

























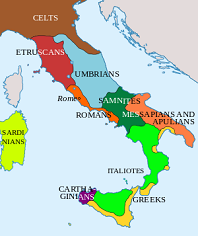







-500 World pop.: 100M. The 70th Olympiad. Roman consuls: Servius Sulpicius Camerinus Cornutus and Manius Tullius Longus. In this cent. the literacy rate in Athens reaches 10%-15%, and goes down from there in Europe until the Industrial Rev.? Some Greek aristocrats are expelled from Naxos, flee to Miletus, and ask Aristagoras of Miletus (son-in-law of Histaeus) for help, and he goes to Artaphernes of the Persians, who decides to help them invade. Middle-aged Confucius (-551 to -479) is appointed crime (justice) minister of Chung-tu in the Chinese state of Lu (modern-day Shantung Province) - the original Charlie Chan? In this cent. the Osco-Umbrian-speaking Rome-hating Aequi invade Latium from the C Apennines, while the Umbrian-speaking Germanic Marsi on the E shore of Fucinus Lake remain there; the Oscan-speaking Paeligni in the Valle Peligna ("Muddy Valley") in modern-cay Abruzzo, Vestini in modern-day Abruzzo in C Italy between the Gran Sasso and the N bank of the Aterno River, and Marrucini on the E coast of modern-day Abruzzo between the Aterno and Foro Rivers inhabit the E side of the Italian peninsula around Teate (Chieti); Oscan-speaking Frentani inhabit the SE Adriatic coast from Apulia to the frontiers of the Marrucini; the SC Apennines are inhabited by the Oscan-speaking Samnites, who by the end of the cent. are united in a loose but formidable confederation. In this cent. the barbaric Iranian Sarmatians a set of tribes (ancestors of the Slavs), incl. the Alani (Alans) (E division), Roxolani and Jazyges (Iazyges) inhabit the region W of the Caspian Sea from Sea of Azov N to the Don River. Yadi'ab Amir (d. -480) becomes the king of Nashan in S Arabia; in this cent. the Qedar Kkingdom of N Arabia has two known kings, Qainu and Geshem, the latter possibly mentioned in the Bible (Neh. 2:19, 6:1). In this cent. the Achaean League is formed by the 12 city-states of Achaea in the N-C Peloponnese of Greece. is formed by the 12 city-states of Achaea in the N-C Peloponnese of Greece. In this cent. the city of Mtskheta 12 mi. N of modern-day Tbilisi at the confluence of the Aragvi and Mtkvari Rivers is founded, going on to become the capital of the Kingdom of Iberia (Kartli) in the 3rd cent. B.C.E., and the birthplace of Christianity in Georgia in 337 C.E., and HQ of the Georgian Orthodox Church. In this cent. after finding salt veins, the Celts settle the city of Salzburg (Ger. "Salt city") (modern-day pop. 150K) in Austria near the N foothills of the Alps, and found the city of Vienna (Vianiomina) (Vindobona) (Gael. "fair/bright settlement/bottomland") (named after Celtic god Vindos?) on the Danube River (modern-day pop. 1.8M/2.6M). About this time the earliest Celtic chariot burials in Britain begin - Ahnuld's ancestors? About this time Celts in France leave burial mounds containing evidence of consumption of red wine, mead, and millet beer. In this cent. the Turkic nomadic Xiongnu (Hsiung-nu) (Chionites) menace China, becoming a major reason that the Chinese later build the Great Wall. In this cent. Lake Chad in Africa becomes inhabited. In this cent. the city of Beroea is founded in Macedonia on the site of modern-day Verroia (Veroia) (40 mi. WSW of Salonika), going on to become the most populous city of Macedonia by the first cent. C.E. About this time the city of Khujand (Khodjent) in Tajikistan on the Syr Darya (Jaxartes) River at the mouth of the Fergana Valley near the borders of Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan (modern-day pop. 181K/931K) is founded, becoming the 2nd largest city in Tajikistan; in 1936-91 C.E. it is renamed Leninabad. In this cent. the Glauberg Plateau in Hesse, Germany reaches its high point of fortifications as part of a network of Celtic fortified sites (oppida) covering S and WC Germany; it is the site of a princely seat, which in the 1990s become an archeological gold mine, incl. the Lord (Prince) of Glauberg statue; the fortifications are abandoned by the 1st cent. B.C.E. under German pressure. In this cent. Carthaginian explorer Himilco I the Navigator becomes the first Mediterranean explorer to reach the NW shores of Europe, incl. the Tin Islands (Brittany?) (Cornwall?) (Ireland?) - the Earth's crust is 10 parts per million (.001%) tin, so good luck? In this cent. the Thracian settlement of Sardica (Serdica) (modern-day Sofia, Bulgaria) (named after the Thracian Serdi tribe), on the elevated plain between the Perlovetz and Bojana Rivers (tributaries of the Iser River) 300 mi. NW of Byzantium is settled by the Thracian Odrysi. In this cent. the Greeks establish the colony of Elibyrge (Elybirge) in S Spain, which later becomes known as Illiberis to the Romans, and later as the city of Granada. In this cent. the Nazca Lines begin to be constructed in S Peru (until 500 C.E.); discovered in 1941 by Long Island City, N.Y.-born historian Paul August Kosok (1891-1959), who discovers their bird and other patterns from the air, along with their astronomical orientation; German mathematician Maria Reiche (1903-98) assists him, staying on after for life after he leaves, becoming known as "the Lady of the Lines". In this cent. the Olmec Culture (founded -1500) disappears. In this cent. the Basket Maker Culture of SW North Am. is founded (ends 700). In this cent. crop rotation is introduced in Greece, leading to large estates worked by slave labor. In this cent. chickens are introduced to Africa through the Nile Valley. In this cent. trapezitai (private bankers) take over the money-exchanging and money-lending business in Greece, and Athenian coinage becomes the predominant medium of exchange in the Greek world. About this time Greek Socratic philosopher ("the Dark or Obscure") (dark clothing) ("the Weeping Philosopher") Heraclitus of Ephesus (-535 to -475) flourishes, becoming the philosopher of the Logos, and Mr. Fire Is the Source of All Things, adding the concept of becoming to that of being, and holding virtue to consist in subordinating the individual to the laws of society, as long they are based on a universal and reasonable harmony, leaving On Nature; he becomes known for the soundbytes: "No man ever steps in the same river twice", "The path up and down are one and the same", and "All entities come to be in accordance with the Logos (word)." In this cent. Greek Pythagorean philosopher Hippasus of Metapontum flourishes, discovering the irrationality of the square root of 2, causing a legend to claim that he is drowned at sea by the gods as punishment. About this time the practice of scalping becomes popular with the Scythians of S Russia, who begin occupying N Russia in this cent.; it is later believed that the Dutch, French, and English introduce it to North Am. aborigines as proof for bounty payment, but archaeological investigations prove it was practiced in pre-Columbian times. About this time Sicilian (born in Syracuse?) Greek comic poet-dramatist Epicharmus of Kos (-540 to -450) thrives, inventing the Doric or Sicilian comedic form; "The wise man must be wise before, not after." Nonfiction: The Epic of Atrahasis is written in Arabia, describing the god Allah (Allah) leading a rebellion against chief god Enlil (Elil). Captive Jews in Babylon are busy churning out fiction which later becomes the first 39 books of the Bible; the Atbash Cypher (first Hebrew letter substituted for last, etc.) is invented, and used to make the Bible funner, e.g., encrypting the name Babel as Sheshach in Jeremiah. In this cent. Jewish minor prophet Joel allegedly lives in or near Jerusalem after the Babylonian Captivity, writing The Book of Joel, which talks about a plague of locusts and how when the Jews get right with Jehovah he will give them plentifiul harvests and establish Jerusalem as a holy city. In this cent. the game of Polo is invented in Persia? In this cent. the Chinese begin breeding miniaturized pugs from giant mastiffs. About this time the Capitoline Wolf, an Etruscan bronze statue is cast in the lower Tiber Valley, showing twin infants Romulus and Remus suckling the she-wolf Attus Navius. The original Tumnus from Narnia? About this time the Greek cult of Pan becomes popular in Athens, with Pratinus of Philius introducing the Satyr Play at the yearly Dionysia (Dionysian festival) in Athens, showing burlesques about Pan's companions the half-goat Satyrs, known for pointy ears, long curly hair and beards, and unstoppable tumescent erections, who are ever-ready but shy, and love to dance with and chase nymphs while swigging wine; the leader of the satyrs is Silenus; Aeschylus allegedly writes the best, only one of which survives; Satyr Suspending a Pipe Case from His Erection (painted on an Attic black-figure plate) and Satyr Balancing a Wine Cup on His Erection (painted on an Attic red-figure psykter) are produced about this time; Greek actors are called "hypocrites" (pretenders) - how low can you go for your master Satan, that about summarizes professional acting? About this time wine is being produced by the Gauls in S France. Perceptive Darius I the Great builds Persepolis, with great statuary, incl. the long staircase leading into his palace, which he uses to awe ambassadors from the 20 or so countries his empire now rules. Celts build tombs in Miesau near modern-day Kaiserslautern in W Germany. About this time the Japanese begin their own mix of Buddhism, Taoism, and Confucianism called Shinto (Way of Divine Power). Earl in this cent. Greek philosopher Leucippus of Miletus flourishes, originating the atomistic theory, which is developed by his student Democritus. In this cent. rival Greek painters Zeuxis of Heraclea Pontica and Parrhasius of Ephesus flourish; Zeuxis allegedly paints such realistic grapes that the birds try to eat them, but Parrhasius paints such a realistic curtain that Zeuxis attempts to draw it aside, losing a painting contest with him because although he had deceived birds, Big Parrot had deceived him, causing Parrhasius to receive Athenian citizenship, and go on to paint the Demos, a personification of the Athenian people, showing their macaroni mix of types. In this cent. the Effigy Mounds in NE Iowa begin to be built (until 1300 C.E.); many are bird-shaped or bear-shaped. The tarnish-free Sword of Gou Jian is made about this time; discovered in 1965 C.E. in Hubei, China. Beermaking begins in Mediterranean France. Inventions: The bitless bridle is first used in Persia during the reign of Darius I the Great.

-499 Aristagoras, tyrant of the city of Miletus goes on a joint expedition with Persian satrap Artaphernes (brother of Darius I the Great) to conquer Naxos, and after Persian gen. Megabates flops and warns them, it turns into a debacle, causing Aristagoras to decide to incite the Greek city-states of Ionia into a rebellion against Darius I to save his position; fellow Milesian tyrant Histiaeus (d. -493) gives the signal to begin the Ionian Revolt (ends -493) by sending a message to Aristagoras tattooed to the scalp of his slave shaving his head first then letting the hair grow back); Militiades the Younger joins the Ionian Revolt, capturing the islands of Lemnos and Imbros, which he eventually cedes to Athens to establish friendly relations; the start of the (Greco-)Persian Wars (end -448). Aeschylus (-525 to -456) enters his first dramatic competition at the Greater Dionysia, going on to become the first Greek playwright to put two actors onstage at the same time. Roman consuls: Titus Aebutius Helva and Gaius Vetrurius Geminus Cicurinus.

-498 Roman consuls: Aulus Postumius Albus Regillensis (dictator) and Quintus Cloelius Siculus and Titus Larcius Flavus. Aristagoras travels to mainland Greece to solicit aid, causing Athens to contribute 20 ships and Eretria five; an Ionian and Athenian fleet sails to Ephesus, and the soldiers disembark and march to fight Persian satrap Artaphrenes, then burn the capital of Sardis and return to Ephesus, where the Persians meet and massacre them; Aristagoras escapes and fights on. Amyntas I dies, and Alexander I Philhellene ("not-a-Greek") (d. -454) becomes king of Macedonia, and later becomes the first Macedonian to participate in the Olympics and win. Cleandrus is murdered, and Hippocrates (d. -491) becomes tyrant #2 of Gela, going on to conquer Leontini (Lentini) (Leontinoi) in -494, making his ally Aenesidemus its tyrant. The Palace of Vouni is built by the Phoenician pro-Persian king of Marion to watch over the pro-Greek city of Soli following an unsuccessful revolt of the latter against the Persians. Darius I begins construction of a palace in Babylon for his son Xerxes (Pers. "monarch", "hero among kings") (finished -496), indicating a possible coregency (-496 to -486) followed by 11 years of sole rule (-486 to -475)? (Jehovah's Witnesses). Births: Greek architect Hippodamus of Miletus (d. -408) in Miletus.
-497 Roman consuls: Aulus Sempronius Atratinus and Marcus Minucius Augurinus. The beginning of the rule of the tyrants in the city of Catania (Katania) in E Sicily. Confucius (-551 to -479) resigns his office and leaves the kingdom of Lu heartbroken after Duke Ding takes 80 singing girls as a present from the state of Qi against his advice, and begins wandering from state to state in China, looking for an ideal ruler which he never finds (ends -484). Architecture: The Temple of Saturn in the Forum Romanum is dedicated. Deaths: Greek philosopher Pythagoras of Samos (b. -580) in Metapont(i)um; dies a believer in the mystical qualities of numbers such as pi, having never touched a bean; about this time the democratic party in S Italy turns on his sect and burns them in their meeting places; leaves his writings to his daughter (by Theano) Damo, who passes them to her daughter Bitale: "The most momentous thing in human life is the art of winning the soul to good or to evil" - how I want a drink, alcoholic of course?
-496 The 71st Olympiad. The Romans (Latins) under dictator Aulus Postumius Albus Regillensis defeat the pesky Etruscans under king Lars Porsena (Porsenna) (Pursenas) (ruling from Clusium) and Octavius Mamilius (son-in-law of Tarquin) at the Battle of Lake Regillus, allegedly with the help of heavenly twins Castor and Pollux; at this time Rome is 400 sq. mi. in area and has 150K pop.; legendary Roman hero Horatius holds the Etruscan army at bay while his fellow Romans cut down the Sublician Bridge the Tiber River, then swims to safety and is awarded as much land as he can plow in a day. A 10-year gap is filled when Hipparchus is elected ruler of Athens. Roman consuls: Aulus Postumius Albus and Titus Verginius Tricostus Caeliomontanus. Births: Greek tragedian Sophocles (Gr. "soph" + "ocles" = "wise" + "famous") (d. -406) in Colonus Hippius, Attica (near Athens); son of Sophillus. Deaths: Chinese philosopher Sun Tzu (b. -544).

