: Canaletto (1697-1768), Four Views of Venice. William Hogarth (1697-1764), The Lottery; The Mystery of Masonry brought to Light by the Gormogons; A Just View of the British Stage. Plays: Allan Ramsay (1686-1758), The Gentle Shepherd (pastoral comedy); a giant hit. Poetry: Henry Carey (1687-1743), Namby Pamby; or, A Panegyric on the New Versification; satire of the stupid verse of Ambrose Philips (1675-1749), enemy of Alexander Pope; causes the term "namby pamby" to become popular for nonsense, and Philips to become known as Namby Pamby; "So the nurses get by heart,/ Namby Pamby's little rhymes". Carlo Goldoni (1707-93), Il Colosso; satire against Pavia girls which gets him expelled from Collegio Ghislieri; Il Quaresimale in Epilogo (1725-6). Alexander Pope (1688-1744) (tr.), The Odyssey of Homer (1725-6); Elijah Fenton tr. books 1, 4, 19 and 20, and William Broome tr. others, and after the news that he had help leaks, his rep. is somewhat soiled; The Complete Works of Shakespeare; a new ed. that "regularized" the meter and changed the verse in several places, demoting 1560 lines to footnotes for being "excessively bad"". William Somerville (1675-1742), The Two Springs, a Fable. James Thompson (1700-48), The Seasons. Edward Young (1683-1765), Love of Fame, the Universal Passion (satires) (1725-7); "Must women have a doctor, or a dance?/ Though sick to death, abroad they safely roam,/ But droop and die, in perfect health, at home:/ For want - but not of health, are ladies ill;/ And tickets cure beyond the doctor's bill." Novels: Eliza Haywood (1693-1756), Memoirs of a Certain Island Adjacent to Utopia. Births: Am. Rev. "Barnstable Patriot" "taxation without represenation is tyranny" statesman-atty. James Otis Jr. (d. 1783) on Feb. 5 in West Barnstable, Mass.; brother of Mercy Otis Waren (1728-1814); educated at Harvard U. Am. Rev. leader (DOI signer) Abraham Clark (d. 1794) on Feb. 15 in Elizabethtown, N.J. French automobile inventor Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot (d. 1804) on Feb. 26 in Void-Vacon, Lorraine. Italian cardinal (1747-) Henry Benedict Maria Clement Stuart (d. 1807) on Mar. 11 in Rome; son of "Old Pretender" James Francis Edward Stuart (1688-1766); brother of "Bonnie Prince Charlie" Charles Edward Stuart (1720-88); 4th and last Jacobite heir, referring to himself as the duke of York until 1688 and Henry IX of England Henry I of Scotland afterwards; the last claimant to the English throne to touch for the King's Evil. Am. Rev. War brig. gen. Lachlan McIntosh (d. 1806) on Mar. 17 in Raits, Badenoch, Scotland; emigrates to the U.S. in 1736. Ottoman sultan #27 (1774-89) Abdul Hamid (Abdulhamid) I (d. 1789) on Mar. 20 in Constantinople; son of Ahmed III (1703-30) and Rabia Sermi Sultan; brother of Mustafa III (1757-74); father of Mahmud II (1785-1839). Am. Rev. Boston pastor Samuel Cooper (d. 1783) on Mar. 28 in Boston, Mass. Italian adventurer-lover-libertine-rake-writer ("king of seduction") Giovanni (Jacques) Giacomo (Jacopo) Girolamo Casanova de Seingalt (d. 1798) on Apr. 2 in Venice; son of two Venetian thespians; educated as a lawyer. Corsican patriot leader (bi?) Filippo Antonio Pasquale de Paoli (d. 1807) on Apr. 6 in Stretta, Morosaglia, Haute-Corse; son of Giacinto Paoli. French adm. Augustus Keppel, 1st Viscount Keppel (d. 1786) on Apr. 25; 2nd son of Willem Anne van Keppel, 2nd earl of Albemarle and Anne van Keppel (daughter of the 1st duke of Richmond, illegitimate son of Charles II); created viscount in 1782. French soldier Louis Philippe I (the Fat) (le Gros), Duke of Orleans (d. 1785) on May 12 in Versailles; son of Duke Louis of Orleans (1703-52); first prince of the blood after 1752; father of Philippe Egalite (1747-93). Am. Rev. War politician Samuel Ward (d. 1776) on May 25 in Newport, R.I.; descendant of Roger Williams. French marshal Jean Baptiste Donatien de Vimeur, Comte de Rochambeau (d. 1807) in Vendome on July 1 in Vendome, Loir-et-Cher; cmdr. of French forces in the Am. Rev. War. French genre-portrait painter Jean-Baptiste Greuze (d. 1805) on Aug. 21 in Tournus, Burgundy. French mathematician Jean Etienne Montucla (Jean-Étienne Montucla) (d. 1799) on Sept. 5 in Lyon. English military leader and opium eater ("British Conqueror of India") maj.-gen. Robert Clive (OE "cliff"), 1st Baron Clive (d. 1775) on Sept. 29 in Styche Hall, Moreton Say, Market Drayton, Shropshire; his Clive (Clyves) family goes back to Henry II. English radical journalist-politician John Wilkes (d. 1797) on Oct. 17 in Clerkenwell, London; ancestor of Am. actor John Wilkes Booth (1838-65); friend of poet Charles Churchill (1731-64); namesake of Wilkes-Barre, Penn. Am. clergyman Martin Boehm (d. 1812) in Nov. 30 in Lancaster, Penn.; Mennonite parents; descendant of Jakob Boehme (1575-1624); father of Henry Boehm (1775-1875); founder of the Church of the United Brethren in Christ. Am. Rev. planter-statesman ("the gentleman revolutionary") ("the reluctant statesman") George Mason (d. 1792) on Dec. 11 in Doeg's Neck, Fairfax County, Va.; his 10th son Thomas Mason is the great-times-seven grandfather of 21st cent. celeb Paris Hilton. English novelist-playwright-satirist William Kenrick (d. 1779) in Watford, Hertfordshire. Am. Rev. War. brig. gen. John Alexander Lillington (d. 1786) in Barbados, West Indies. English stock breeder Robert Bakewell (d. 1795); first to breed cattle for food rather than pulling plows; creator of the Dishley Longhorn cattle breed, the English Leicester sheep breed, and the Shire horse breed. English astronomer Nathaniel Pigott (d. 1804) in Whitton, Middlesex; father of Edward Pigott (1753-1825). English abolitionist divine and "Amazing Grace" hymn writer John Newton (d. 1807); infidel slave trader for 20 years converts to Christ and spends the rest of his life seeking to make amends. Deaths: French New France gov.-gen. (1703-25) Philippe de Rigaud, Marquis de Vaudreuil (b. 1643) on Oct. 10. Italian sculptor Giambattista Foggini (b. 1652) on Apr. 12 in Florence. Am. Congregational minister John Wise (b. 1652). Japanese dramatist Chikamatsu Monzaemon (b. 1653). Japanese writer Arai Hakuseki (b. 1657) on June 29. Italian composer Alessandro Scarlatti (b. 1660) on Oct. 24; wrote 115 operas, 20 oratorios, 500 chamber and solo cantatas, 10 masses, plus a load of instrumental music - she doesn't even hear me when I talk? French dramatist-actor Florent Carton Dancourt (b. 1661) on Dec. 7. Spanish architect-sculptor Jose Benito de Churriguera (b. 1665) on Mar. 2. Russian tsar (1682-1725) Peter I the Great (b. 1672) on Feb. 8 (Jan. 28 Old Style) in St. Petersburg (uremia after wading into the cold Baltic to rescue shipwrecked soldiers).