-495 Roman consuls: Appius Claudius Sabinus Inregillensis and Publius Servilius Priscus Structus. Ilisami II Nabat (d. -475) becomes king of Kaminahu in S Arabia. Births: Athenian statesman-gen.-orator and first citizen Pericles (Gr. "all-around famous, far-famed") (d. -429) in Athens; son of Athenian gen. Xanthippus; pupil of Sophist music master Damon and philosopher Anaxagoras of Clazomenae, who teaches him freedom of thought and freedom from superstition; big friends with big names incl. Sophocles (-496 to -406), Protagoras, Phidias, and Herodotus; known for his high cranium, he is so self-conscious about his pointed head that he only poses for portraits wearing a helmet; his cultured non-Athenian mistress Aspasia of Miletus wields considerable political power. Greek philosopher Zeno the Dialectician of Elea (d. -435) in Elea (Velia), Italy.

-494 Roman consuls: Marcus Valerius Volusus Maximus (dictator) and Aulus Verginius Tricostus Caeliomontanus. On Oct. 20 the Ionian Revolt (begun -499) fails with a naval defeat by the Persians at the Battle of Lade (Ladé) (Lades), followed by the sacking of Miletus, which is later rebuilt on a new site after all men are killed, the women and children are sold into slavery, and the young men castrated; historian Hecateaeus of Miletus conducts the negotiations with satrap Artaphernes, obtaining his consent to restore the constitution of the Ionic cities; Zancle in Sicily is burned and all the inhabitants (mainly from Samos) are enslaved by the Persians, who vow to get even with Athens for supporting the revolt; rebel leader Miltiades (-550 to -489), tyrant of Chersonesus flees to Athens, where he rises to prominence despite opposition by the Alcmaeonidae. King Cleomenes I of Sparta attacks and defeats Argos, slaughtering 6K in the Battle of Sepeia, and forcing it into the Peloponnesian League and giving Sparta hegemony in S Greece; Cleomenes tries to punish Aegina for supporting Persia but is blocked by the other Spartan king Demaratus. The First Plebeian Secession (gen. strike) in Rome (ends -493) is caused by outrage at patrician creditors enslaving pleb legionaries returning from the Volscian War; disobeying the orders of the consuls, they march to the Sacred Mount up the Tiber, beyond the Anio River, and threaten to found a new city unless their rights are respected; the patricians yield, giving them the institution of the tribuni plebis, the privilege of having officers of their own (tribunes and aediles) to protect them, with veto power over the patrician magistrates.

-493 By now the Persians control all the Greek city-states of Asia Minor, and now begin an extensive preparation for an attack on the free cities of the Greek mainland. The Romans under Spurius Cassius (Lat. "vain") Vecellinus negotiate the Foedus Cassianum (Treaty of Cassius), a treaty with the Latin League which establishes a defensive alliance against the Aequi and Volsci, with joint annual campaigns and alternating generals, equal booty distribution, and joint colonies to be established on reconquered territories. Themistocles (-514 to -462), leader of the anti-Persian party is elected ruler (archon) of Athens, persuading Athens to expand its naval power by building 200 triremes and fortifying the three natural harbors of the Piraeus. The strategic city of Zancle in NE Sicily is captured by Anaxilas, tyrant of Rhegium (Reggio di Calabria) across the Strait of Messina with assistance from the refugees from Mssina; he expels the remaining Samians and resettles the city with Messenians, then renames it Messana (Messina). Roman consuls: Postumius Cominus Auruncus and Spurius Cassius Vecellinus.
-492 The 72nd Olympiad. After his son Metiochos is captured by the Persians, Militiades the Younger flees to Athens, and talks his way into becoming one of the 10 strategoi (generals) for -490. Darius I the Great sends a 600-ship Persian fleet under Gen. Mardonius (d. -479) to punish Athens and Eretria for aiding the Ionian Revolt, but it is destroyed in a storm on the cliffs of mean Mount Athos while rounding the Chalcidice - they weren't worth a daric? Roman consuls: Titus Geganius Macerinus and Publius Minucius Augurinus.

-491 Eurypontid Spartan king Demaratus is deposed by Cleomenes after being accused of being illegitimate, despite the opposition of the ephors, and more controllable Leotychidas II (-545 to -469) becomes Eurypontid king of Sparta (until -476), going on to lead the Spartans in the Persian Wars of -490 to -478; Demaratus goes into exile with the Persians and becomes bitter - have a seat right over there please? Hippocrates dies, and Gelon (Gelonos) (Gelo) (d. -478), son of Deinomenes becomes ruler of Gela, founding the Deinomenid Dynasty. Roman consuls: Marcus Minucius Augurinus and Aulus Sempronius Atratinus.

-490 Meany Cleomenes I (r. since -520) goes mad, is imprisoned, and either commits suicide or is executed by the pissed-off Spartan ephors, and next year his half-brother Leonidas (Gr. "son of the lion") I (-520 to -480) becomes Agiad king #17 of Sparta (until Aug. 11, -480); his wife is Cleomenes I's daughter Queen Gorgo, mother of future Spartan king (-480 to -458) Pleistarchus, who becomes one of the few female historical figures mentioned by Herodotus. Darius I the Great sends a 2nd Persian force under Artaphernes and Datis, this time going across the Aegean Sea, which sieges Eretria on Euboea until it falls through treachery; on Sept. 12 after aged I-ain't-as-good-as-I-once-was ex-tyrant Hippias talks him into it, Darius I lands at Marathon, center of Peisistratid strength; the Battle of Marathon, AKA the Battle of Fennel Fields sees an Athenian army of 10K-20K under Gen. Miltiades (one of 10 strategoi) lure then defeat an invading Persian army of 15K-25K in a field of fennel, with losses of 192 Greeks vs. 6.4K Persians (incl. Hippias?), making good use of the phalanx, and pioneering double envelopment; Athenian messenger Pheidippides (Phidippides) (Philippides) (Thersipus?) (Erchius?) (Eucles?) is sent in full armor to run to Athens 41 km (26 mi.) away to announce the Greek V with the message "Nike" (victory) (actually "Nenikekamen" = "We are victorious), after which he drops dead after running the first marathon; the first mention of the runner is in Plutarch's "On the Glory of Athens" in the 1st cent. C.E., and what really happened was that Pheidippides was sent before the battle to Sparta 140 mi. away to ask for help, and they refused because they were holding a sacred festival, and after the battle the Athenian army marched 25 mi. back to Athens to head off the Persian fleet, and the two events got confused; Greek gen. Miltiades dedicates his helmet to Zeus, and it ends up in a museum; Aeschylus fights in the front lines against the Persians; in Sept. 1970 C.E. the skeletons of five warriors who died in the battle are discovered by archeologists in the Soros of the Plataians 26 mi. NE of modern Athens; the Persians then try an end-around run, sailing around Cape Sunium to attack Athens, but the fleet-footed Athenians beat them to the city, causing the Persians to chicken out and retreat to Asia. After the Greek V (nike) at Marathon, gen. Miltiades (-550 to -489) sends a flotilla to Paros Island W of Naxos (known for its fine white Parian marble) to demand a ransom for supporting the Persians, but he fails and breaks a leg, and is charged with treason ("deceiving the people") by the Athenian court, then jailed when he can't pay the huge fine of 50 talents - no leg to stand on jokes here? After the Greek V (nike) at Marathon, a shield signal is raied on Mt. Pentelicon above Marathon to signal the Persian navy to sail around Cape Sounion and attack unguarded Athens, which is widely attributed to the treachery of the Alcmaeonidae and their leader Megacles. The gamoroi (landed aristocracy) begin to lose control in Syracuse to a disorganized democracy, causing them to invite tyrants in. The city of Patna (Pataliputra) on the Ganges River in NE India (modern-day pop. 1.69M/2.0M) is founded by the king of Magadha, becoming the capital of the Magadh Empire under the Haryanka, Nanda, Mauryan, Shunga, Gupta, and Patna Empires, known as a center of learning, fine arts, and astronomers incl. Aryabhata, Vatsyayana, and Chanakya, reaching 400K pop. by 300 B.C.E.; it goes on to become a pilgrimage center for Buddhists, Hindus, Jains, and Sikhs; after the fall of the Gupta Empire, it declines until it is revived in the 17th cent. by the British as a center of internat. trade; after the partition of the Bengal presidency in 1912, it becomes the capital of Bihar and Orissa Province. About this time Sicilian chef Mithaecus (Mithaikos) flourishes, bringing Sicilian cooking to Greece after being expelled from Sparta to Athens, writing the first known cookbook. Roman consuls: Quintus Sulpicius Camerinus Cornutus and Spurius Larcius Flavus. Births: Greek painter Polygnotus (d. -447); develops the technique of large-scale painting. Greek philosopher Empedocles (d. -430) in Agrigentum, Sicily. Greek Sophist philsopher (first) Protagoras of Abdera (d. -420) (-481 to -411?) in Abdera, Thrace.
-489 Theron of Acragas (Aeragas) (d. -472) of modern-day Agrigento, Sicily ousts Terillus of Himera, who calls for help from the Carthaginians, who stall for almost a decade but finally send an army. Athens begins a war with Aegina for helping the Persians (ends -483). Militiades the Younger (b. -550) leads an Athenian expedition of 70 ships to punish the Greek islands that supported the Persians, and attacks Paros, but fails to take it; Militades suffers a severe leg wound which incapacitates him; after returning without accomplishing the mission he is convicted of treason, and sentenced to death, but the sentence is reduced to 50 talents, which is beyond anybody's ability to pay, and he ends up dying in prison of gangrene. Roman consuls: Gaius Julius Iullus and Publius Pinarius Mamertinus Rufus. Deaths: Greek gen. Miltiades (b. -550) in Athens; dies in prison of war wounds.
-488 The 73rd Olympiad sees tyrant Gelo of Syracuse (d. -48) win a victory in the chariot race, causing sculptor Glaucias of Aegina to make a statue of him, followed by more statues of Olympian athletes incl. Philon of Corcyra, Glaucus of Carystus, and Theagenes of Thasos.
About this time Greek sculptor Phidias is commissioned to execute a large bronze group of nat. heroes at Athens with the central figure being Marathon hero Miltiades. Roman consuls: Spurius Nautius Rutilus and Sextus Furius Medullinus (?)-487 Anti-Persian party candidates Themistocles (leader of the commoners) and Aristeides (leader of the aristocrats) are elected rulers of Athens, which reforms its constitution to make it more democratic. Hipparchus, relative of the tyrant-traitor name-is-mud Hippias of the Pisistratus Dynasty is the first person to be officially ostracized after over 6K ostraka (potsherds) with his name written on them are cast by the assembly, causing him to be exiled from Athens for 10 years while retaining his property and citizenship; the vote is called for by a show of hands in the assembly, and at least 10K of them ostrakon thingies have to be cast for a valid ostracism, requiring him to leave Athens for 10 years min. without loss of property, civil rights or stigma, and subject to a recall vote by the assembly. Roman consuls: Titus Sicinus Sabinus and Gaius Aquillius Tuscus.
-486 Alcmaeonid leader Megacles of Athens is ostracized, which doesn't stop him from winning the chariot race in the Pythian Games, according to Pindar. The Greeks invent comedy. Roman consuls: Spurius Cassius Vicellinus and Proculus Verginius Tricostus Rutilus.


-485 Roman consuls: Servius Cornelius Maluginensis and Quintus Fabius Vibulanus. Darius I the Great (b. -549) dies, and his son Xerxes (Khshayarsha) (Ahasuerus) (Pers. "monarch") I (d. -465) becomes sole king of Persia, demanding "earth and water" (total submission) from the Greek states, most of whom tell him to fork off. Spurius Cassius (d. -485) proposes the first agrarian laws, attempting to give some land in Gaul to the poor plebeians (who had to leave their farms in neglect and fall into debt during military service) instead of to the patricians, who divide it up among themselves; too bad, the patricians have him executed for attempting to achieve royal power, and his agrarian laws never come into effect. The patrician Gens Fabia (Lat. "bean grower") rises to power in Rome), with brothers Quintus Fabius Vibulanus, Marcus Fabius Vibulanus, and Caeso Fabius Vibulanus< dominating the consulship until -478; this year Quintius Vibulanus lodges the spoils of a victory with the patricianu-run aerarium rather than the pleb-run publicum, pissing-off the plebs; meanwhile the patrician Gens Cornelia (Lat. "cornu" = horn) (of Etruscan origin) finally attains the consulship, after which its members get 30% of all consulships. The exiled oligarchs of Syracuse appeal for help to Gelon of Gela, who then conquers Syracuse and makes it his base, turning it into Sicily's leading city by transporting pops. of conquered neighbors; Sicily is now ruled by tyrants backed by the landed aristocracy. Deaths: Greek love poet Anacreon (b. -582); leaves Odes; the U.S. anthem "The Star-Spangled Banner" comes from the song To Anacreon in Heaven, composed by members of the Anacreontic Club in 1780 C.E. Persian king (-522 to -485) Darius I the Great (b. -549). Greek Athenian (Alcmaeonid) leader ("Father of Democracy") Cleisthenes (b. ?).
-484 The 74th Olympiad. Aeschylus wins his first Athenian first prize for drama. An artificial limb (foot) is first mentioned. In the 3rd year of his reign Xerxes I (Ahasuerus) holds a 7-day banquet for his nobles, while his wife Vashti ("beautiful woman") holds one for the women at the royal house; Xerxes calls her to his banquet to show off her beauty, but she refuses, causing Prince Memucan to successfully advise him to depose her (Esther ch. 1-2) to prevent all the royal women from getting uppity with the royal face - just whisper in my ear, you're a butterfly? Roman consuls: Lucius Aemilius Mamercus and Caeso Fabius Vibulanus. Births: Greek historian #1 ("the Father of History" - Marcus Tullius Cicero) ("Father of Historical Lies"?) Herodotus (Heródotos) (d. -425) in Halicarnassus, Caria (modern-day Bodrum, Turkey) in SW Asia Minor (a Doric colony under Persian domination, making him a Persian subject); the first Greek to know that the Red Sea connects to the Indian Ocean? Persian king #5 (-465 to -424) Artaxerxes ("his reign is through truth") I Longimanus ("long hand" - right hand longer than the left) (d. -424); son of Xerxes I; grandson of Darius I.


-483 The war between Athens and Aegina (begun -489) ends indecisively. After a rich new vein of silver is discovered at the mines at Mt. Laurium, Themistocles convinces the assembly to use the money to build a fleet of 200 triremes; Aristides opposes the measure, and is ostracized. Roman consuls: Marcus Fabius Vibulanus and Lucius Valerius Potitus. Births: Greek Sophist philosopher ("the Nihilist") Gorgias (d. -378) in Leontini. Deaths: A dog - a panic in a pagoda? Hindu sage Sidhartha Gautama Buddha (b. -563) in Kushinagar, Uttar Pradesh; dies from mushroom poisoning after feasting on pork and uttering the soundbytes: "With coarse rice to eat and my bended arm for my pillow I still have joy", and "All composite things pass away. Strive for your own liberation with diligence"; he tells his disciples to follow no leader, only his teachings, which doesn't stop them from electing a new leader after his body is cremated and the relics placed in stupas (monuments), incl. his right tooth, which is put in the Temple of the Tooth (Sri Dalada Maligawa) in Sri Lanka; Buddhist pagodas have eight sides and an odd number of stories; Buddhism teaches the Four Noble Truths: 1. Life means suffering. 2. The origin of suffering is attachment. 3. The cessation of suffering is attainable. 4. The Path to the cessation of suffering is the Eightfold Path; it also teaches the 31 Planes of Existence that beings are reborn into during their long wandering through samsara.
-482 In Aug. Bel-Shimanni seizes the throne of Babylon, and is KIA; Shamash-Eriba takes his place in Sept., and is killed by Megabysus, brother-in-law of Xerxes I; this is the last independence revolt of the Babylonians, since the economy collapses and Babylon slips into decay. Confucius returns to the state of Lu and devotes the remaining four years of his life to completing his work of compiling and editing the Chinese Classics, the first three of the five king (canonical books), while sitting under a gingko biloba tree, composing the Spring and Autumn Annals as a supplement to the 3rd king, covering from -722 to -481, becoming the earliest surviving Chinese historical text in annals form. Roman consuls: Quintus Fabius Vibulanus and Gaius Julius Iullus.
-481 Xerxes I's army gathers in Cappadocia and winters in Sardis, planning to kick Greek butt next spring; meanwhile the Congress at the Isthmus of Corinth agrees to end the war between Athens and Aegina; the Greek states, led by Sparta and Athens set up the Hellenic League to resist the Persians, with Themistocles of Athens as CIC (strategos autocrator), who refuses to place the army under command of Spartan king Leonidas, but agrees to allow the navy to serve under a Spartan adm.; after Sparta and Athens refuse the offer of Gelon of Syracuse to become CIC, he leaves quick to stop an invasion by Carthage; too bad, Thebes and Thessaly refuse to support Athens against the Persians, and Crete remains neutral. Roman consul Fabius Vibulanus leads an army to break the siege by the Aequi of Ortona, routing them with a cavalry charge; too bad, the infantry refuses to pursue them, which doesn't stop him from returning to Rome claiming a V. Roman consuls: Caeso Fabius Vibulanus and Spurius Furius Fusus.




-480 The 75th Olympiad; Theagenes (Theogenes) of Thasos defeats Euthymus in boxing; later a statue of him is made by sculptor Glaucias of Aegina, which is scourged by a man who had a grudge against the athlete, after which it fell on him and killed him, causing the statue to be tried and convicted of murder and thrown in the sea, then retrieved after the Delphic Oracle declares that the country will be barren until it's back. Roman consuls: Marcus Fabius Vibulanus and Gnaeus Manlius Cincinnatus. In the spring Persian Zoroastrian king (since -486) Xerxes (Khshayarsha) (Ahasuerus) (Pers. "monarch") I the Great (-518 to -465) personally leads an invasion of Greece against the ?!*! pesky free-thinking polytheist Greek hooligan terrorists, assisted by bitter exiled Spartan king Demaratus, marching through Thrace and Macedonia with 200K-2M men, incl. units of Arabs on camels (Herodotus Bk. 7 says 5M plus camp followers), plus a fleet of 600-1,200 ships, cutting a canal through the 1 mi. wide Isthmus of Chalkidiki (Chlacidice) for them; on Aug. 9-11 (Aug. 16-18?) (Sept. 8-10?) (Aug. 20?) the Battle of Thermopylae sees a Greek allied army of 7K hoplites (incl. 300 Spartans, 400 Thebans, 700 Thespians, 900 Helots, and 1K Phocians) block the 50-yd.-wide (as wide as a wagon track in some places) coastal pass (6 mi. from the sea, which turns into a swamp then a rocky plain in modern times) of Thermopylae (Thermopilai) (Gr. "hot gates") in E Greece (between Mt. Oeta and the S shore of the Gulf of Maliakos) for three days, while a fleet of 270 Greek ships protects the Gulf of Artemisium; on Aug. 19 after a Greek traitor shows the Persians a bypass route which allows them to turn the Greek position, most of the Greeks retreat, except 300 Spartans and 700 Lesbians, er, Thespians (famous for their worship of Eros and the Muses) under Spartan Agiad king (since -490) Leonidas I (-520 to -480), who make a stand, and are all KIA in a legendary fashion after responding to the Persian demand to surrender their weapons with the immortal soundbyte "Molon labe" (come and take them); later Simonides of Keos turns this into the immortal soundbyte "Go tell the Spartans, stranger passing by, that here, obedient to their laws, we lie"; meanwhile half of the Persian fleet is lost to storms, and the naval Battle of Artemisium is a push, but the loss of Thermopylae causes the Greek navy to withdraw, and the Boeotians, Phocians, and Lorians to flop to the Persian side; Artemisia I of Caria commands five ships for the Persian side, followed by the Battle of Salamis, becoming the first known female admiral in history?: the Greek army retreats to the Peloponnese and builds a wall across the Isthmus of Corinth, and the Greek fleet moves to the Saronic Gulf between Athens and Salamis, causing the Athenians to flee and the Persians to occupy Attica and sack and destroy Athens, but on Sept. 23 the Greeks score a big V at the naval Battle of Salamis in the Straits of Salamis after the Persians make the mistake of attacking in a narrow strait which takes away their numerical advantage; Paros switches sides after the battle, and joins the Athenian League; Xerxes heads back to Persia with what remains of his navy and a third of his army, leaving Gen. Artabazus in charge of one-third in Thrace, and Gen. Mardonius in charge of the rest, who withdraws from Athens, burning everything in his path, and winters in Boeotia; the Acropolis in Athens is destroyed. Leonidas I dies, and his son Pleistarchus (d. -458) becomes Agiad king of Sparta. Theron of Acragas and Gelon and Hieron of Syracuse win the Battle of Himera in Sicily against Terillus of Himera, Anaxilas of Rhegium and the invading Carthaginians under Hamilcar; Syracuse begins expanding into the Tyrrhenian Sea along the Italian coast, stopping the Etruscans; the Carthaginian invasion of Sicily is stopped for 70 years, causing them to turn inland and take over the fertile Libyan hinterland. After a search for the most beautiful and suitable virgins in his kingdom, who are taken to the royal palace and beautified for the king's inspection under the eunuch Hegai, Xerxes I (Ahasuerus) in the 7th year of his reign marries the orphaned Jewess Hadassah (Heb. "myrtle") of the tribe of Benjamin, who changes her name to Esther of Susa (Shushan) to hide her Jewishness at her uncle Mordecai's direction (Esther 2:8-17), and passes info. from Mordecai to the king to save him from an assassination plot (Esther 2:20-22). Art: Centauromachy; Greek red-figure kylix. Births: Greek #1 sculptor-architect-painter Phidias (Pheidias) (d. -430) in Attica; son of Charmides. Greek tragedian Euripides (d. -406) in Salamis on Sept. 23 (on the day of the great battle against the Persians); son of Mnesarchides and Clito; one of the three great Attic tragic poets (Aeschylus (-525 to -456), Sophocles); uses long explanatory prologues, which are ridiculed by Aristophanes; also known for deus ex machina ("god from the machine"), and recognitions (changing legends to fit his plots); first to use natural dialogue and recognize the scientific intellectual rev. that is rejecting religion; in 1997 C.E. the cave on the island of Salamis where he works is discovered by archeologists. Greek Pythagorean philosopher Philolaus of Croton (d. -385) in Croton, Magna Grecia (S Italy). Deaths: Greek philosopher Xenophanes of Colophon (b. -570): claims to be writing to create "fame that will reach all of Greece and never die while the Greek kind of songs survives": "Ethiopians make their gods snub-nosed and black; the Thracians make theirs blue-eyed and red-haired... Mortals imagine that the gods are begotten, and that the gods wear clothes like their own and have language and form like the voice and form of mortals. But if oxen or lions had hands and could draw and do the work with their hands that men do, horses would have drawn the form of gods like horses and oxen gods like oxen and they would represent the bodies of the gods just like their own forms." Spartan hero king Leonidas I (b. -520) in Thermopylae, Greece (KIA).