1726 Pop. of London: 700K. On Feb. 26 Maximilian II Emanuel (b. 1662) dies, and his son Charles VII Albert (1697-1745) becomes elector of Bavaria, maintaining good relations with his Hapsburg relatives while waiting for them to die out so he can become HRE Charles VII on Jan. 24, 1742. On May 5 French ballerina Marie Anne de Cupus de Camargo (1710-70) makes her debut at the Paris Opera. In July Benjamin Franklin leaves England after visiting his ancestral home in Ecton Village in Northamptonshire, where his ancestors lived for 3 cents., many engaging in the blacksmithing (vilage smithy) trade, borrowing a coat of arms from some English family named Franklin that he eventually has engraved on a silver tankard; he returns to Philadelphia and works as a clerk for Thomas Denham; during the voyage he writes a "Plan for Future Conduct", pledging to be frugal, honest, industrious, and "to speak ill of no man whatever"; a few mo. after landing Denham dies, and Franklin goes back to Keimer's print shop next year. In Sept. 25-y.-o. married maidservant Mary Toft (Tofts) (1701-63) is claimed by her physician John Howard to have given birth to 17 rabbits in Godalming, England, fooling several other physicians incl. George I's surgeon Nathaniel St. Andre and Sir Richard Manningham, until it is revealed to be a hoax, exposing the abysmal state of medicine. 73-y.-o. Cardinal Andre Hercule de Fleury (1653-1743) becomes PM of France under Louis XV until his death at age 90 (1743). Dutch ambassador to Spain (1715-25) Johan Willem (John William) (Juan Guillermo), Baron of Ripperda (Ripperdá), 1st Duke of Ripperda (1686-1737) is dismissed for incompetence and imprisoned, and the 1725 agreement with Austria is repudiated; Prussia withdraws from the Alliance of Herrenhausen, and signs the Treaty of Wusterhausen, guaranteeing the Pragmatic Sanction, leaving Austria and Prussia on one side, Britain and France on the other, and Spain swinging loose; Ripperda the ripoff artist escapes to Holland in 1728, then allegedly goes to Morocco and becomes a Muslim. Orthodox Catholic Russia and the Roman Catholic Holy Roman Empire ally against Turkey. Turkoman Qizilbash Afshar tribal leader Khouli Khan (1687-1747) (later Nadir or Nader Shah the Great) of N Persia helps Prince Tahmasp (son of Soltan Husayn) reconquer Persia from the Afghans, Russians, and Ottomans, acknowledging him as shah Tahmasp II (1704-40) until he can finish the job and take over for himself and become the Napoleon and Alexander the Great of Persia in 1736. Poor riots rock Philadelphia. 16-y.-o. castrato Caffarelli (1710-83) debuts in Rome in Domenico Sarro's Valdemaro, going on to rise to the top of his profession behind Farinelli. Jonathan Edwards becomes minister of the Congregational church in Northampton, Mass. St. John of the Cross is canonized. After pissing-off some aristocrats, French lit. giant Voltaire (Francois-Marie Arouet) (1694-1778) is exiled in Britain (until 1728), living at 10 Maiden Lane in Covent Garden, London, where he develops an interest in the works of Shakespeare, which are still relatively unknown in Europe, admiring them for having more on-stage action than French plays; too bad, as Shakespeare becomes popular in France, he gets jealous, dissing him for his barbarities and trying to set his own plays up as a counterexample; in May he meets 83-y.-o. Isaac Newton in London, and may have attended his funeral - and discussed the secret formula for eternal life? Charles IV of Spain selects the fishing village of El Ferrol in Galicia (NW Spain), whose harbor is so narrow that only one ship at a time can pass, yet has the one of the largest harbors in Spain as the site for a naval station and shipbuilding yards. The first written reference to shamrocks being worn on St. Patrick's Day appears in the diary of a traveling Protestant minister, "...it being a Current Tradition, that by this Three Leafed Grass, he emblematically set forth to them the Mystery of the Holy Trinity". Bavarian elector Maximilian II Emanuel founds the Royal Order of Saint George for the Defense of the Immaculate Conception as a dynastic order of the royal house of Bavaria; it is confirmed by a papal bull on Mar. 15, 1728. Allan Ramsay establishes the world's first circulating library in Edinburgh. The Academy of Ancient Music is founded in London for musical works over 150 years old (prior to 1625), becoming the first use of the word "ancient". Italian violinist Giuseppe Tartini (1692-1770) establishes a violin school in Padua. Gen. George Wade begins building 250 mi. of military roads in the Scottish Highlands (finished 1737). Architecture: Colin Campbell designs Compton Palace in Eastbourne, Sussex, England. Henry Somerset-Scudamore, 3rd Duke of Beaufort (1707-45) commissions the construction of the ebony Badminton Chest (Cabinet) in Florence; in 2004 Prince Hans-Adam II of Liechtenstein buys it for $35M, making it the most expensive piece of furniture in the world. The Baroque Frauenkirche in Dresden, Germany, designed by George Bahr (Bähr) (1666-1738) begins construction (finished 1743), featuring a 314-ft.-high 12K-ton sandstone dome called the Steineme Glocke (Stone Bell), which gives the city a distinctive silhouette. St. Martin's-in-the-Fields Anglican Church at the NE corner of Trafalgar Square in London, begun in 1721, by architect James Gibbs is finished, inspiring a number of Am. Georgian churches. Inventions: John Harrison (1693-1776) of England invents the gridiron pendulum, with alternate rods of steel and brass to equalize thermal variations. Science: English clergyman Stephen Hales (1677-1761) first measures blood pressure. You might as well be walking in the Sun? On Apr. 15 William Stukeley dines with Sir Isaac Newton; "After dinner, the weather being warm, we went into the garden and drank thea, under the shade of some appletrees, only he and myself. Amidst other discourse, he told me, he was just in the same situation, as when formely, the notion of gravitation came into into his mind. It was occasion'd by the fall of an apple, as he sat in a contemplative mood. Why should that apple always descend perpendicularly to the ground, thought he to himself. Why should it not go sideways or upwards, but constantly to the earths centre? Assuredly, the reason is, that the earth draws it... That there is a power, like that we here call gravity, which extends its self thro' the Universe." Nonfiction: Anon., Tadhkirat al-Muluk; a manual of the Persian Safavid admin., detailing the powers of the grand vizier, the influence of the harem over rulers, and the 50+ royal guilds that produce articles for them, incl. textiles and carpets for export. Richard Bentley (1662-1742) (ed.), The Works of Terence. George Berkeley (1685-1753), America, or the Muse's Refuge: A Prophecy; pub. in 1752 as "Verses by the Author on the Prospect of Planting Arts and Learning in America"; "Westward the course of empire takes its way;/ The four first Acts already past,/ A fifth shall close the Drama with the day;/ Time's noblest offspring is the last." Joseph Butler (1692-1752), Fifteen Sermons Preached at the Rolls Chapel. The Berleburg Bible (8-vol.); trans. for the Pietist movement within German Luthernism by Johann Haug begins to be pub. from Bad Berleburg, 100 mi. N of Frankfurt am Main, where Count Casimir von Wittgenstein Berleburg grants them asylum. Jean Cavalier (1681-1740), Memoirs of the Wars of the Cevennes under Col. Cavalier. Benito Jeronimo Feijoo y Montenegro (1676-1764), Teatro Critico Universal (1726-39) (essays); shows influence by Christian Thomasius and Thomas Browne, combating popular superstitions; he once allegedly proves that exorcism is bunk by reading from Boccaccio's "Decameron" to a possessed person, who becomes cured? August Hermann Francke (1663-1727), Lectiones Paraeneticae (1726-36). Jean Hardouin (1646-1729), Conciliorum Collectio Regis Maxima (Acta Conciliorum et Epistolae Decretales ac Constitutiones Summorum Pontificum); critical ed. of the Roman Catholic Church councils; printed at the expense of the French king, and not released to the public until 1715. William Law (1686-1761), The Absolute Unlawfulness of Stage Entertainment Fully