-479 On Aug. 27 (morning) after the Persians invade Attica again, the Greeks ignore their differences and unite against the common Persian foe, fielding an army of 110K incl. 39K Spartans in the land Battle of Plataea; the Persians under gen. Mardonius are defeated by Greek forces under Spartan gen. Pausanias (-510 to -468), with a total loss of 250K; Mardonius is KIA and his body stolen and his camp plundered; meanwhile on Aug. 27 (afternoon) after the Samians and Chians convince king Leotychides II of Sparta to take his small Greek fleet guarding the Cyclades to surprise the Persians after the latter make the mistake of drawing their ships up on the beach at Mycale near Samos, the naval Battle of Mycale sees the Athenians under gen. Xanthippus (father of Pericles) destroy the Persian fleet and complete the Greek repulse of Persia; both battles take place near a temple of the Eleusinian Demeter (Herodotus, Bk. 9); too bad the town of Thespiae in SC Boeotia in EC Greece, E of Mt. Helicon (10 mi. WSW of Thebes and 10 mi. WNW of Plataea) (whose pop. fought at both Thermopylae and Plataea) is destroyed by the Persians; on Sept. 6 the Greeks siege Thebes, demand that they turn over Persian collaborators Timagenidas and Artaginus, and when they refuse, capture the town, abolish the oligarchy, and institute a democracy; the Ionian cities of Asia Minor along with several island cities (Chios, Lesbos, Samos) see their chance and revolt from the Persian melon-heads, forming an allied Greek fleet that sieges the Persian stronghold of Sestos in the Thracian Chersonesus at the mouth of the Aegospotami River; the Spartans return home in the fall, but the Athenians and Ionians stay and capture Sestos early next year; meanwhile a tsunami in Potidaea, Greece (first in recorded history) saves the town from a Persian invasion. After Caeso Fabius Vibulanus supports the plebeians, the otherwise illustrious patrician Fabian (Fabius) family becomes un-PC and is forced into exile to Veii, several mi. above Rome on the banks of the Cremera River. Roman consuls: Caeso Fabius Vibulanus and Titus Verginius Tricostus Rutilus. Deaths: Chinese sage Confucius (b. -551) in Lu; after his death his disciples compile the Li-Ki (Book of Rites) as the 5th king, and later the four shu; his first grandson becomes a great philosopher; by the year 2009 C.E. he has 2 million descendants (83 generations); "Do not do to others what you do not want done to yourself"; "Without recognizing the ordinances of Heaven it is impossible to be a superior man"; "At 50 I knew the will of heaven, at 60 I was ready to listen to the will of heaven"; "A true teacher is one who, keeping the past alive, is also able to understand the present."

-478 The Persian threat behind them, the Golden Age of Athens (endw -404) begins, during which Athens grows into an empire, reaching the height of wealth and powah and producing its greatest philosophers, historians, physicians, etc. On Feb. 17 a solar eclipse occurs as Xerxes is departing for his expedition against Greece, as mentioned by Herodotus Bk. 7. Gelon dies, and his brother Hieron (Hiero) I (d. -467) becomes tyrant of Syracuse, making it the most powerful state in Sicily, creating the first Greek secret police, relocating entire cities while conspiring against his last brother Polyzelos and patronizing culture, with Greek poets Pindar, Bacchylides, Aeschylus, Epicharmus, and Simonides of Keos (Ceos) (-556 to -468) (inventor of the idea of the Memory Palace, along with four letters of the Greek alphabet) moving to his court and churning out poetry, little of which survives to modern times - everybody committed it to memory and didn't need to write it down? An allied Greek fleet led by Pausanius sacks Cyprus and Byzantium; the Spartan ephors recall Pausanius and try him for treasonous negotiations with the Persians, but he is acquitted and sent back to Byzantium; meanwhile the Spartans send Dorcis to command the allied fleet, but the Ionians refuse to recognize the dorkus and make an alliance with the Athenians in order to finish expelling all remaining Persians from Greek territory, setting up the Delian League (Athenian maritime confederacy, incl. the cities of Rhodes, Camirus, Lindus, and Ialysus), and commissioning Gen. Aristides the Just (-530 to -468) to set up a HQ on the island of Delos to collect the tribute from each member; the gen. assembly (synhedrion) consists of one voting member per ally, but big kid on the block Athens soon manages to take it over incl. its treasury, putting half of Athens on the govt. payroll; Miletus joins the Delian League and recovers from its sacking. Roman consuls: Lucius Aemilius Mamercus and Gaius Servilius Ahala. Art: About this time the 1.8m bronze Charioteer of Delphi is sculpted to commemorate the V of tyrant Polyzalus of Geta in Sicily in the Pythian Games; discovered in 1896.
-477 In the spring Persian gen. Mardonius departs from Sparta to Thessaly, and on Aug. 1 a solar eclipse is observed in Sparta according to Herodotus, Bk. 7. On Sept. 8 emperor #4 (since -477) Itoku (b. -533) dies, and Koushou (Kosho) (-506 to -393) becomes Yamato emperor #5 of Japan (until -393) - what does he take? The Fabian gens, fighting as a unit on behalf of Rome against the Etruscan city of Veii are annihilated by the Veientes at the Battle of the Cremera River; only one member survives to keep the line going. Roman consuls: Gaius Horatius Pulvillus and Titus Menenius Lanatus. Deaths: Japanese Yamato emperor #4 (-510 to -477) Itoku (b. -533) on Sept. 8.
-476 The 76th Olympiad. Cimon, son of Miltiades is elected strategos of Athens, and leads an expedition to Thrace, capturing most of the Persian forts on the coast (incl. Eion) and expelling Pausanias from Byzantium. Leotychidas II (d. -469) is deposed and banished for taking a bribe, and Archidamus II (d. -427), son of Zeuxidamus (Cyniscos) becomes Eurypontid king of Sparta. Hieron I of Syracuse evacuates Catana to the Sicelian city of Inessa (Inessum), and renames it to Aitna (Aetna) (Gr. "I burn"), with capital at Hieron, repopulating it with 10K people from Syracuse and the Peloponnesus; in -465 Aetna begins manufacturing silver coins of unsurpassed workmanship. Zhou Jing Wang dies, and Zhou Yuan Wang (d. -468) becomes Dong Zhou king #14 of China. Roman consuls: Aulus Verginius Tricostus Rutilus and Spurius Servilius Structus. Deaths: Greek historian Hecataeus of Miletus (b. -550); leaves Travels Round the Earth (Periodos Ges) (Periegesis) (2 vols.), which contains his World Map, an improvement on Anaximander's; "I laugh when I see that many have designed maps of the earth, yet no one has been able to present the matter in an intelligent way. They draw an Ocean flowing round the earth, which they present as exactly circular, and they make Asia equal in size to Europe." (Herodotus); also leaves Genealogies (Histories); history of the Greek heroes, of which about 40 survive; "Hecataeus of Miletus thus speaks: I write what I deem true; for the stories of the Greeks are manifold and seem to me ridiculous." (opening line)

-475 11K-ft. Mount Etna on the E coast of Sicily begins erupting continuously, and both Pindar and Aeschylus describe it. Cimon captures Eion on the NE Greek mainland at the mouth of the Strymon River from the Persians after a long siege, then defeats the pirates on the island of Scyros; Athens sends cleruchs to both. The city of Carystus in Euboea is forced to join the Delian League. Gou Jian of the Yue kingdom surrounds the Wu Kingdom, causing the suicide of the Wu king Fu Cha. Haman the Agagite, a descendant of King Agag of the Jew-hating Amalekites works his way up to PM to Persian king Xerxes I (Ahasuerus), and in the 12th year of his reign talks him into ordering the annihilation of all the Jews in the 127 districts of the empire (Esther 3:7-13), but Esther (Heb. "hidden") ("I will surely hide [as-thir] my face on that day" - Deut. 31:18) braves instant death by approaching the king in his royal court without being summoned (Esther 4:1-17), and invites him to a banquet (Esther 5:1-8), where she reveals that she is a Jew, and gets Haman hung on the gallows that Haman had prepared for her uncle Mordecai (Esther 6:14-7:10), then gets the Jews saved (Esther chs. 8-9), and Mordecai raised to PM in Haman's place (Esther 10:1-3), causing Jews to begin celebrating the festival of Purim (Esther 9:20-32), hiding their faces in masks and dressing up in costumes; the reason that modern-day Jews won't use the name of God?; the Amalekites were the first nation to attack the Israelites after the Exodus, causing Jehovah to order their annihilation (Ex. 17:8-16), but Saul goofs and spares King Agag, causing Samuel to hack Agag to pieces (1 Sam. 5:2-33), but somehow some of his line survive, lusting for revenge, so Haman is just too good not to be true?; Mordecai then writes the Bible Book of Esther, which surprisingly never mentions God. Xerxes dies late in the year after 11 years of reign (counting co-reign), and his 16-y.-o. son Artaxerxes I Longimanus (d. -424) succeeds him as king of Persia, according to Thucydides, the historian Justin (III,1), and the Jehovah's Witnesses. Roman consuls: Publius Valerius Poplicola and Gaius Nautius Rutilus. Science: Iron finally comes into use in China. About this time Greek philosopher Parmenides of Elea (-515 to -445) founds (with Xenophanes) the Eleatic School of Philosophy, which considers the real to be motionless, and distinguishes between belief and knowledge, influencing Plato; he claims that the Moon shines by reflected light; "To think and to be is the same thing." Deaths: Greek philosopher Heraclitus (b. -535); leaves On Nature: "No man ever steps in the same river twice", "The path up and down are one and the same", and "All entities come to be in accordance with the Logos (word)."
-474 The Etruscan fleet is destroyed by the Greeks of Syracuse under tyrant Hieron I allied with tyrant Aristodemus of Cumae in the naval Battle of Cumae in S Italy, securing the independence of the Greeks in Italy; meanwhile the Gauls invade Italy from the N, and the Etruscans are crushed and disappear from history, with the region being absorbed by the Romans under the name Tuscia. Roman consuls: Lucius Furius Medullinus and Aulus Manlius Vulso.
-473 Roman consuls: Lucius Aemilius Mamercus and Vopiscus Julius Iullus.

-472 The 77th Olympiad. Roman consuls: Lucius Pinarius Mamercinus Rufus and Publius Furius Medullinus Fusus. Theron of Acragas dies, and the alliance with Syracuse dies with him; his mean son Thrasydaeus succeeds as tyrant of Acragas; he is defeated and deposed by Hieron I of Syracuse, and both Acragas and Himera set up democracies; Hieron I becomes big boss of Sicily, known for cruelty, but also a patron of poets and philosophers incl. Pandar and Aeschylus, and a champion athlete, winning the chariot race at Delphi in -470 and at Olympia in -468 - the original Godfather? Architecture: The Doric Temple of Zeus in Olympia, Greece is begun (finished -456), complete with a giant 40-ft.-tall 22-ft.wide seated Statue of Zeus at Olympia (finished -435) by sculptor Phidias (Pheidias) (-480 to -430), which is later copied in the Abraham Lincoln Memorial in the U.S.; it is paid for by funds from the Elean defeat of Pisa; the architect is Libon of Elis. Plays: Aeschylus (-525 to -456), The Persians (Persae).
-471 Praxiergus becomes archon in Athens this year and next. Argos, Tegea, and all of Arcadia except Mantinea form an anti-Spartan alliance (until -469). Cimon gets Themistocles ostracised, causing him to flee to Argos and conduct anti-Spartan activity in the Peloponnese, possibly causing Elis to unite; in the 20th cent. C.E. more than 500 ostraka bearing Themistocles' name are dug up in Athens near the Acropolis and Agora. Roman consuls: Appius Claudius Crassinus Inregillensis Sabinus, Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus. Births: Greek Athenian "History of The Peloponnesian War" historian ("Father of Scientific History") Thucydides (d. -400) (-460 to -411 or -395?) in Halimous (Alimos) (Kalamaki), SW Greece; son of Olorus; owns gold mines opposite Thasos in Thrace.
-470 Roman consuls: Lucius Valerius Potitus and Tiberius Aemilius Mamercus. Hanno ("merciful") the Navigator (Hanno II of Carthage) makes a celebrated voyage beyond the Pillars of Hercules down the African coast as far as Senegal, Sierra Leone, Cameroon, Gabon, or Nigeria, establishing a dye manufacturing plant in Mogador (Mogadore) in Morocco; he first describes gorillas, describing them as a savage hirsute people whose males couldn't be captured and the three females that were were so vicious that they had to kill them and transport their skins instead - once you go black you'll never go back? Alfalfa is introduced by the Persians to the Greeks - along with a macrobiotic diet? Births: Chinese philosopher Mo Tzu (Mozi) (Mo Di) (d. -391).
-469 Argos captures Tiryns and destroys once-great Mycenae, but is defeated with its allies at the Battle of Tegea and the Battle of Diplaea, and Sparta restores its hegemony. Roman consuls: Titus Numicius Priscus and Aulus Verginius Caeliomontanus. Births: Greek (Athenian) plug-ugly philosopher (gay?) Socrates (d. -399) in Athens; son of sculptor Sophroniscus and midwife Phaenarete; sculpts a statue of the Three Graces which stands at the entrance to the Acropolis until the 2nd cent. C.E.?; father of the Maieutic (Gr. "midwife") Method of dialectic, based on "Socratic irony", an ironical profession of ignorance ("As for me, all I know is that I know nothing"); his main teaching is that all vice is ignorance, therefore no man is willingly bad, he just has to be enlightened with knowledge to act virtuously (he never heard of the Bible?); "How many things there are that I do not need" he exclaims, wearing one garment all year long and going barefoot in the snow; his student Plato writes down his ideas which otherwise would be lost since Socrates believes that writing distorts ideas, and writes nothing of his own - he could never have been a cop? Greek (Athenian) friend of Socrates Crito of Alopece (d. ?). Deaths: Spartan king Leotychidas II in exile.