Demonstrated - Shakespeare rolls over in his grave? Johann Lorenz von Mosheim (1693-1755), Institutionum Historiae Ecclesiasticae libri IV; gets him appointed abbot of Marienthal by the duke of Brunswick, with an income from Michaelstein Abbey. Jean-Philippe Rameau (1683-1764), Nouveau Systeme de Musique Theorique. Charles Rollin (1661-1741), Traite des Etudes (Paris) (1726-31); attempts to reform education by ditching Latin for the vulgar tongue and discarding medieval traditions, along with studying nat. history. Music: G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Scipione (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Mar. 12); libretto by Antonio Salvi and Paolo Antonio Rolli; based on Roman gen. Scipio Africanus; features March of the Grenadier Guards; Alessandro (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (May 5); libretto by Paolo Antonio Rolli based on "La Superbia d'Alessandro" by Ortensio Mauro, about Alexander the Great's journey to India, where he meets King Poro; stars Faustina Bordoni as Rossane, and Francesca Cuzzoni as Lisaura. Reinhard Keiser (1674-1739), Der Iacherliche Printz Jodelet (opra) (Hamburg). Art: William Hogarth (1697-1764), Engravings for Samuel Butler's "Hudibras". G.B. Tiepolo, Frescoes in the Udine Palace (1726-8). John Vanderbank (Michael Dahl?), Portrait of Sir Isaac Newton at Age 83. Plays: Henry Carey (1687-1743), Faustina; or the Roman Songstress; A Satyr on the Luxury and Effeminacy of the Age; a satire of opera and singer Faustina Bordoni, who has a fight with Francesca Cuzzoni during a performance of Handel. Poetry: Ludvig Holberg (1684-1754), Metamorphosis. James Thomson (1700-48), The Seasons (1726-30); poetic tetralogy; early Romantic work. Novels: Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), The Four Years Voyages of Captain George Roberts. Jonathan Swift (1667-1745), Gulliver's Travels (Travels into Several Remote Nations of the World, in Four Parts, By Lemuel Gulliver, First a Surgeon, and then a Captain of Several Ships); Lemuel Gulliver visits the countries of Lilliput and Blefuscu (6-in. tall people, Lilliput's capital city Mildendo is surrounded by a 2.5-ft. wall), Brobdingnag (60-ft. tall giants), Laputa (flying island of scientific quacks), Glubdubdrib (sorcerers), Luggnag (island where the Stuldbrugs live forever while suffering the infirmities of old age), the land of the Houyhnhnms, where intelligent horses rule over savage humanoid Yahoos, and Balnibarbi (failed inventors and projectors, capital Lagado); a satire of all things English, or just English modernism?; "If I had to make a list of six books which were to be preserved when all others were destroyed, I would certainly put 'Gulliver's Travels' among them" (George Orwell); "He [the emperor of Lilliput] is taller by almost the breadth of my nail, than any of his court, which alone is enough to strike an awe into the beholders"; "I cannot but conclude the bulk of your natives [Brobdingnag] to be the most pernicious race of little odious vermin that nature ever suffered to crawl upon the surface of the earth"; "He had been eight years upon a project for extracting sunbeams out of cucumbers, which were to be put in vials hermetically sealed, and let out to warm the air in raw inclement summers [Laputa]"; "I said the thing which was not. (For they have no word in their language to express lying or falsehood.) [Houyhnhnms]"; "Poor Nations are hungry, and rich Nations are proud, and Pride and Hunger will ever be at Variance [Houyhnhnms]"; "And he gave it for his opinion, that whosoever could make two ears of corn or two blades of grass to grow upon a spot of ground where only one grew before, would deserve better of mankind, and do more essential service to his country, than the whole race of politicians put together." Lewis Theobald (1688-1744), Shakespeare Restored, or a Specimen of the many Errors as well Committed as Unamended by Mr Pope in his late edition of this poet; designed not only to correct the said Edition, but to restore the true Reading of Shakespeare in all the Editions ever published; a variorum ed. of Shakespeare's works in reaction to Alexander Pope's 1725 ed., pointing out many errors that Pope grudgingly acknowledges by changing his 2nd ed. in 1728, while only admitting to "about twenty-five words", knocking Theobald in his anon. 1728 work "The Dunciad"; in 1733 Theobald pub. a 2nd ed. in 7 vols., which becomes a std. work; the 1740 ed. contains 35 frontispieces engraved by Hubert-Francois Gravelot. Births: Canadian soldier-judge Joshua Winslow (d. 1801) on Jan. 23 in Portsmouth, N.H.; father of Anna Green Winslow (1759-80). Russian Anglophile adm. Vasily Yakovlevich Chichagov (d. 1809) on Feb. 28 in St. Petersburg; father of Pavel Chichagov (1767-1849); educated in Britain. British adm. ("Black Dick") Richard Howe, 1st Earl Howe (d. 1799) on Mar. 8 in London; brother of William Howe (1729-1814) and George Howe (1725-58). French writer Louise Florence Petronille Tardieu d'Esclavelles, Madame d'Epinay (d. 1783) on Mar. 11 in Valenciennes. Am. Va. gov. #5 (1781-4) (DOI signer) Benjamin Harrison V (d. 1791) on Apr. 5 in Charles City County, Va.; son of Benjamin Harrison IV and Anne Carter; educated at the College of William and Mary; father of William Henry Harrison (1773-1841); great-grandfather of Benjamin Harrison (1833-1901). English "General History of Music" music historian-composer Charles Burney (d. 1814) on Apr. 7 in Shrewsbury; educated at Shrewsbury School; father of Fanny Burney (1752-1840); friend of Sir Joshua Reynolds. Scottish uniformitarian geologist ("Father of Modern Geology") James Hutton (d. 1797) on June 3 in Edinburgh; educated at the U. of Edinburgh, and U. of Leyden; starts out a physician, turns to agriculture, then becomes a scientist. Am. clergyman Philip William Otterbein (d. 1813) on June 3 in Dillenburg (near Wiesbaden), Germany; emigrates to the U.S. in 1752; co-founder of the United Brethren in Christ. British lt.-gen. Robert Monckton (d. 1782) on June 24 in Yorkshire. Am. politician-scientist James Bowdoin II (d. 1790) (pr. BOH-din) on Aug. 7 in Boston, Mass.; son of James Bowdoin I (1676-1747); father of James Bowdoin III (1752-1811). French composer and chess player Francois-Andre Danican Philidor (d. 1795) on Sept. 7. Am. Rev. leader and surgeon James Warren (d. 1808) on Sept. 28 in Plymouth, Mass.; descendant of Mayflower passengers Richard Warren and Edward Doty; brother of Joseph Warren (1741-75); educated at Harvard U.; husband (1754-) of Mercy Otis Warren (1728-1814). German-Polish painter-printmaker Daniel Nikolaus Chodowiecki (d. 1801) on Oct. 16 in Danzig (Gdansk); Huguenot ancestry. Am. Rev. War brig. gen. (DOI signer) Oliver Wolcott Sr. (d. 1797) on Dec. 1 in Windsor, Conn.; educated at Yale U.; father of Oliver Wolcott Jr. (1760-1833). Am. Rev. War brig.-gen. William Alexander, Lord Stirling (d. 1783) in New York City. British lt.-gen. Sir Eyre Coote (d. 1783) near Limerick, Ireland. Polish Jewish religious leader Jacob Joseph Frank (Jakub Lejbowicz) (d. 1791) in Korolowka. Scottish physicist John Anderson (d. 1796) in Dunbartonshire; educated at Glasgow U.; founder of the U. of Strathclyde. British soldier-politician col. Isaac Barre (Barré) (d. 1802) in Dublin; son of a French refugee; educated at Trinity College, Dublin; coiner of the term "Sons of Liberty". Deaths: English anti-theater Anglican cleric Jeremy Collier (b. 1650) on Apr. 26. French composer-organist Michel Richard de Lalande (b. 1657) on June 18 in Versailles. Bavarian elector (1679-1726) and Maximilian II Emanuel (b. 1662) on Feb. 26 in Munich. English dramatist-architect Sir John Vanbrugh (b. 1664) on Mar. 26: "Lie heavy on him, Earth! For he/ Laid many heavy loads on thee!" British caged queen Sophia Dorothea of Celle (b. 1666) on Nov. 13 in Ahlden, Germany. Am. Penn. proprietor (1712-26) Hannah Callowhill Penn (b. 1671) on Dec. 20 in Penn. (stroke). French mapmaker Guillaume Delisle (b. 1675) on Jan. 25 in Paris. Italian composer Antonio Bononcini (b. 1677) on July 8 in Modena. Italian composer-organist Domenico Zipoli (b. 1688) on Jan. 2 in Cordoba, Argentina. Swiss mathematician Nicholas Bernoulli (b. 1695) on July 31.










1727 On Jan. 22 German-born composer Georg Friedrich Handel, now George Frideric Handel (1685-1759), who moved into a new house at 25 Brook St. in London in 1723 becomes a British subject, going on to stay there for life while composing his biggest hits, after which it becomes the Handel House Museum. In Feb. after Philip V's 1721 request to the Brits to restore Gibraltar in return for renewal of trade licenses, war begins between England and Spain as the Spanish begin a siege of Gibraltar with 12K-25K troops that lasts for 14 mo. (its 13th siege and second by the Spanish) (ends 1728); the defending Brits only have 1.5K-5K troops, but it's one tough rock to siege? On Mar. 31 (Mar. 20, 1726 Old Style) Sir Isaac Newton (b. 1643) (b. 1642 Old Style) dies in London after saying that his greatest accomplishment is lifelong celibacy; his brainy disciple Samuel Clarke (1675-1729) (known for leaping over chairs and tables and swimming on tables?) turns down his £1K-a-year job as master of the mint because it's a govt. job and he's a clergyman?; his VIP burial is attended by royalty and presided over by his friend Alexander Pope (1688-1744), who gives a stirring eulogy before sprinkling dirt on his tomb, with the soundbyte: "Nature and Nature's Laws lay hid in Night/ God said, Let Newton be! and All was Light". On May 17 (May 6 Old Style) having expelled the Jews from the Ukraine, Catherine I (b. 1684) dies, and on May 18 after her will is forged, pampered, secluded Peter II (1715-30), the only male-line grandson of her deceased hubby Peter I the Great is proclaimed Russian Romanov tsar #7 (until 1730). On May 19 the Bishop of London states that holding Christians as slaves does not contradict Christian doctrine - especially as he has some? On June 22 (June 11 Old Style) (10 weeks after Isaac Newton) Hanoverian king of Great Britain #1 (since Aug. 1, 1714) George I (b. 1660) dies of a stroke en route to Hanover, becoming the last British monarch to be buried outside the U.K. (until ?), and his Hanover-born son George (Georg) II (1683-1760) is crowned the 51st British monarch (until Oct. 25, 1760); Handel's Coronation Chorus is first used at his coronation; his wife (a strong Robert Walpole backer) Caroline of Brandenburg-Ansbach (1683-1737) is a brain babe who corresponds with Leibniz, and is appointed regent when her hubby is in Hanover, causing the rhyme "You may strut, dapper George, but 'twill all be in vain,/ We all know 'tis Queen Caroline, not you, that reigns." On Nov. 18 the city of Jaipur in Rajasthan, India (modern-day pop. 3.1M) 167 mi. from modern-day New Delhi is founded as a trading city and new capital by Rajput maharaja (1699-1743) and astronomer Sawai Jai Singh II (1688-1743) of Amber, becoming known for its Havelis, courtyard mansions; in 1876 the city is pained pink to welcome English Prince Albert Edward of Wales (future Edward VII) , causing the city to be nicknamed "the Pink City"; the Jantar Mantar (magical device), a network of three observatories based in and S of Delhi is built there by the maharaja, who designs masonry structures and crude instruments because his Jesuit advisers were prohibited by the Church from accepting the views of Galileo and Copernicus; the city is designed according to Hindu doctrine in seven rectangular areas according to the caste system, with the palace in the 7th and holiest one, and the observatory in the place of the temple; other observatories are built in Delhi, Mathura, Ijjain, and Varanasi. The Amur frontier between Russia and China is rectified via the Kiakhta (Kyakhta) Treaty, negotiated by Bosnian Serbian Russian minister Count Sava Lukich Vladislavich Raguzinsky (1669-1738) in Peking, governing their relations until the mid-19th cent. The Shawnees migrate from the Upper Delaware Valley to the Ohio Valley. A police regulation in Paris requires actresses and female dancers to appear on the stage wearing drawers; women still don't wear underwear, so men can peek up their dresses. Kansas (Kan.) (Sioux "south wind people") is settled. West Virginia (W. Va.) is settled. Some Quakers begin demanding abolition of slavery - strapped with puffed oats and ready to blow? Scottish witch Janet Horne (b. ?) becomes the victim of the Last Execution for Witchcraft in England takes place in Dornoch, Sutherland (June 1722?) - it takes time for the message to filter to the colonies? The Brazilian coffee industry is founded with seedlings smuggled from Paris; cultivation is slow until independence in 1822, after which massive areas of rainforest are cleared near Rio de Janeiro and Sao Paulo. The city Concord, N.H. (originally Penacook) on the Merrimack River (modern-day pop. 42K) is founded by colonists from Haverhill, Mass. led by Capt. Ebenezer Eastman on the site of the main Pennacook Indian village; originally named Penacook, the name is changed to Rumford in 1733, and incorporated on Feb. 9, 1734; in 1765 after a 20-year boundary dispute with Mass. (which claims the Merrimack River) it is reincorporated as Concord to celebrate peace being declared with them; it goes on to become the capital of N.H. The Moravians of Herrnhut split from the Lutheran Church, with Count von Zinzendorf as leader. The Ursulines found the oldest institution of learning for women in the U.S., in New Orleans. The Tidjani (Tijani) moderate branch of Sufism is founded in Morocco and Algeria by Sheik Ahmad al-Tidjani (1735-1815), spreading throughout W Africa, incl. Chad, N Nigeria, and Sudan; to become a murid (disciple) of the order, one must receive from a muqaddam (rep of the order) a wird, or sequence of holy phrases to be repeated twice daily. The English word "fun", orginally meaning trick, hoax, or joke takes on the meaning of "amusement"; Samuel Johnson calls it a "low, cant word"; by the middle of the 19th cent. it funnily (which is an adverb) becomes a verb and an adjective, and becomes proper? Charles Radclyffe, 5th Earl of Derwentwater (1693-1746) succeeds Isaac Newton as grandmaster of the Priory of Sion (until 1746) :). The Am. Philosophical Society is founded in Philadelphia, Penn. Cherney's Racing Calendar (records of horse races run the previous year) begins pub. by John Cherney. The first marriage ad appears in a newspaper in Manchester, England. The Gentleman's Mag., the first modern mag. begins pub. Miscellanies in Prose and Verse, a satirical periodical by Alexander Pope (1688-1744), Jonathan Swift (1667-1745), and Dr. Arbuthnot begins pub. (until 1732); it contains the first use of the name "Vanessa". 24-y.-o. Jonathan Edwards (b. 1703) marries 17-y.-o. Sarah Pierrepont (1710-58), daughter of New Haven's most prominent minister, who composed "Jingle Bells" on July 28; they have 11 children, 8 boys, and 3 girls; John Pierrepont Morgan is one of their descendants. Architecture: Mirabell Palace in Salzburg (begun 1721) is completed. Science: After discovering slight magnetic fluctuations on his compass to be correlated with the latter's observations of aurorae, English watchmaker George Graham (1674-1751) and Swedish scientist Anders Celsius (1701-44) discover that sunspots are really magnetic storms. French scientist George-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon (1707-88) discovers the Binomial Theorem. Nonfiction: Henri de Boulainvilliers (1658-1722), Histoire de l'ancien gouvernement de la France (posth.); divides the French into the aristicratic French race descended from the Germanic Franks, and the peasant class Gallo-Roman race, which the aristocrats have the right to dominate by right of conquest, becoming the predecessor of scientific racism; Etat de la France, Avec des Memoires sur l'Ancien Gouvernement (posth.). Richard Bradley (1688-1732), Ten Practical Discourses Concerning Earth and Water, Fire and Air, as They Relate to the Growth of Plants; The Country Housewife and Lady's Director; first English cookbook containing recipes using pineapple. Cadwallader Colden (1688-1776), History of the Five Nations; the first English colonial rep. to the Iroquois gives the Iroquois side of the story along with the British; revised ed. pub in 1757, read by Benjamin Franklin. Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), The Complete English Tradesman. Stephen Hales (1677-1761), Vegetable Staticks, or, Statical Essays; founds the science of plant physiology. Francesco Scipione Maffei, Istoria Diplomatica. Eliza Smith, The Compleat Housewife; or, Accomplished Gentlewoman's Companion; contains the first recipe for "English Katchop". John Spencer (1630-93), De Legibus Hebraeorum Ritualibus et Earum Rationibus (posth.); master of Corpus Christi College, Cambridge U. claims that Jews learned their religious practices from the Egyptians. Voltaire (1694-1778), An Essay Upon the Civil Wars of France, Extracted from Curious Manuscripts; Essay Upon Epic Poetry of the Euuropean Nations, from Homer Down to Milton; pub. in English while living in exile at 10 Maiden Lane, Covent Garden, London (1726-8). Music: J.S. Bach (1685-1750), St. Matthew Passion, BWV 244 (sacred oratorio); libretto by Picander; based on the Gospel of Matthew Chs. 26-27; rev. 1736, 1739, 1745; first performed on Mar. 15 (Good Friday), 1729 in St. Thomas Church, Leipzig. G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Zadok the Priest (HWV 258); coronation anthem for George II, based on 1 Kings 1:38-40 ("And all the people rejoic'd, and said: 'God save The King, long live The King, may The King live for ever!, Amen, Hallelujah!'"), sung at every British coronation service since, during the anointing of course; Admeto, Re di Tessaglia (Admetus, King of Thessaly) (opera) (Haymarket Theatre, London) (Jan. 31); libretto by Nicola Haym based on Euripides' "Alcestis"; stars Faustina Bordoni as Alcestis, and Francesca Cuzzoni as Antigona; Riccardo Primo (Richard I) (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Nov. 11); libretto by Paolo Antonio Rolli, based on Francesco Briani's "Isacio Tiranno"; written to celebrate the coronation of George II. Art: Elias Gottlob Haussmann (1695-1774), Portrait of Gottfried Reiche (1667-1734); shows him holding a hunter's trumpet and a music ms. containing his famous Abblasen (Fanfare), which is used as the theme music for the TV show CBS Sunday Morning. William Hogarth (1697-1764), The Large Masquerade Ticket. William Kent (1685-1748), The Designs of Inigo Jones. John Michael Rysbrack (1684-1770), Sculpture of George I. Plays: Prosper Jolyot de Crebillon (1674-1762), Pyrrhus. Philippe Destouches, Le Philosophe Marie (comedy). Moses Hayyim Luzzatto, Migda Oz (in Hebrew). Lewis Theobald (1688-1744), Double Falsehood; or, The Distrest Lovers (Drury Lane, London) (Dec.); inspired by Don Quixote; claims he based it on three of Shakespeare's mss., and is called a fraud by Alexander Pope, who lampoons him as Dulness in his Dunciad; in 2010 English prof. Brean Hammond claims that it is based on William Shakespeare's lost play "Cardenio". Poetry: Henry Carey (1687-1743), Masking Is Catching; satire of opera castrato Senesino. John Gay (1685-1732), Fables, Vol. 1; vol. 2 in 1738. William Somerville (1675-1742), Occasional Poems. Jonathan Swift (1667-1745), The Furniture of a Woman's Mind; "A set of phrases learnt by rote;/ A passion for a scarlet coat;/ When at a play to laugh, or cry,/ Yet cannot tell the reason why:/ Never to hold her tongue a minute;/ While all she prates has nothing in it"; "For conversation well endued;/ She calls it witty to be rude;/ And, placing raillery in railing,/ Will tell aloud your greatest failing"; On Dreams; "Those dreams that on the silent night intrude,/ And with false flitting shapes our minds delude/ ...are mere productions of the brain./ And fools consult interpreters in vain." Novels: Eliza Haywood (1693-1756), The Court of Carmania. Births: British gen. James Wolfe (d. 1759) on Jan. 2 in Westerham, Kent. French gen. Charles Deschants de Boishebert (Boishébert) de Raffetot (d. 1797) on Feb. 7 in Quebec, Canada. Am. Rev. War brig. gen. John Nixon (d. 1815) on Mar. 1 in Framingham, Mass. Bavarian elector (1745-77) Maximilian III Joseph (d. 1777) on Mar. 28 in Munich; eldest son of HRE Charles VII and Marie Amalie of Austria (daughter of HRE Joseph I). German deaf educator (not deaf) Samuel Heinicke (d. 1790) on Apr. 10 in Nautschutz. French #1 economist (physiocrat) Anne-Robert-Jacques Turgot, Baron de Laune (d. 1781) on May 10 in Paris; from an old Norman family; educated at the Sorbonne. English "Blue Boy" portratist and landscape painter Thomas Gainsborough (d. 1788) on May 14 in Sudbury, Suffolk. French actress Marie Justine Benoite Favart (nee Duronceray) (d. 1772) on June 15; wife of playwright Charles Simon Favart (1710-92). Am. Rev. War Gen. Horatio Gates (d. 1806) on July 26 in Maldon, Essex, England; godson of Horace Walpole. Belgian (Flemish) sculptor (in France) Jean Pierre Antoine Tassaert (d. 1788) on Aug. 19 in Antwerp; student of Rene Michel Slodtz; teacher of Johann Gottfried Schadow (1764-1850). Italian engraver (in London) Francesco Bertolozzi (d. 1815) on Sept. 21 in Florence; moves to London in 1764-1802. Am. politician-jurist William Samuel Johnson (d. 1819) on Oct. 7 in Stratford, Conn.; educated at Yale U., and Harvard U.; first pres. of Columbia College (1787-1800). English "Letters on the Improvement of the Mind" Bluestockings writer Hester Chapone (nee Mulso) (d. 1791) on Oct. 27 in Twywell, Northamptonshire; wife (1760-) of John Chapone (1728-51), son of Sarah Chapone (1699-1764). Russian educator ("the Maecenas of the Russian Enlightenment") Ivan Ivanovich Shuvalov (d. 1797) on Nov. 1 in Moscow; boy toy of Tsarina Elizabeth Petrovna. Am. Rev. War maj. gen. Artemas Ward (d. 1800) on Nov. 26 in Shrewbury, Mass. Am. scholar-diarist and Congregational clergyman Ezra Stiles (d. 1795) on Nov. 29 in North Haven, Conn.; educated at Yale U.; pres. of Yale (1778-95). Am. Rev. leader (DOI signer) William Ellery (d. 1820) on Dec. 22 in Newport, R.I. Am. atty. (loyalist) John "the Tory" Randolph (d. 1784) in Williamsburg, Va.; son of Sir John Randolph; husband (1750-) of Ariana Jenings (1727-1808); brother of Peyton Randolph (1721-75); father of Edmund Randolph (1753-1813); friend of Thomas Jefferson. Italian painter-engraver Giovanni Battista Cipriani (d. 1785) in Florence. English cabinetmaker George Hepplewhite (d. 1786) in Durham; known for small chairs with heart-shape or shield-shape backs, slender tapering legs, spade feet, and painted or inlaid ornamentation. Am. Rev. War loyalist printer Samuel Loudon (d. 1813). British gen. (CIC of British North Am. in 1783-7) John Campbell of Strachur (d. 1827) in Argyll, Scotland. Deaths: Now make a 3-inch incision between the abdominal muscles? Shouldn't you be doing this? English #1 scientist-mathematician-alchemist Sir Isaac "Apples Happen" Newton (b. 1643) (b. 1642 Old Style) on Mar. 31 (Mar. 20 Old Style) in Kensington, Middlesex, London; a few weeks before his death he burns numerous boxes of mss. and personal papers, and doesn't request last rites on his deathbed; first scientist buried in Westminster Abbey; his funeral is presided over by "A. (Alexander) Pope"; after a lifetime studying the Corpus Hermeticum, he leaves a sealed trunk with 100K pages on alchemy, astrology, and the occult, incl. works rejecting the Bible Book of Revelation (after all, he lived through 1666 personally so it failed the empirical test?); also leaves The Chronology of Ancient Kingdoms Amended (begun 1689), which tries to establish the origins of the institution of kingship to Israel, and touts its primacy over the cultures of antiquity; "Newton was not the first of the Age of Reason. He was the last of the magicians, the last of the Babylonians and Sumerians... He looked on the Universe and all that is in it as a riddle... He regarded the Universe as a cryptogram set by the Almighty" (John Maynard Keynes): "If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants"; "To myself I am only a child playing on the beach, while vast oceans of truth lie undiscovered before me" - having a sense of the mathematical designs and codes in Nature, and believing he can concentrate hard enough to decode anything, he falls for Satan's offer to be a god and enjoy immortality if he can just find the code for the right potion, laboring to the point of mental breakdown to find it, thinking that Satan is Lucifer, the Angel of Light, who will be his god forever, while all that Be As A Child, Have Faith, Jesus Saves, Armageddon is Nigh, and Leave It To Beaver, er, Jehovah to Resurrect You stuff sails over his proud head? Sicilian-born French chef Procopio Cuto (b. 1651) on Feb. 10 in Paris. French-born Canadian bishop of Quebec Jean-Baptiste de La Croix de Chevrieres de Saint-Vallier (b. 1653) on Dec. 26 in Quebec City. French Protestant minister Jacques Abbadie (b. 1654) on Sept. 25 in Marylebone, London, England. English king (1714-27) George II (b. 1660) on June 11. Italian composer Francesco Gasparini (b. 1661) on Mar. 22 in Rome. German educator August Hermann Francke (b. 1663) on June 8. English composer William Croft (b. 1678) on Aug. 14 in Bath. Russian empress (1725-) Catherine I (b. 1684)on May 17 (May 6 Old Style).