-468
The 78th Olympiad.
Under Spartan pressure, Athens condemns Themistocles to death in absentia and sends officers to arrest him,
causing him to flee for safety from Argos to Corcyra, Epirus, and Macedonia.
Sophocles (-496 to -406)
wins the Athenian prize for drama over rival Aeschylus - it's a brand new day?
Zhou Yuan Wang dies, and Zhou Zhen Ding Wang (d. -441)
becomes Dong Zhou king #15 of China.
Persian king Artaxerxes I authorizes
-467 Roman consuls: Tiberius Aemilius Mamercus and Quintus Fabius Vibulanus. Hieron I dies, and his brother Thrasybulus (Thrasyboulos) becomes ruler of Syracuse for 10 mo. The Greek colonies of Rhegium and Taras in S Italy are defeated by the native Iapyges, who establish a democracy in Taras and expel the bean-eschewing Pythagoreans from all Italian Greek cities. Naxos attempts to withdraw from the Delian League, causing Athens to defeat them and force them to raze their city walls and surrender their navy; Athens now rules the Delian League completely, with its courts assuming jurisdiction in all disputes, and punishing rebel allies by confiscating lands and establishing an Athenian colony (cleruchy), consisting of unemployed Athenians; one-sixtieth of the League's tribute is dedicated to the Temple of Athena. Plays: Aeschylus (-525 to -456), Seven Against Thebes - starring Ulysses Brynner?
-466 Cimon of Athens defeats the Persians in the double naval-land Battle of the Eurymedon River on the S coast of Asia Minor (-469?) - don't they ever give up? Thrasybulus is overthrown, and expelled and a democracy set up; Hieron's supporters are allowed to settle at Imessa, while the original inhabitants of Catana are allowed to return home; rash Tyndaridas unsuccessfully attempts to establish a tyranny using the standing army, causing Syracuse to introduce petalism, their own form of ostracism, with ballots made of petala (leaves) instead of ostraka (potsherds); a gen. movement against oligarchies and toward democracies in the West is now underway? Roman consuls: Quintus Servilius Priscus and Spurius Postumius Albinus Regillensis.

-465 Thasos attempts to leave the Delian League. Xerxes is assassinated by one of his courtiers (or his son), and his son Artaxerxes ("his reign is through truth") I Longimanus ("long hand" - right hand longer than the left) (-484 to -424) succeeds him as king of Persia (until -424) - long remaining is an art? A serious earthquake sparks the Messenian helots to revolt, starting the Third Messenian War (ends -461); the Spartans defeat them in battle, causing them to retreat to the stronghold of Mt. Ithome, causing Sparta to summon the Hellenic League, incl. Athens. After running a guerrilla war in the W Nile Delta since -411, Amyraeus of Sais (grandfather of the dude who takes over Egypt in -404) and Libyan chief Inarus (Inaros) (II) (grandson of Psametik III) begin an unsuccessful revolt against Persian satrap Artaxerxes II (ends -463). Roman consuls: Quintus Fabius Vibulanus and Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus.

-464 The 79th Olympiad. Messina calls the Carthiginians for aid against Syracuse, sowing the seeds of the First Punic War. Themistocles arrives in Persia, where he spends a year studying Persian so that he can have an audience with Artaxerxes I. About this year Ionian-born Greek philosopher Anaxagoras of Clazomenai (-510 to -428) settles in Athens, bringing philosophy to it, becoming the teacher of Socrates, and the first to explain that the Moon shines due to reflected sunlight, that it has mountains, and might be inhabited; he rejects Empedocles' 4-element theory in favor of an infinite number of unique particles making up all objects, and introduces the cosmological concept of Nous (mind); proves that the Sun is matter not a divinity, going on to attempt scientific explanations of natural phenomena incl. eclipses, meteors, rainbows, the Sun (a mass of blazing metal larger than the Peloponnese), heavenly bodies (masses of stone torn from Earth and ignited by rapid rotation, too far away to feel their heat), and the Earth (flat, floating on "strong air", whose disturbances cause earthquakes); too bad, in -450 he is charged with impiety and forced into exile in Lampsacus in Troad in NW Anatolia despite his student Pericles speaking in his defense. Roman consuls: Aulus Postumius Albinus Regillensis and Spurius Furius Medullinus Fusus.
-463 Cimon of Athens crushes Thasos, then returns to Athens, where he is charged by Ephialtes (d. -461), head of the popular party (dem. opposition) with taking a bribe from Alexander I Philhellene of Macedon, but is acquitted. Artaxerxes I meets with Themistocles, and grants him sanctuary in Persia with honors, making him gov. of Magnesia. A series of conflicts leaves the mercenaries of the deposed Sicilian tyrants in possession of Messana (formerly Zancle). Roman consuls: Publius Servilius Priscus and Lucius Aebutius Helva.
-462 Ephialtes is elected ruler of Athens. Cimon leads an Athenian force to the Peloponnesus to help the Spartans against the Messenian helot rebels, but Sparta mistrusts their intentions and sends them home, insulting Athens and ending their alliance. Megara gets into a border war with Corinth, and appeals to Sparta for aid, but is rebuffed, causing the Megarians to ally with Athens; Athens makes hay while the sun shines and soon makes alliances with Thessaly and Argos. Roman consuls: Lucius Lucretius Tricipitinus and Titus Veturius Geminus Cicurinus. Deaths: Greek (Athenian) statesman-gen. Themistocles (b. -514) in exile in Persia.


-461 The Messenian stronghold of Mt. Ithome falls, ending their revolt (begun -465). Cimon is blamed for the Spartan insult of -462 and is ostracized, and Ephialtes gets the assembly to deprive the Areopagus council of all powers except jurisdiction in homicide cases, and divides the 6K-member popular court (heliaea) into juries of 201 or more; Ephialtes is then murdered by political opponents, and pointy-headed Pericles (-495 to -429) replaces him as head of the popular party, and is elected ruler of Athens, becoming the peoples' choice for the next 30 years, with his non-Athenian wife Aspasia by his side, launching the Age of Pericles; Pericles appoints sculptor-architect Phidias (Pheidias) (-480 to -430). as his gen. supt. of public works for Athens, commissioning him to erect splendid statues and bldgs., incl. the Propylaea, Parthenon, Statue of Zeus, and gold-ivory Statue of Athena Parthenos. The Athenians use Delian League tribute money and begin constructing the 4-mi.-long Long Walls connecting Athens and its main port of Piraeus (finished -457); destroyed in -404. The Qin (Ch'in) Kingdom (westernmost) attacks the Xirong and Dali. Roman consuls: Publius Volumnius Amintinus Gallus and Spurius Sulpicius Camerinus Cornutus.

-460 The 80th Olympiad. The First Peloponnesian War (ends -445) begins between the Athenians and the Peloponnesians, who are pissed-off by pointy-headed Athens' alliance with Megara and Argos; meanwhile Athens sends a fleet of 200 ships to Egypt to aid its revolt against the Persians, defeating a Persian fleet on the Nile River and sieging the Persian army in the citadel of Memphis. Art: About this time the lifesize bronze Poseidon (Zeus) of Cape Artemision is sculpted, showing the Greek god hurling his trident or his thunderbolt at the east (Persians). Roman consuls: Publius Valerius Poplicola and Gaius Claudius Inregillensis Sabinus. Births: Greek Athenian Thirty Tyrants leader and tragedian Critias (d. -403) in Athens; son of Callaeschrus; uncle (great-uncle?) of Plato and friend of Socrates; appears in Plato's dialogues. Greek Sophist philosopher-mathematician Hippias of Elis (b. -399) in Athens. The original day-tripper and reason all doctors are hypocrites? Greek physician ("Father of Medicine") ("Asclypiad of Cos") Hippocrates (the Asclepiad) (d. -377) (d. -370?) on the island of Cos (Kos) in the Dodecanese (Gr. "twelve islands") in the SE Aegean Sea off the coast of Asia Minor; son of Heraclides and a mother who descends from Hercules?; student of Democritus and Gorgias; trained at the Asklepieion of Kos; after curing people in Thrace, Thessaly, Athens, Delos, and Cos, and refusing a delegation of Persians who attempt to bribe him away from Greece, he spends his last years in Larissa in Thessaly; his first biographer is 2nd cent. C.E. gynecologist Soranus of Ephesus - he had probable cause to be a hypocrite? Greek materialist (atomist) philosopher ("the Laughing Philosopher") ("the Mocker") ("Father of Modern Science") Democritus (Gr. "chosen of the people") of Abdera (d. -370) (b. -470?) in Abdera, Thrace; wealthy father leaves him great wealth, which he spends on world travels to Egypt, Asia, India, Ethiopia et al.; pupil of Leucippus; friend of Hippocrates; teacher of Protagoras.
-459 The Athenians defeat the combined forces of Corinth and Epidaurus at the Battle of Halieis, and win a V at the naval Battle of Cecryphaleia in the Saronic Gulf between Aegina and the coast of Epidaurus. The number of Roman tribunes is raised to 10. Roman consuls: Quintus Fabius Vibulanus and Lucius Cornelius Maluginensis Uritinus.

-458 Roman consuls: Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus Pennus (dictator) and Gaius Nautius Rutilus. Aegina joins the Peloponnesian alliance against Athens, but their combined fleet is defeated at the Battle of Aegina; Athenian cmdr. Leosthenes lands on the island of Aegina and sieges it, causing the Corinthians to invade Attica in an attempt to make them raise the seige, but are defeated by a reserve force (home guard) of old men and boys under Myronides, then a 2nd Corinthian force is surrounded and annihilated in the Megarid. Pleistarchus dies, and Pausanias' son Pleistoanax (d. -409) becomes Agiad king of Sparta (until -409). Roman aristocrat Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus (Lat. "curly hair") (-519 to -430) is called from his farm to become dictator of Rome and lead the army against the pesky Aequi from the E in the led by Cloelius Gracchus at the First Battle of Mount Algidus Pass in Latium (2nd in -431), then returns to the farm after the victory rather than seek power for himself; in 1783 C.E. a group of Continental Army officers in the U.S. forms the Society of the Cincinnati in his honor. Plays: Aeschylus (-525 to -456), Oresteia (trilogy) (only ancient Greek theater trilogy to survive to modern times); incl. Agamemnon, The Libation Bearers, and The Eumenides; how Trojan War CIC Agamemon, son of King Atreus of Mycenae has his daughter Iphigenia sacrified at Aulis to secure the favor of the gods for his voyage to kick Troy's butt after Prince Paris kidnaps Helen, wife of Menelaus; on his return his wife Clytemnestra and son Aegisthus murder him, and Clyt boasts that she would enjoy drinking a toast with her hubby's blood, causing his children Orestes and Electra to avenge him (Electra recognizes her long-lost brother Orestes by the fact that their footprints match); meanwhile witch Cassandra, daughter of Trojan king Priam spins her web in the wings?
-457 Aegina surrenders and turns its fleet over to the Athenians and joins the Delian League, causing the Spartans to enter the war and send an army across the Gulf of Corinth, restoring the Boeotian League under Theban hegemony; they defeat the Athenians at the Battle of Tanagra, but then screw up and return home, leaving the Athenians free to defeat the Boeotians at the Battle of Oenophyta, destroying the Boeotian League (until -447) and enrolling all Boeotian cities except Thebes in the Devilish, er, Delian League; Phocis (home of Delphi) (the Parnassus Mt. region W of Boeotia and N of the Gulf of Corinth) and Locris Opuntia (Opuntian Locrus, N of Phocis) also join; Pericles brings a Golden Age to Atheist-Free Athens, making the propertied hoplite zeugitai class eligible for the office of archon, and later the propertyless non-military thetes class; 25% of the 400K pop. are slaves; 20K slaves work in the silver mines of Laureion; Anaxagoras of Milegus becomes Pericles' teacher. The Long Walls (begun -461) connecting Athens and Piraeus are finished (demolished in -404). Roman consuls: Gaius Horatius Pulvillus and Quintus Minucius Esquilinus.
-456 The 81st Olympiad. A Persian force under Gen. Megabyzus defeats the Athenians at the citadel of Memphis in Egypt, causing them to retreat to the island of Prosopitis in the Nile Valley, then get sieged in turn. Roman consuls: Marcus Valerius Maximus Lactuca and Spurius Verginius Tricostus Caeliomontanus. Deaths: Greek playwright Aeschylus (b. -525); dies after an eagle drops a tortoise on his head?: "Everyone's quick to blame the alien."
-455 In Mar. Persian king (since -465) Artaxerxes I in his 10th year "sent forth the word to rebuild Jerusalem" (Dan. 9:20-27; Neh. 2:1-8), and authorizes the Jews to make their 2nd return to Jerusalem under high priest Ezra the Scribe, who gives a speech exhorting the people to follow the Torah Law and not intermarry with strange religions, and later writes the Book of Ezra; and First and Second Chronicles; this is a key year if you believe in Millennial Bible Chronology; the Jehovah's Witnesses consider this to be the 20th year of Artaxerxes I; the walls of Jerusalem are commissioned to be rebuilt, and the prophecy of the 70 weeks of years in Daniel 9:24-25 begins fulfillment, leading up to the baptism of Jesus in 29 C.E. (69 weeks of years = 483 years) (Luke 3:1-2;21-22, Dan. 9:1-4, Jer. 29:10), followed by his death in 33 C.E. (Mark 10:45) - and three more years for the Jews to accept him before they let gentiles in? Athenian gen. Tolmides talks the govt. into giving him a fleet with 4K soldiers to cruise around the Peloponnesus, and he raids the coast and burns the Spartan naval base at Gytheum (Gytheion) (Gytheio), in Laconia then recruits Achaea into the Delian League. Roman consuls: Titus Romilius Rocus Vaticanus and Gaius Veturius Cicurinus. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), Peliades (The Daughters of Pelias) (first play); fails to win the Dionysia.