1728 On Feb. 28 the Battle of Palkhed near Nashik in Maharashtra, India sees the Marathas under Baji Rao I decisively defeat Nizam ul-Mulk. On Mar. 21 after running away from Calvinist Geneva, 15-y.-o. Jean-Jacques Rousseau meets French Roman Catholic Madame Francoise-Louise de la Tour, Baronness de Warens (1699-1768) in Annecy, who converts him to Roman Catholicism, then in 1733 ends his virginity. In early June the Spanish siege of Gibraltar ends after 14 mo.; on June 14 the Congress of Soissons begins in hopes of ending all the disputes plaguing Europe, and ends in failure after a year of pissing contests (ends 1729). On Dec. 23 HRE Charles VI and Frederick William of Prussia sign the Treaty of Berlin. Let's get something straight between us? Danish-Russian explorer Vitus Jonassen Bering (Behring) (1681-1741) begins exploring the N Pacific basin (until 1741), and discovers that Asia and America are two separate continents joined by the Bering Strait; he discovers the two Diomede Islands halfway between Alaska and Siberia, which later becomes the U.S.-Soviet boundary line, with Little Diomede on the U.S. side and Big Diomede on the Soviet side. The town of Fredericksburg, Va. is founded on 50 acres of land with a trading post and warehouse; during the U.S. Civil War it becomes the scene of the battles of Fredericksburg, Chancellorsville, the Wilderness and Spotsylvania Court House, with a total of 100K casualties. John Wesley is ordained. Ben Franklin opens his own print shop in Philly with Hugh Meredith, and composes his own epitaph: "The body of B. Franklin, Printer (like the cover of an old book, its contents worn out, and stripped of its lettering and gilding) lies here, food for worms. But the work shall not be lost, for it will (as he believed) appear once more, in a new and more elegant edition, revised and corrected by the Author". Walter Churchman opens an apothecary shop in Bristol, England, which next year is granted a patent by Charles II for chocolate-making, and after Quaker physician Joseph Stores Fry purchases the patent and recipes in 1761, it goes on to become J.S. Fry & Sons, becoming the oldest chocolate firm in Britain to survive to modern times. English actress Lavinia Fenton (1708-60) achieves theatrical fame in only two years, and goes on the meat market looking for a duke. Architecture: Castle Nymphenburg near Munich (begun 1664) is finished. The Palladian Queen Square in Bath, England, designed by John Wood the Elder (1704-54) is begun (finished 1729). The Madrid Lodge of Freemasons is founded; too bad, the Inquisition soon shuts it down. Inventions: Sheet-iron rolling is discovered in England. Science: James Bradley detects the aberration of light from fixed stars using the star Etamin (gamma Draconis) in Draco (between the Big and Little Dipper). Nonfiction: John Balguy, The Foundation of Moral Goodness. Isaac Joseph Berruyer, Histoire du Peuple de Dieu (3 parts) (1728-58); a Jesuit delights in the sexual exploits of the patriarchs, pissing-off popes Benedict XIV and Clement XIII and resulting in his deposition in 1756 by the Parliament of Paris. William Byrd II (1674-1744), The History of the Dividing Line Betwixt Virginia and North Carolina; his survey in 1728; Matrimony Creek is named for its brawling waters. Ephraim Chambers (1680-1740), Cyclopaedia, or An Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences ("containing the definitions of the terms, and accounts of the things signify'd thereby, in the several arts, both liberal and mechanical, and the several sciences, human and divine: the figures, kinds, properties, productions, preparations, and uses, of things natural and artificial; the rise, progress, and state of things ecclesiastical, civil, military, and commercial: with the several systems, sects, opinions, &c; among philosophers, divines, mathematicians, physicians, antiquaries, criticks, &c: The whole intended as a course of ancient and modern learning") (4 vols.) (1728-53); basis of the French Encyclopedie after a 1743 French trans. James Dalton (-1730), Genuine Narrative of My Street Crime Career; head of a street robbery gang in London, who is pardoned after going king's evidence last May; recounts his experience with "back door gentlemen" (sodomites); too bad, he is hanged for robbery at Tyburn on May 11, 1730 after being framed. Pierre Fauchard (1678-1761), Le Chirurgien Dentiste, ou Traite des Dents (The Surgeon Dentist); disproves the worm theory of dental decay; and invents the profession of dentistry and the word dentist; invents an improved tooth drill. James Gibbs, Book of Architecture. Johann Christoph Gottsched (1700-66), Ausfuhrliche Redekunst. Francis Hutcheson, An Essay on the Nature and Conduct of the Passions and Affections; Illustrations upon the Moral Sense. William Law (1686-1761), A Serious Call to a Devout and Holy Life. John Martyn (1699-1768), Historia Plantarum Rariorum (1728-37). Isaac Newton (1646-1727), The Chronology of Ancient Kingdoms Amended (posth.); "They have made the antiquities of Greece three or four hundred years older than the truth." John Oldmixon (1673-1742), Essay on Criticism. Jonathan Swift (1667-1745), A Short View of the State of Ireland; Essay on the Fates of Clergymen; "This evil fortune, which generally attends extraordinary men in the management of great affairs, has been imputed to divers causes, that need not be here set down, when so obvious a one occurs, if what a certain writer observes be true, that when a great genius appears in the world the dunces are all in confederacy against him." Christian Wolff (1679-1754), Philosophia Rationalis, sive Logica. Music: G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Siroe, Re di Persia (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Feb. 17); libretto by Nicola Francesco Haym, based on Pietro Metastasio's "Siroe"; Tolomeo, Re di Egitto (HWV 25) (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Apr. 3); libretto by Nicola Francesco Haym, based on Carlo Sigismondo Capece's "Tolometo et Alessandro"; his 13th and last opera for the Royal Academy of Music; stars Senesino as Tolomeo, Francesca Cuzzoni as his wife Seleuce, Giuseppe Maria Boschi as King Araspe of Cyprus, and Faustina Bordoni as his sister Elisa. Reinhard Keiser (1674-1739), Lucius Verus oder Die Siegende Treue (opera) (Hamburg). Art: Jean-Baptiste-Simeon Chardin (1699-1779), The Ray (La Raie). William Hogarth (1697-1764), The Wanstead Assembly; The Politician. Plays: Colley Cibber (1671-1757), The Provok'd Husband; stars Ann Oldfield as Lady Townly, of whom Cibber says "She did her usual Outdoing". Henry Fielding (1707-54), Love in Several Masques (comedy) (first play) (Theatre Royal, London) (Feb. 16) (4 perf.). John Gay (1685-1732) and Johann Christoph Pepusch (1667-1752), The Beggar's Opera (comic ballad opera) (Lincoln's Inn Fields Theatre, London) (Jan. 29); a big hit, running for a record 62 consecutive perf., helping build the new London Royal Opera House; runs for 1,463 perf. in 1920 at the Lyric Theatre in Hammersmith; satirizes Italian opera; Newgate prisoner Macheath is helped to escape by the cruel gov.'s daughter Lucky Lockit, and returns to London's criminal underworld to woo Polly Peachum; a satire of Sir Robert Walpole, pioneering the device of using lower-class criminals to satirize upper-class society; incl. Fill Every Glass, Over the Hills and Far Away. Pierre de Marivaux (1688-1763), Triomphe de Plutus; the sequel Polly: An Opera, Being the Second Part of the Beggar's Opera (ballad opera) sees Polly Peachum going to the West Indies to search for Macheath and his ho Jenny Diver, after which Macheath is executed and Polly marries Indian prince Cawwawkee; performance is banned by the govt. after Sir Robert Walpole is no longer amused, but gets pub. and widely read until its debut in England on June 19, 1777 at the Haymarket Theatre in London - mama don't take my pollychrome away? Poetry: Alexander Pope (1688-1744), The Dunciad (3 vols.); pub. anon. in Dublin; a satire of witless critics, using initials for the targets, with Lewis Theobald ("Tibbald") (who pub. a criticism of his 1725 ed. of Shakespeare in 1726) as King of Dunces, appointed by the goddess Dulness to succeed Elkannah Settle on Lord Mayor's Day in 1724 to degenerate Great Britain; goes after George II with "Still Dunce the second rules like Dunce the first", and takes on Protestants, Whigs, and hack writers Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), Ambrose Philips (1674-1749), Nahum Tate (1652-1715), Thomas Heywood (1570-1641), and Sir Richard Blackmore (1654-1729), also Susanna Centlivre (1667-1723), who stays awake through a reading of Richard Blackmore's boring epics longer than anyone except Folly; "Books and the Man I sing, the first who brings/ The Smithfield Muses to the Ear of Kings" (opening); "How, with less reading then makes felons 'scape,/ Less human genius than God gives an ape,/ Small thanks to France and none to Rome or Greece,/ A past, vamp'd, future, old, reviv'd, new piece,/ 'Twixt Plautus, Fletcher, Congreve, and Corneille,/ Can make a Cibber, Johnson, or Ozell" (1.235-40); causes a big reaction, creating a ton of lifelong enemies, who love to slander him, which isn't hard to do?; he begins taking his Great Dane attack dog Bounce with him while walking, with loaded pistols in his pocket; a satirical print from "Pope Alexander" pub. in 1729 portrays him as an ape wearing papal vestments, suggesting Darwin's Theory of Evolution?; in 1729 he anon. pub. "The Dunciad Variorum", followed in 1742 by "The New Dunciad", and in 1743 by "The Dunciad in Four Books", with Bays replacing Tibbald. Allan Ramsay (1686-1758), Poems. Richard Savage (1697-1743), The Bastard; "O Memory! thou soul of joy and pain!" Novels: Daniel Defoe (1659-1731), Memoirs of Captain George Carlton. Abbe Prevost (1697-1763), Mémoires et Aventures d’un Homme de Qualité qui s’est Retiré du Monde (4 vols.) (1728-9) (Paris). Births: English poet laureate (1785-90) and critic Thomas Wain Warton the Younger (d. 1790) on Jan. 9 