-454 The Athenians holed-up on Prosipitis in Egypt are defeated after an 18-mo. siege, with all but a few killed or captured; a relief expedition of 50 ships is destroyed, causing the treasury of the Delian League to be moved from Delos to Athens; the revolt of the Egyptians, aided by the Athenians is put down by the Persians. Pericles becomes strategos (military commander) of Athens, and leads a force which lands in Sicyon and defeats the Sicyonians; he is then joined by the Achaean League, and unsuccessfully tries to take Oeniadea on the Corinthian Gulf, then returns to Athens. Alexander I dies, and Perdiccas (Perdikkas) (Perdica) II (d. -413) becomes king of Macedonia (-448 to -413)?. The Sicels under Ducetius (d. -440) defeat the mercenaries controlling Messana, and establish the federal capital of a Sicel state at Menaenum, which later moves to Palice. Greek epic poet Panyassis (Panyasis) of Halicarnassus is executed in the Persian Doric colony of Halicarnassus in SW Asia Minor by the tyrant Lygdamis II for conspiracy, causing his 20-something nephew Herodotus to flee into exile to the Greek island of Samos, under Athenian control. Roman consuls: Spurius Tarpeius Montanus Capitolinus and Qulus Aeternius Varus Fontinalis.
-453 The towns of Segesta and Halicyae in Sicily start a war with Selinus (Selinunte) in SW Sicily, then ask Athens for an alliance, which they grant. Roman consuls: Sextus Quinctilius and Publius Curiatius Fistus Trigeminus.
-452 The 82nd Olympiad. The Roman decemvirs move the month of February from the end of the year to the month after January; it stays 29 days long (truncated to 23, 24, or 27 days at certain intervals) until one of its days is transferred to the month of August in the Julian Calendar, making it the only month in which no full moon is a possibility (e.g., 1999, 2018 C.E.). Roman consuls: Titus Menenius Lanatus and Publius Sestius Capitolinus Vaticanus.
-451 Cimon returns to Athens after 3 years of exile, and negotiates a 5-year truce with Sparta; Argos loses Athenian protection and is forced to make a 30-year peace with Sparta. In Athens jurors (dicasts) in the popular courts are issued compensation, allowing poor citizens to serve. Pericles passes a law limiting the right to vote to those who can trace their Athenian lineage through both parents (repealed in -429, reenacted in -403). After a long struggle by the plebeians to have the patricians write the laws down so that they could not change them by pulling on the ropes and stuff, the Twelve Tables (originally 10 tables until -450) are written by the 10-patrician Decemviri Lat. "10 men") (Ten Consuls), appointed in place of the ordinary magistrates, giving Rome a basic law code, the Decemviral Code (Law of the Twelve Tables), becoming the basis of all Roman law, prescribeing a 2.5 ft. interval between houses, which breaks down during the rapid expansion after 390 B.C.E., causing the building of unsafe 5-6 story slum tenements (insulae) separated by 12-ft.-wide streets where wheeled traffic is forbidden during daylight. Roman consuls: Appius Claudius Crassus Inregillensis Sabinus and Titus Genucius Augurinus.




-450 A large Athenian force led by Cimon goes to Cyprus, and defeats the Persians at the Battle of Salamis in NE Cyprus, then sieges the city of Citium (until -449). Syracuse and Acragas defeat the Sicels under Ducetius at the Battle of Noae; Ducetius is banished to Corinth (until -446), causing the Sicel federation to fall apart. After plebeian agitation two more tables are added to the law tables, giving 12 total. About this time the Pythagoreans in S Italy are violently stamped out. Gashmu (Gashem) becomes king of Qedar in N Arabia (until -430); mentioned in Nehemiah 6:6? About this time Greek philosopher (Parmenides of Elea's pupil) Zeno of Elea (-495 to -435) from Elea (Velia), Italy formulates his mathematical Zeno's Paradoxes, becoming the first to use the reductio ad absurdum argument. About this time Greek Pythagorean philosopher Hippasus of Metapontum (b. -530) dies after discovering the irrational numbers; the gods drown him at sea for divulging his discovery? About this time the La Tene (Tčne) Culture (ends 1st cent B.C.E.) develops from the Iron Age Hallstatt Culture on the N side of Lake Neuchatel in Switzerland, as discovered in 1857 by Hansli Kopp, and spreads to E France, Switzerland, Austria, SW Germany, Czech., Slovakia, and Hungary, being influenced by Greek and Etruscan culture; meanwhile the Jastorf Culture (ends 1st cent. B.C.E.) develops in N Germany; about this time the first Celtic invasions of Italy and the British Isles begin, incl. the Boii, who migrate from N of the Alps and settle in the Po Valley - how many years to William Wallace? The Andalusian horse or Iberian warhorse is developed in Spain; it is interbred with the desert Barb horse of North Africa, creating a unique breed by the 15th cent. C.E., right before the Spanish discover the New World and bring them over. About this time Greek materialist (atomist) philosopher Leucippus (d. -420?) flourishes, becoming the teacher of Democritus of Abdera, uttering the immortal soundbytes: "Everything is driven by necessity", and "Nothing is created by coincidence (at random), rather there is reason and necessity for everything." Architecture: About this time the Temple of Apollo Epicurius is built in Bassae (Gr. "little vale in the rocks") in Arcadia in NE Messenia, Greece. Emain Macha (Gael. "Macha's Neck Brooch", "Macha's Twins") (Navan Fort) is built in County Armagh, Northern Ireland. Art: About this time the bronze sculpture The Discobulus (Gr. "discus thrower") is finished by Greek sculptor Myron of Eleutherae, becoming famous and spawning Roman copies, which is good since the original is lost; in 1781 the Discobulus Palombara, a 1st cent. C.E. copy is discovered on the Esquiline Hill in Rome; in 1937 it is acquired for 5M lire by Adolf Hitler, who displays it in the Glyptothek in Munich, Germany until the end of WWII, after which it is returned in 1948; in 1790 another copy is discovered in Hadrian's Villa. Births: Greek Athenian gen.-statesman Alcibiades (d. -404) in Athens; son of Cleinias; nephew of Pericles; last of the Alcmaeonidae; known for flip-flopping his political allegiance multiple times. Indian Nanda king #1 Mahapadma Nanda (d. -362). Deaths: Greek dramatist Epicharmus of Kos (b. -540). Greek philosopher Hippasus of Metapontum (b. -530); drowned at sea by the gods as punishment for divulging his discovery of irrational numbers?

-449 Cimon dies of disease during the siege of Citium, and the Athenians run low on supplies and return home. The Second Sacred War (ends -448) begins when Sparta takes Delphi from Phocis and makes it independent, causing Athens to intervene. The Delian League led by Athens and Persia sign the the Peace of Callias; the Persians give up the coast of Asia Minor in return for an Athenian promise not to invade Persian territory, ending the Persian Wars (begun -500) - I'm happy with who I am? The second Decemviri (Appius Claudius Crassus Inregillensis Sabinus, Marcus Cornelius Maluginensis, Marcus Sergius Esquilinus, Lucius Minucius Esquilinus Augurinus, Quintus Fabius Vibulanus, Quintus Poetelius Libo Visolus, Titus Antonius Merenda, Kaeso Duillius Longus, Spurius Oppius Cornicen, Manius Rabuleius) overreach themselves, attempt a patrician counter-rev., and have to be forcibly disbanded after another plebe march to the Sacred Mount; lead decemvir Appius Claudius commits suicide in prison; the new patrician consuls Lucius Valerius Potitus and Marcus Horatius Barbatus pass the Valerio-Horatian Laws, establishing the right of appeal of magisterial decisions (provocatio), and affirming the inviolability of tribunes and aediles. Roman consuls: Lucius Valerius Potitus and Marcus Horatius Barbatus. Architecture: The Doric Temple of Theseus (Theseion) (Theseum) on the NW end of the Agora in Athens on the Agoraios Kolonos Hill is begun (finished -415), later becoming the Temple of Hephaestus, and suviving to modern times. Deaths: Athenian gen.-statesman Cimon (b. -507).
-448 The 83rd Olympiad. Athens takes Delphi from the Spartans and restores it to the Phocians, ending the Second Sacred War (begun -449). The rebuilding of the Acropolis (destroyed in -480) begins (ends -433). Roman consuls: Spurius Hermenius Cortinesanus and Titus Verginius Tricostus Caeliomontanus. Births: Greek comedian ("Father of Comedy") ("Prince of Ancient Comedy") Aristophanes (d. -380) in Athens; son of poor man Philippos; comes from the same Kudathenaion deme as Cleon.



-447 Boeotia revolts from the Delian League, and the Athenians send an inadequate force, which is crushed at the First Battle of Coronea (2nd in -394); the Boeotian League is reestablished with a federal assembly based on proportional city rep., and oligarchies are set up in all Boeotian cities; Phocis and Locris also quit the Deleterious Delian League. Quaestors begin to be popularly elected in Rome rather than appointed by consuls. Herodotus settles in Athens after lengthy travels around Greece and Asia Minor, incl. Aegina, Cerigo, Crete, Cyprus, Delos, Paros, Rhodes, Samothrace, Thasos, Persia (Sardis to Susa), the W shore of the Black Sea to the mouth of the Dnieper River, Thrace, Scythia and Egypt, giving public readings of his in-progress historical works which wow the white is right Greek brain men, esp. poet Sophocles (-496 to -406), who becomes his friend. The Chu kingdom brings an end to the Cai. Roman consuls: Marcus Geganius Macerinus and Gaius Julius (Iullus). Architecture: I should have known better with a girl like you? The Doric Parthenon (Gr. "virgin's apartments") temple of Athena on the Acropolis in Athens is begun (finished in -438), designed by Greek architects Ictinus (Iktinos) and Callicrates (Kallicrates), with sculpture by Phidias (Pheidias) (-480 to -430), who begins the Athena Parthenos (Athena the Virgin) chryselephantine (gold-ivory) sculpture housed in the Parthenon; uses fine marble from Mt. Pentelikon (Pentelikón) in Attica NE of Athens; below the Acropolis are a number of sacred caverns, incl. the seat of the Cumaean Sibyl. Births: Roman gen.-statesman Marcus Furius Camillus (d. -365). Deaths: Greek painter Polygnotus (b. -490).

-446 Roman consuls: Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus and Agrippa Furius Fusus. In the fall Athens receives a free gift of grain from Egypt, and revises its citizenship rolls, removing 5K names. In Dec. after Athens finally recognizes the growing power of Sparta, the Athenians and Spartans conclude a Thirty Years' Peace, with Athens giving up political power over the states on the Greek mainland in exchange for Sparta recognizing the Athenian empire; Megara is returned to the Peloponnesian League; Troezen and Achaea become independent; Aegina becomes autonomous but also a tributary to Athens, with disputes to be settled by arbitration. Euboea revolts, and an Athenian army led by Pericles sets out to put it down, but is forced to return after a Peloponnesian invasion of the Megarid begins, driving out the Athenian garrison; the Peloponnesians reach Eleusus but withdraw after coming to terms with the Athenians, allowing Pericles to cross back to Euboea, put down the revolt, and establish a cleruchy in Histaiaea. Ducetius returns to Sicily. The Volscians and Aequians revolt in Rome, setting up a base in Corbio and launching raids into Roman territory, causing a Roman army led by consults Titus Quinctius Capitolinus and Furius Agrippa Fusus to attack them with three infantry and one cavalry divs.; when Agrippa's left wing begins faltering, Agrippa chucks the battle standards over the enemy lines, forcing his men to fight and win to recover their honor. Pericles founds an Athenian colony at Thourioi (Thurii) (Thurium) in Magna Grecia upriver from the former Sybaris in Magna Graecia (S Italy), and stocks it with colonists from all over Greece, incl. Greek historyscoper Herodotus, who spends the last 20 years of his life there reminiscing about his extensive travels and writing his history; Sicilian-born Greek eclectic vegetarian philosopher (last to write in verse) Empedocles of Acragas (Agrigentum) (-490 to -430) visits Pericles' new Athenian colony, going on to establish the four elements (roots) incl. Fire (Zeus), Air (Hera), Water (Nestis), and Earth (Aidoneus), which are brought into union and parted by the divine powers of Love and Strife; they started in an original pure state in a sphere; he claims that light streams out of our eyes and touches objects, and believes in the transmigration of the soul; he commits suicide by throwing himself into the active volcano at Mount Etna in Sicily to make his disciples believe that he is immortal.
-445 Roman consuls: Marcus Genucius Augurinus and Gaius (Agrippa) Curtius Philo. Early in the year the 30-year truce between Athens and Sparta is finalized; anti-Spartan forces attempt to get Pericles ostracized, but he turns the tables and gets opposition leader Thucydides, son of Melesias ostracized instead, and basks in his own sunlight while sponsoring great building and cultural programs equal to his high high crown. Syracuse and Acragas fight over the division of territory from the former Sicel federation, and Syracuse wins, becoming the top dog in sizzling Sicily. The Lex Canuleia (Lex de canubia patrum et plebis, permitting marriage (conubium), with children inheriting the father's status, proposed by pleb tribune Gaius Canuleius is passed in Rome despite fierce opposition by the patricians and their consuls until the plebs go on a military strike and refuse to defend Rome; a proposal to permit plebs to become consuls is prevented by Senator (consul in -460) Gaius Claudius Sabinus Regillensis, who gets a proposal substituted to allow the election of military tribunes with consular power, which is done next year; "So that, you see, if Miss Plebs wanted Mr. Patrician to marry her, and he said he couldn't, she probably replied: 'Oh yes, you can, you liar!' " ("Goodbye, Mr. Chips", 1939) This is the 20th year of Artaxerxes I, when the walls of Jerusalem are commissioned to be rebuilt. The Chu kingdom brings an end to the Ji. Births: Greek Cynic philosopher Antisthenes (d. -365) in Athens; disciple of Socrates; eacher of Diogenes of Sinope; founder of the Cynic School of philosophy, which rejects all conventional desires and believes in living a simple life free from possessions. Persian king (-404 to -358) Artaxerxes ("whose reign is through truth") II Mnemon ("exceptional memory") (d. -358); eldest son of Darius II; birth name Arsames. Deaths: Greek philosopher Parmenides of Elea (b. -515).
-444 The 84th Olympiad. In Sept. the walls of Jerusalem are completed. Two patrician censors are established in Rome, along with military tribunes (possibly plebeian) with consular power, who alternate irregularly with consuls until -363 or -367. Roman consuls: Aulus Sempronius Atratinus and Lucius Atilius Luscus and Titus Cloelius Siculus.
-443 Rhegium, Leontini, Catana, and Naxos ally with Athens as a counterweight to Syracuse. About this time Nehemiah (Heb. "Jehovah comforts") "founded a library and collected books about the kings and prophets, and the writings of David, and letters of kings about votive offerings" (Neh. 2:13-5), writing the Book of Nehemiah, which by -400 is combined with the Book of Ezra. Roman consuls: Marcus Geganius Macerinus and Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus.
-442 Roman consuls: Marcus Fabius Vibulanus and Postumius Aebutius Helva Cornicen. Deaths: Greek lyric poet Pindar (b. -518).

-441 Miletus and Samos go to war, and Miletus appeals for aid to the Athenians, who intervene and replace the oligarchy in Samos with a democracy. Zhou Zhen Ding Wang dies, and Zhou Ai Wang (d. -441) becomes Dong Zhou king #16 of China; he dies, and Zhou Si Wang (d. -440) becomes Dong Zhou king #17 of China. 40-y.-o. Euripides (-480 to -406) wins the Athenian (Attic) prize for drama after 14 years of trying; he wins again only 4x - that really rips me up to my knees? Roman consuls: Gaius Furius Pacilus Fusus and Manius Papirius Crassus.



-440 The 85th Olympiad. Roman consuls: Proculus Geganius Macerinus and Titus Menenius Lanatus. Samos revolts against Athens and throws out the forced democracy, causing the Athenians to siege it. Ducetius restores the Sicel federation in Sicily, then dies, and Syracuse breaks it up and destroys the capital of Palice. There is a famine in Rome; wealthy plebeian Spurius Maelius (d. -439) attempts to found a popular tyranny upon it, but is assassinated next year. Zhou Si Wang dies, and Zhou Kao Wang (d. -425) becomes Dong Zhou king #18 of China. Heracleitus declares that dreams are not supernatural journeys. About this time Abdera, Thrace-born Greek philosopher (Democritus' pupil) Protagoras of Abdera (-490 to -420) becomes the first Sophist (Gr. "sophistes" = one who does wisdom), with the immortal soundbyte: "Man is the measure of all things: of things which are, that they are, and of things which are not, that they are not"; their practice of charging young nobles for education in wisdom pisses-off Socrates, who calls them specious or deceptive. Architecture: The Temple of Poseidon in Cape Sounion S of Athens is completed to replace the one destroyed by Xerxes I's Persian troops in -480, replacing a Persian trireme captured at the Battle of Salamis. Art: About this year the bronze Doryphoros (Spear-Bearer) statue is cast by Greek sculptor Polykleitos (Polycletus) (Polycleitus) (Gk. "much renowned") of Sicyon/Argos, becoming one of the first examples of contrapposto (the figure rests most of his weight on one foot); the original is lost, and only marble copies survive. Nonfiction: Malachi (Heb. "my messenger"), the last book of the Hebrew scriptures is written about this time; Jehovah speaks no more for 400+ years, but when Jeezey comes along, his fulfillment of all them oldy moldy prophecies makes for quite a splash among the gentiles, if not the Jews? Plays: Sophocles (-496 to -406), Ichneutae (Searching Satyrs); satyr play; Antigone; too bad he didn't write one for her sister Ismene? Births: Athenian orator-statesman Andocides (Andokides) (d. -390).
-439 Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus becomes dictator of Rome for a 2nd time (first in -458). Athens takes Samos, razes its walls and confiscates its fleet, leaving Chios and Lesbos as its only allies in the Delian League who can contribute ships. Roman consuls: Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus (dictator) and Agrippa Menenius Lanatus and Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus.

-438 Fidenae (9 mi. N of Rome) revolts, killing the Roman ambassador and reverting to their Hatfield-McCoy-style hatred of Romans (until -426). The Parthenon (begun -447) on the Athenian Acropolis, dedicated to Athena Parthenos is completed; the statue of Athena by Phidias (Pheidias) (-480 to -430) is dedicated; there are few straight lines, all the steps are of different sizes, and the distance between each of the Doric (baseless) columns in the peristyle varies, all to give an illusion of strict balance. Spartacus of Thrace overthrows the Archaenactidae Dynasty (founded -480) and founds the Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus (Bosporan Kingdom) (ends 370 C.E.) in E Crimea and the Taman Peninsula on the shores of the Kerch Strait, ruled by the Spartocid Dynasty (ends -110). Roman consuls: Mamertus Aemilius and Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus and Lucius Julius Iullus. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), Alcestis; she sacrifies her life for her hubby King Admetus of Thessaly, then is rescued from Hades by Hercules.

-437 The Athenians found the city of Amphipolis in E Thrace (home of the ancient Edoni people), controlling the mines of Mt. Pangaeus. Pericles leads an expedition into the Euxine and establishes good relations with Panticapaeum (modern-day Kerch) on Mount Mithridates in the Tauric Chersonese (founded -600), a source of grain. Athenian strategos Phormio makes an alliance with the Acarnanians in the Gulf of Corinth. Athenians settle cities in the Pontus. Roman consuls: Mamertus Aemilius Mamercinus (dictator) and Marcus Geganius Macerinus and Lucius Sergius Fidenas. Architecture: The Propylaea (Propylea) (Propylaia) (Gr. "pro" + "pyle" = before the gates) monumental gateway to the Acropolis is begun by Mnesicles (Mnesikles), who quits in -432 before it is finished.

-436 The 86th Olympiad. About this time Greek sculptor Agoracritus (Agorakritos) (born on Paros) becomes the favorite pupil of Phidias, their work later being confused; he sculpts the colossal Nemesis of Rhamnus, starting with a statue of Aphrodite which loses a contest with rival Alcamenes. Roman consuls: Lucius Papirius Crassus and Marcus Cornelius Maluginensis.
-435 The Corinthian-Corcyrean War (ends -432) begins when Corcyra (Corfu) in NW Greece objects to Corinthian interference with their joint colony of Epidamnos (Epidamnus) (founded -627) (later Dyrrachium) (modern-day Durazzo or Durrës or Durres on the Albanian coast 30km W of Tirana), and calls on Athens for help after an initial V against the more powerful state only makes them madder. The Etruscan town of Fidenae on the Via Salaria 5 mi. N of Rome is finally conquered by the Romans after ages of ill will and feuding. Roman consuls: Quintus Servilius Priscus Structus Fidenas (dictator) and Gaius Julius and Lucius Verginius Tricostus. Art: The Statue of Zeus at Elis is completed by the sculptor Phidias (Pheidias) (-480 to -430). Births: Greek Socratic philosopher Eucleides (Euclides) (Euclid) of Megara (d. -365) in Megara; pupil of Socrates; founder of the Megarian School of Philosophy in Megara in N Isthmus of Corinth opposite Salamis Island. Greek hedonist philosopher Aristiuppus of Cyrene (d. -356) in Cyrene, Libya; founder of the Cyrenaic school of philosophy, which considers individual sensual pleasure the greatest good - hard or gentle strokes? Deaths: Greek philosopher Zeno of Elea (b. -495).
-434 Roman consuls: Gaius Julius Iullus and Lucius (Proculus) Verginius Tricostus.
-433 Pericles concludes a defensive alliance with Corcyra, and renews alliances with Rhegium and Leontini in the W; meanwhile Corinth, Megara, and Aegina appeal to Sparta to take arms against Athens. Roman consuls: Mamertus Aemilius Mamercinus (dictator) and Marcus Fabius Vibulanus and Marcus Folius Flaccinator and Lucius Sergius Fidenas.
-432 The 87th Olympiad. In the spring the Corinthian colony (a subject of Athens) of Potidaea in the Chalcidice (founded in -600) revolts against Athens, backed by the Peloponnesian League, causing Athens to pass the Megarian Decree excluding Megarian merchants from Athenian harbors and markets; Megara, Corinth and Aegina pressure Sparta, and the ephor Sthenelaidas convinces the assembly over King Archidamus II' opposition to declare the Thirty Years' Peace broken, and declare war against Athens, causing fruitless negotiations with Athens all winter, and beginning the First Peloponnesian War between (ends -404); barefoot philosopher Socrates serves as an infantryman with conspicuous bravery at Potidaea, and saves Pericles' nephew Alcibiades. On June 27 the summer solstice (New Year) is observed in Athens by Meton of Athens, who on July 13 introduces the Metonic Cycle for intercalation, based on the observed period of 19 tropical years being equal to 235 synodic months (6,940 days), which becomes the basis for the 19-year cycle of the Hebrew calendar. Roman consuls: Lucius Pinarius Mamercinus and Lucius Furius Medullinus and Spurius Postumius Albinus (Regellensis).