in Basingstoke, Hampshire. German composer-organist Johann Gottfried Muthel (Müthel) (d. 1788) on Jan. 17 in Molln (near Hamburg); first to use the term "pianoforte" (fortepiano) (1771). French neoclassical architect Etienne-Louis Boullee (Étienne-Louis Boullée) (d. 1799) on Feb. 12 in Paris; student of Jacques-Francois Blondel, Germain Boffrand, and Jean-Laurent Le Geay. Scottish surgeon-anatomist ("Father of Modern Scientific Surgery") (founder of modern dentistry) John Hunter (d. 1793) on Feb. 13 in Long Calderwood (near Glasgow); youngest of 10 children; George III's surgeon (1776-); surgeon-gen. of the British army (1793). Russian pro-Prussian Romanov tsar #11 (1762) ("the Prussomaniac") Peter III (d. 1762) on Feb. 21 in Kiel; son of Duke Karl Friedrich of Holstein-Gottorp (1700-39) (nephew of Charles XII of Sweden) and Tsarina Elizabeth Petrovna (1708-28), daughter of Peter I the Great (who dies from childbirth). English architect John Wood the Younger (d. 1782) on Feb. 25 in Bath; son of John Wood the Elder (1704-54). French chemist Antoine Baume (Baumé) (Ger. "tree") (d. 1804) on Feb. 26 in Senlis; inventor of Baumé (Bé.) specific gravity hydrometer scales. German painter-critic (precursor to Neoclassical painting) Anton Raphael Mengs (d. 1779) on Mar. 12 in Usti (Aussig), Bohemia; converts from Protestant to Roman Catholic. Swiss anti-masturbation physician Samuel Auguste Andre (André ) David Tissot (d. 1797) on Mar. 20 in Grancy, Canton de Vaud. Scottish chemist Joseph Black (d. 1799) on Apr. 16 in Bordeaux, France; one of 16 children; son of a Scottish wine merchant from Ulster; educated at Glasgow U., taking chemistry from William Cullen; discoverer of latent heat (1761); teacher of James Watt. British Cornish navigator Samuel Wallis (d. 1795) on Apr. 23 in Lanteglos-by-Camelford (near Camelford), Cornwall; starts out serving under Capt. John Byron. German piano maker Johann (Georg) Andreas Stein (d. 1792) on May 16 in Heidesheim; inventor of the Viennesse piano. Am. Rev. War flip-flopping loyalist jurist ("the Weathercock") William Smith (d. 1793) on June 18 in New York City; educated at Yale U.; chief justice of New York Province (1763-82); ends up fleeing to Canada and becoming chief justice of Quebec Province in 1786-93. Scottish Neoclassical architect Robert Adam (d. 1792) on July 3 near Kirkcaldy, Fife; son of William Adam (1689-1748); brother of John Adam (1721-92) and James Adam (1732-94);rival of Sir William Chambers (1723-96) and James Wyatt (1746-1813). German "very bright" mathematician-physicist-philosopher Johann Heinrich Lambert (d. 1777) on Aug. 28 in Mulhouse. Am. Rev. War gen. ("Hero of Bennington") John Stark (d. 1822) on Aug. 28 in Londonderry, N.H.; coiner of the phrase "Live free or die" in 1809. English engineer Matthew Boulton (d. 1809) on Sept. 3 in Birmingham. Am. poet-playwright-historian ("Conscience of the American Revolution") Mercy Otis Warren (d. 1814) on Sept. 14 in Barnstable, Mass.; first Am. female playwright; voice of the "Old Republican" elite; #3 of 13 children born to Col. James Otis (1702-78) and Mary Allyn Otis (1702-74) (a descendant of Mayflower passenger Edward Doty); brother of James Otis Jr. (1725-83); wife (1754-) of James Warren (1726-1808). English physician and obstetric surgery pioneerCharles White (d. 1813) on Oct. 4 in Manchester. French diplomat-spy-swordsman Chevalier Charles Genevieve Louis Auguste Andre Timothee d'Eon de Beaumont (d. 1810) on Oct. 5 in Tonnerre; 18th cent. Europe's most famous transvestite. Am. Rev. leader (DOI signer) (asthmatic) Caesar Rodney (d. 1784) on Oct. 7 in Byfield Farm, Dover Hundred, Kent County, Del.; featured on the first Del. quarter (1999); helps break the deadlock on the DOI; known for a giant Great Caesar's Ghost rotten skin cancer on his face, which he covers with a green scarf. English exploring fool and sea captain James Cook (d. 1779) on Oct. 27 in Marton, North Yorkshire. Serbian Jesuit priest and scientist Franz Xaver von Wulfen (d. 1805) on Nov. 5 in Belgrade; Swedish descent father, Hungarian mother. Anglo-Irish "The Vicar of Wakefield", "The Deserted Village" poet-dramatist-novelist-essayist Oliver Goldsmith (d. 1774) (b. 1730?) on Nov. 10 near Ballymahon, County Longford (Elphin, County Roscommon?); educated at Trinity College, Dublin, U. of Edinburgh, and U. of Leiden; wanders through Europe playing a flute and begging, then settles in England, working as a physician and writing hack works to order until he gets famous enough to go legit. Egyptian Mamluk ruler (1760-72) Ali Bey Al-Kabir (d. 1773) in Abkhasia (Georgia, Caucasus); starts out as a young slave carried to Egypt, becoming a Mamluk soldier. Am. Rev. War brig. gen. ("Hero of Oriskany") Nicholas Herkimer (Nikolaus Herchheimer) (d. 1777); son of German Palatinate immigrants in German Flatts in the Mohawk Valley of New York. English type-founder and chocolatier (Quaker) Joseph Fry (d. 1787); son of poet John Fry (-1775); father of Joseph Storrs Fry (1767-1835). Am. Rev. Tory leader Capt. John Butler (d. 1794) in New London, Conn. Italian composer Nicola Piccini (d. 1800); Christoph Gluck's rival in Paris. English industrialist (pioneer in cast iron use) John "Iron-Mad" Wilkinson (d. 1808) in Clifton, Cumberland. Deaths: Scottish-born Am. newspaper publisher John Campbell (b. 1653). Am. colonial official Robert Livingston the Elder (b. 1654) on Oct. 1. British royal gov. Sir Francis Nicholson (b. 1655) on Mar. 5 in London. Italian composer Agostino Steffani (b. 1653) on Feb. 2 in Frankfurt, Germany - no doubt a relation to Gwen? German jurist-philosopher Christian Thomasius (b. 1655) on Sept. 23. Am. purest of pure white Puritan clergyman Cotton Mather (b. 1663): "Historians are to be read with moderation and kindness, and it is to be remembered that they can not be in all circumstances like Lynceus." British adm. Sir Hovenden Walker (b. 1666).









1729 Nobody at the time knew it, but 1729 is the smallest taxicab number? On Feb. 14 Penn. passes a debt servitude law allowing the jailing of debtors. On Aug. 19 French dauphin Louis Ferdinand (1729-65) is born to Louis XV and his queen Marie Leszczynska, saving the decimated French royal Bourbon line, causing celebrations in all major French cities as well as Rome and Euro courts; too bad, he dies before ascending the throne. On Oct. 2 (Sept. 29?) Nadir Khan defeats the Afghans at the Battle of Damghan and kills Afghan shah (since 1727) Ashraf (b. 1700), driving them out of Persia, then reconquers the NW provinces from the Ottomans. On Oct. 15 Paul Atkinson dies in Hurst Castle after 30 years of imprisonment, becoming the last Roman Catholic confessor in chains in Protestant England. On Nov. 9 France, Spain, and England sign the Treaty of Seville, restoring their conquests and confirming the asiento. On Nov. 29 after the Natchez tribe attacks French colonists near modern-day Natchez, Miss., the Natchez Massacre (Revolt) ends in a massacre of 230 French colonists in Fort Rosalie, with most of the women and African slaves spared, causing the French in New Orleans to send out an army that wipes out the Chaouacha people then allies with the Choctaw to wipe out the Natchez, selling hundreds into slavery while the remnant seek refuge with the Chickasaw, Creek, and Cherokee until they are kaput by 1736; in 1731 the French crown takes control of La. from the French West India Co., and in 1732 La. gov. Etienne Perier is recalled to France to pay for the massacre. ending all their wars with them (begun 1716); reps of the Illiniwek nation give allegiance to the French. Portugal loses Mombasa on the coast of Kenya to the Arabs. Corsica becomes independent of Genoa (until 1732). South Carolina (S.C.) officially separates from North Carolina (N.C.), and the latter becomes a royal colony. To cope with the Gin Craze caused by the accession of Protestant William of Orange in 1688, which started out as an alternative to Roman Catholic French brandy, causing Londoners to ditch beer, the English Parliament passes the Gin Act, increasing the duties on gin, doing ditto in 1736, 1743, 1747, and 1751; "Drunk for 1 d.; dead drunk for 2 d.; straw for nothing" appears on a sign over a gin shop in 1736. The Kingdom of Travancore in S India is founded (until 1949), covering most of C and S Kerala. The city of Baltimore, Md. (AKA B'more, Charm City, Mobtown, Monument City, Ravenstown, City of Firsts) on the upper Cheseapeake Bay at the mouth of the Patapsco River (modern-day pop. 620K/2.7M) is founded as a tobacco port, becoming the largest independent city in the U.S. by modern times (until ?), becoming known as the home of celebs Edgar Allan Poe, Frederick Douglass, H.L. Mencken, Eubie Blake, Babe Ruth, Billie Holiday, and Francis Scott Key's nat. anthem "The Star-Spangled Banner". Emperor Qing Shi Zong prohibits opium smoking in China - him and what army? Italian composer Domenico Scarlatti (1685-1757), son of Alessandro Scarlatti settles in the Spanish court at Madrid for life - the fresh face of 1729? After the fallout from the 451 Council of Chalcedon works its magic, the Melkite Greek Catholic Church splits with the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch and aligns with the Roman Catholic Church while keeping Arabic as its official language. The Academia de Buenas Letras is founded in Barcelona, Spain. Benjamin Franklin and James Franklin buy the The Pennsylvania Gazette (until 1765), turning it into the most popular Am. colonial newspaper. Sports: 6' 200 lb. John "Jack" Broughton (1704-89), who founded the London Prize Ring Rules after he killed somebody in the ring takes over the English bare-knuckle boxing title (until 1750) from his teacher James Figg, who retires. The Godolphin Arabian (1724-54), the last of three stallions on which English Thoroughbreds are based is imported, joining Byerly Turk (1686) and Darley Arabian (1729); his bay colt by English mare Roxana named Lath (1724-53) becomes a top racehorse, followed by Regulus (1739-65), who goes undefeated. Architecture: Old South Church (Meeting House) in Boston, Mass. is built, becoming the largest bldg. in Boston, used by 5K colonists as the HQ for organizing the Boston Tea Party of Dec. 16, 1773. John Wood begins building Queen Square in Bath, England (finished 1736). Science: French scientist Pierre Bouguer (1698-1758) pub. Essai d'optique sur la gradation de la lumiere (lumière), a study of the quantity of light lost passing through the atmosphere, announcing the Beer-Lambert Law, which states that the absorbance is directly proportional to its path length. Stephen Gray of England discovers electrical conductivity by passing static electricity through threads and wires. French scientist Jean-Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan (1678-1771) first observes the Circadian Rhythm in the plant Mimosa pudica. Nonfiction: Elijah Fenton (1683-1730), The Works of Edmund Waller. Ludvig Holberg (1684-1754), Description of Denmark and Norway. Andrew Motte (tr.)., Isaac Newton's 'Principia Mathematica'; tr. from Latin to English - it's still Greek to me? Thomas Sherlock (1678-1761), A Tryal of the Witnesses of the Resurrection of Jesus. Jonathan Swift (1667-1745), A Modest Proposal; the classic children's cookbook?; satire written after a famine in Ireland caused by an oat crop failure, proposing that infants be sold for food; "I have been assured by a very knowing American of my acquaintance in London, that a young healthy child well nursed is at a year old a most delicious, nourishing, and wholesome food, whether stewed, roasted, baked, or boiled; and I make no doubt that it will equally serve in a fricassee or a ragout." Music: G.F. Handel (1685-1759), Lotario (Lothair) (opera) (King's Theatre, London) (Dec. 2); libretto adapted from Antonio Salvi's "Adelaide"; flops after 10 perf. Jean-Joseph Mouret (1682-1738), Two Suites de Symphonies; incl. Fanfare-Rondeau, used as the theme of the PBS TV program "Masterpiece Theatre". Art: Canaletto (1797-1768), The Stonemason's Yard (Campo St. Vidal and Santa Maria della Carita); overlooks the Grand Canal; two children are playing in the left foreground, and one falls and pisses involuntarily in surprise. Alexandre Desportes, Still Life with Oysters. J.F. de Troy, Rape of the Sabines. Plays: Samuel Madden (1686-1765), Themistocles, the Lover of His Country (tragedy) (Theatre Royal, London); the Athenian dude who lived from -528 to -462. Poetry: Albrecht von Haller (1708-77), Die Alpen (The Alps). Births: German mathematician Johann Daniel Titius (d. 1796) on Jan. 2; discoverer of the misnamed Bode's Law of Planetary Distances - the law of godly titties? Italian scientist (physiologist) (spontaneous generation disprover) Lazzaro Spallanzani (d. 1799) on Jan. 10 in Scandiano; educated at the U. of Bologna. British statesman-orator-writer Edmund Burke (d. 1797) on Jan. 12 in Dublin; educated at Trinity College, Dublin. German "Nathan the Wise" Christian dramatist-critic (Freemason) Gotthold Ephraim Lessing (d. 1781) on Jan. 22 in Kamenz, Upper Lusatia, Saxony. British col. gov. of N.C. (1765-71) and N.Y. (1771-80) William Tryon (b. 1788) on Jan. 27 in Norbury Park, Surrey, England. English "The Hermit of Warkworth", "O Nanny, Wilt Thou Gang with Me?", "Reliques of Ancient English Poetry" poet-antiquary-bishop and "Tatler", "Guardian", "Spectator" ed. Thomas Percy (d. 1811) on Apr. 13 in Bridgnorth, Shropshire; bishop of Dromore. Russian Romanov tsar #12 (1762-96) Catherine (Yekaterina) II (the Great) (Sophia Augusta Petrovna) (d. 1796) on May 2 (Apr. 21 Old Style) in Stettin, Prussia; daughter of Christian August, prince of Anhalt-Zerbst (1690-1747) and Johanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp; 1st cousin of Gustav III of Sweden and Charles XIII of Sweden. Austrian field marshal Michael Friedrich Benedikt, Baron von Melas (d. 1806) on May 12 in Radeln, Transylvania (modern-day Roades, Romania); of Saxon descent. French dauphin Louis Ferdinand (d. 1765) on Aug. 4 in Versailles; only surviving son of Louis XV and Marie Leszczynska; husband of (1744-6) Maria Teresa Rafaela of Spain, and (1747-65) Marie Josephe of Saxony; father of Marie Therese (1746-48), Louis XVI, Louis XVIII, and Charles X. German statesman-educator Franz Friedrich Wilhelm von Furstenberg (Fürstenberg) (d. 1810) on Aug. 7 in Herdringen, Westphalia. German philosopher (Jewish) Moses Mendelssohn (d. 1786) on Sept. 6 in Dessau; the 3rd Moses after Moses Maimonides and Moses One; grandfather of Felix Mendelssohn (1809-47). English "Feminead" writer-poet-clergyman John Duncombe (d. 1786) (AKA Crito) on Sept. 29 in London; educated at Essex and Corpus Christi College, Cambridge U. British Gen. Charles "No Flint" Grey, 1st Earl Grey (d. 1807) on Oct. 23 in Northumberland; 4th son of Sir Henry Grey, 1st Baronet of Howick; created earl in 1806. French soldier-explorer-mathematician adm. Louis-Antoine, Comte de Bougainville (d. 1811) on Nov. 12 in Paris; writes a treatise on integral calculus at age 25; discoverer of Bouvainville Island. French fur trader Pierre Laclede (Laclède) Liguest (d. 1778) on Nov. 22 in Bedous, Bearn. Russia field marshal Count Alexander Vasilievich "Rimnikski" Suvorov (d. 1800) on Nov. 29 in Moscow; of Swedish ancestry; son of Vasily Ivanovich Suvorov; uncle of Prince Alexander Ivanovich Gorchakov; last generalissimo of the Russian Empire, who won all 60+ battles. Am. Rev. leader Charles Thompson (d. 1824) on Nov. 29 in Gorteade, Tobermore (near Maghera), County Londonderry, Ireland; Scots-Irish parents; emigrates to Penn. in 1739. emigrates to North Am. at age 8; secy. of the Continental Congress (1774-89). English Methodist minister (John Wesley's successor) John William Fletcher (b. 1785) in Nyon, Switzerland. Am. loyalist Episcopal minister Rev. Samuel Seabury (d. 1796) (AKA A.W. Farmer) on Nov. 30 in Ledyard, Groton, Conn.; first Am. Episcopal bishop and first bishop of Conn. Spanish composer Antonio Soler (d. 1783) on Dec. 3 in Olot, Gerone, Catalonia. Italian opera composer-organist Giuseppe Sarti (d. 1802) on Dec. 28 in Faenza. Am. playwright John Leacock (d. 1802); Philadelphia silversmith, member of the Sons of Liberty, and an associate of Benjamin Franklin and John Dickinson. Scottish "Zeluco" physician-novelist John Moore (d. 1802) in Stirling; father of Gen. Sir John Moore (1761-1809) and Adm. Sir Graham Moore (1764-1843). English "The Old English Baron" novelist Clara Reeve (d. 1807) in Ipswitch. Deaths: Am. Congregationalist pastor Solomon Stoddard (b. 1643) on Feb. 11 French scholar Jean Hardouin (b. 1646) on Sept. 3. English poet Sir Richard Blackmore (b. 1650). French actor Michel Baron (b. 1653) on Dec. 22 in Paris. Dutch explorer adm. Jakob Roggeveen (b. 1659) on Jan. 31 in Middelburg. Indian Maratha adm. Kanhoji Angre (b. 1669) on July 4 in Alibag, Maharashtra. French Roman Catholic priest Jean Meslier (b. 1664); leaves Memoir of the Thoughts and Feelings of Jean Meslier: Clear and Evident Demonstrations of the Vanity and Falsity of All the Religions of the World, revealing that he turned atheist, knocking all religions, with the soundbyte that he wishes that "all the great men in the world and all the nobility could be hanged, and strangled with the guts of the priests", which Denis Diderot turns into "Let's strangle the neck of the last king with the entrails of the last priest"; Voltaire becomes a big fan; the first Westerner to pub. a complete book in support of atheism? English steam engine inventor Thomas Newcomen (b. 1664) on Aug. 5 in London. French composer Elisabeth Jacquet de La Guerre (b. 1665) on June 27. English gardener Thomas Fairchild (b. 1667) on Oct. 10. English neoclassical Restoration poet-dramatist William Congreve (b. 1670) on Jan. 19 in London. Scottish economist John Law (b. 1671) on Mar. 21 in Venice (pneumonia); dies poor. Irish writer Sir Richard Steele (b. 1672) on Sept. 1 in Carmarthen, Wales. English philosopher Samuel Clarke (b. 1675) on May 17 in London. Scottish architect Colen Campbell (b. 1676) on Sept. 13 in London, England. English Deist philosopher Anthony Collins (b. 1676) on Dec. 13. German composer Johann David Heinichen (b. 1683).