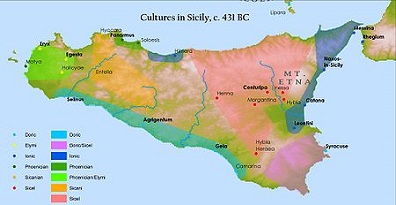
-431 Roman consuls: Titus Quinctius Pennus Cincinnatus and Gaius (Gnaeus) Julius Mento. In Apr. B.C.E. a fifth column of 300 Thebans unsuccessfully attacks Plataea, the only pro-Athenian city in Boeotia, with the Plataeans taking 180 POWs and putting them to death, after which Athens supports Plataea and Sparta supports Thebes, enlisting the help of the Greek cities in Sicily and Italy, while both sides appeal to Persia for help in vain; making use of accusing the Athenians of crowing about saving Greece at the Naval Battle of Salamis while increasingly imposing an extortion racket, Archidamus II of Sparta gains support by calling for the liberation of the Hellenes from Athenian despotism, launching the Second Pelopponesian War (ends -404); the Spartan war strategy is to burn the fields of Attica to lure the Athenians into a land battle, while Pericles' strategy is to sit it out in Athens, protected from starvation by the Long Walls connecting them with the port of Piraeus, and wear out the Spartans with naval raids, replacing the pop. of Aegina Island with Athenians; after 30 years of Pericles, famous adm.-gen. Phormio is elected ruler of Athens when an expedition under Pericles' command fails, and Cleon seizes on it to prosecute him, and Plutarch accuses Pericles of starting the war to revive his fading popularity, causing Pericles to be suspended from command and fined; Spartan gen. Brasidas (d. -422) first distinguishes himself by courage shown relieving the seaport town of Methoni (Methone) in Pieria from a hostile attack - his ass is made of brass? Greek Athenian gen. Thucydides begins writing "History of the Peloponnesian War"; on Aug. 3 "At last all was ready, and they were on the point of sailing away, when an eclipse of the Moon, which was then at the full, took place" (total solar eclipse) (Thucydides); he records another eclipse seven years later on Mar. 21, -424, and a 3rd eclipse 11 years after that on Aug. 27, -413; in 1907 C.E. Russian mathematician Nikolai Alexandrovich Morozov (1854-1946) claims that the first eclipse occurred on Aug. 2, 1133 C.E., and Russian mathematician Anatoly Fomenko (1945-) uses this to back his claim that all of ancient chronology is moose hockey, and that Jesus Christ was born in the 12th cent. C.E. - TLW needs to create an All New Revised Historyscope, yikes, he hopes not? On June 18 after Rome declares war on the pesky Aequi from the E and Volsci from the W, and the consuls can't agree on a dictator, and consul Titus Quinctius Cincinnatus Pennus nominates his father-in-law Aulus Postumius Tubertus, the Romans decisively defeat them at the Second Battle of Algidus Pass (first in -458), becoming the last major battle with the Aequi, after which Postumius receives a triumph; too bad, Postumius' son is so eager to attack that he abandons his post, causing daddy to have him put to death - that was my favorite dog? The Chu Kingdom in China eliminates the Lu Kingdom. Empedocles propounds the theory that the Universe consists of four elements: earth, fire, air, and water, which are ruled by the forces of attraction (love) and repulsion (strife), and that human body has four humors (humours): blood, bile, black bile and phlegm - no good humor? Architecture: The first Temple of Apollo is dedicated in Rome in the Campus Martius, the parade ground between the N bend of the Tiber Riber and the Quirinal and Capitoline hills, where city development has been overflowing into. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), Medea, enters it in the festival of Dionysos, and comes in last (3rd); first place goes to Euphorion; one of his few plays with a steadily-developing plot. Births: Greek "Anabasis" lover-fighter-scholar-historian ("the Attic Muse") Xenophon (Gr. "foreign voice") of Athens (d. -354) in Athens; student of Socrates.
-430 Plague breaks out in Rome. Pericles is reelected ruler of Athens; the first known visitation of plague (smallpox?) (scarlet fever?) breaks out in overcrowded Athens after entering through the port of Piraeus, killing 25% of the pop., spreading to the army besieging Potidaea; Pericles' eldest son dies, followed by his sister and another son; in Aug. Pericles sends a peace mission to Sparta without success; he gives the Funeral Oration for all the Athenians killed during the first year of the Peloponnesian War, becoming a classic defense of Greek democratic ideals, incl. the value of free discussion as a condition for a wise action (the most eloquent oration in human history?); late in the year Potidaea falls to Athens. Young Tharrhypas (d. -392) (ancestor of Alexander III the Great) becomes king of Epirus, introducing Athenian culture to the Molossians. Qaynu becomes king of Qedar in N Arabia (until -410). Abkarib I (d. -415) founds the kingdom of Main in S Arabia (ends -55). Roman consuls: Lucius Papirius Crassus and Lucius Julius Iullus. About this time Greek painter Agatharchus from Samos invents scene painting, and is the first to use perspective on a large scale? About this time Sophron of Syracuse composes mimes in the Doric dialect, which Plato later introduces to Athens. Science: About this time Greek sophist Hippias of Elis discovers the mathematical Quadratix of Hippias (Dinostratus), used for angle trisection. About this time Greek Pythagorean philosopher Philolaus of Croton (-480 to -385) of Croton in Magna Grecia (S Italy) gets the credit for originating the theory that the Earth is not the center of the Universe; he claims that humans have immortal souls which are imprisoned as a punishment for bad behavior during life. Births: Sicilian tyrant Dionysius the Elder (d. -367); of humble birth, works as a govt. clerk until his coup of -405. Deaths: Roman gen. Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus (b. -519). Greek sculptor Phidias (b. -480); dies in prison for embezzlement of gold appropriated for a statue of Athena?; dies in banishment?; dies in prison for impiety for putting his and Pericles' portraits on Athena's shield?
-429 In Sept. after one-third to two-thirds of the pop. of Athens dies of the plague while orgying free at last from fear of the gods, Pericles (b. -495) dies of the plague., and Cleon (Gr. "renowned") (-475 to -422) is elected ruler of Athens; Socrates shows more bravery at Potidaea. In the fall Phormio wins naval battles against two Peloponnesians fleets at the Battle of Chalcis and the Battle of Naupactus. Roman consuls: Hostus Lucretius Tricipitinus and Lucius Sergius Fidenas. Deaths: Athenian statesman Pericles (b. -495) in Sept. in Athens (plague): "Just because you do not take an interest in politics doesn't mean politics won't take an interest in you."
-428 The 88th Olympiad. Roman consuls: Aulus Cornelius Cossus and Titus Quinctius Cincinnatus Pennus. In June Mytilene, chief city of Lesbos revolts against Athens. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), Hippolytus; debuts in the Dionysia; Hippolytus, son of the Amazon Hippolyta after her rape by King Theseus of Athens agonizes over the conflict between asceticism and sexual desire, swearing chastity and honoring Artemis instead of Aphrodite, who gets even by inspiring his stepmother Phaedra to fall in love with him, causing her to starve herself to die with honor. Deaths: Greek philosopher Anaxagoras of Clazomenae (b. -510) in Lampasacus (in exile): "Appearances are a glimpse of the unseen"; "The seed of everything is in everything else"; "The descent to Hades is the same from every place."

-427 Roman consuls: Gaius Servilius Structus Ahala and Lucius Papirius Mugillanus. In July after Spartan adm. Alcidas helps the Lesbos rebels but flees at the sight of Athenian warships, Lesbos goes down, er, falls. Archidamus II dies, and his son Agis II (d. -401) becomes Eurypontid king #18 of Sparta; the Spartans score their first V with the capture of Plataea. A war breaks out in Sicily (ends -424), with Syracuse, Gela, Messana, Himera, Lipara and Locri vs. Naxos, Catana, Leontini, Rhegium, Camarina and the Sicels; Gorgias of Leontini goes to Athens to appeal for aid, which is granted. Nonfiction: The Hindu astronomical Siddhantas (Sansk. "Doctrine/Tradition") begin to be compiled, containing the Hindu numerals and zero. Plays: New Athenian playwright Aristophanes (-448 to -380) takes 2nd place in the Theater of Dionysus with his first play The Banqueters. Births: Greek flatulent philosopher ("Father of Western Philosophy") (founder of the Academy in Athens) Plato (Gr. "broad") (real name Aristocles) (d. -347) (b. -428?) (d. -348?) (AKA Eflatun, meaning spring of water or knowledge) on May 21 in Athens; student of Socrates; son of wealthy aristocrats Ariston and Perictione; relative of politician Critias; first to propose that the brain is the seat of mental processes, and to propose the Great Chain of Being.
-426 In June after Athenian gen. Demosthenes (d. -413) and the demagogue Cleon revitalize Athen's military, and rich merchant Nicias (d. -413) turns gen. and leads a middle class revolt against them, Demosthenes raises an army in Acarnania while Nicias invades Thebes by way of Tanagra (suggesting a great Star Trek episode idea?); Demosthenes is ambushed by Aetolian natives and escapes to Naupactus, defending it from Spartans sent from Delphi under Eyrylochus; Demosthenes then defeats the Spartans at Olpae and Idomene, returning in triumph to Athens; Messina (Messana), lost since -493 is retaken by the Ionians under Nicias. The democratic faction of Corfu massacres Spartan supporters and secures the island for Athens. The Romans conquer pesky Fidenae again, and sell the pop. into slavery, turning it into a small village with a large amphitheater by ?. Roman consuls: Mamertus Aemilius Mamercinus (dictator) and Titus Quinctius Poenus Cincinnatus and Gaius Furius Pacilus Fusus and Marcus Postumius Albinus Regillensis and Aulus Cornelius Cossus.

-425 Roman consuls: Aulus Sempronius Atratinus and Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus and Lucius Furius Medullinus and Lucius Horatius Barbatus. Demosthenes captures Pylos (modern-day Navarino) on the W coast of the Peloponnesus on the Coryphasium promontory at the N entrance to Pylos Bay (home of legendary heroes Neleus and his son Nestor), then after reinforcements under Cleon arrive, he defeats the Spartans at the naval Battle of Pylos (Navarino Bay) in Messenia, then sphincters, er, cuts off a stranded Spartan force on the neighboring island of Sphacteria (modern-day Sphagia) at the Battle of Sphacteria; 120 Spartan hostages are held to prevent another invasion of Attica, and the Spartans sue for peace, but Cleon gets the assembly to reject the overtures despite opposition by Nicias. Zhou Kao Wang dies, and Zhou Wei Li Wang (d. -401) becomes Dong Zhou king #19 of China. Plays: Aristophanes (-448 to -380), The Achamians; a plea to end the war. Euripides (-480 to -406), Hecuba. Deaths: Greek historian Herodotus (b. -484) in Thurii (Thurium), Magna Graecia (S Italy) (Pella, Macedon?); leaves the first-ever The Histories (History) (Gr. "investigations") (earliest example of Greek/Euro prose to survive to modern times); "I, Herodotus of Halicarnassus am here setting forth my history, that time may not draw the color from what man has brought into being, nor those great and wonderful deeds, manifested by both Greeks and barbarians fail of their report, and, together with all this, the reason why they fought one another" (first line); "The only good is knowledge, the only evil is ignorance"; "Very few things happen at the right time, and the rest do not happen at all. The conscientious historian will correct these defects"; "Of old the Hellenic race was marked off from the barbarian as more keen-witted and more free from nonsense."

-424 The 89th Olympiad. Roman consuls: (Appius) Claudius Crassus and Spurius Natius Rutilus and Lucius Sergius Fidenas and Sextus Julius Iullus. On Mar. 21 there is a solar eclipse visible in Greece? In the summer aristocrat Hermocrates of Syracuse persuades the warring cities of Sicily to make peace at the Congress of Gela, ending the Sicilian War (begun -427). The Athenians under Nicias capture the island of Cythera off the coast of Laconia, then send an army to aid a democratic revolt in Megara, but Spartan Gen. Brasidas outmaneuvers them and relieves the city, and Megara remains a Peloponnesian ally; Brasidias then leads a small force overland to Thrace and whips up a revolt of Athenian allies there and in Macedonia, displaying great diplomacy and eloquence, then marches to Chalcidice, offering protection to cities rebelling against Athens, causing the Athenians to invade Boeotia, but Theban gen. Pagondas of Thebes crushes them at the watershed Battle of Delium (Delion), where Socrates again shows his bravery; Amphipolis in Thrace surrenders to Brasidas, and a force from the N under Thucydides arrives too late; Cleon exiles Thucydides for 20 years; the battle inspires a tragedy by Euripedes and through survivor Socrates alters the direction of Western philosophy? Persian king (since -465) Artaxerxes I (b. -484) dies, and is succeeded by his son Xerxes II (d. -424), who reigns either 1 year or 2 mo., and is succeeded by his brother Sogdianus (d. -423), who rules 7 mo. Plays: Aristophanes (-448 to -380), The Knights; play #4; satire of populist hawk Cleon during the Peloponnesian War; carries out his promise in "The Acharians" to get revenge on Cleon for prosecuting him for slandering the polis, winning first prize at the Lenaia Festival. Euripides (-480 to -406), Andromache; Hecuba. Sophocles (-496 to -406), Oedipus Rex; King Oedipus ("swollen foot") of Thebes and sister-wife Jocasta; sisters-daughters Antigone and Ismene, sons-brothers Polynices and Eteocles, brother-in-law Creon, blind soothsayer Tiresias; the son of King Polybos from Corinth solves the riddle of the sphinx, kills Laios and marries Jocasta, becoming king of Thebes; after his daddy dies and he becomes king of Corinth too, he finds out that Laios was his real daddy and Jocasta his sister, and she freaks and commits hari-kari, while he freaks, gouges out his own eyes and goes into exile; Aristotle later calls it the best drama of all time. Deaths: Persian king #5 (-465 to -424) Artaxerxes I Longimanus (b. -484).

-423 Roman consuls: Gaius Sempronius Atratinus and Quintus Fabius Vibulanus. In the spring Sogdianus is slain by Artaxerxes I's bastard son Darius II Ochus (Nothus) (the Bastard) (d. -404), whose mother was a Babylonian concubine; his wife and half-sister Parysatis manipulating him, he sides with Sparta in the Peloponnesian War to regain some Greek cities in Asia Minor; is he the Darius referred to in Nehemiah 12:22? In Apr. the 1-year Truce of Laches is concluded between Athens and Sparta, but Spartan Gen. Brasidas ignores it and takes Scione and Mende in Thrace, causing the Athenians to break off peace neogiations and Nicias to retake Mende. Date of the destruction of the First Temple of Jerusalem by the Babylonians according to some Jewish historians. Plays: Aristophanes (-448 to -380), The Acharnians (satirizes Euripides); The Clouds; portrays Socrates as running a "thinking shop" where he teaches young men to make bad reasoning appear good, which is later used against him at his trial. Euripides (-480 to -406), The Cyclops; based on Homer's "The Odyssey" Bk. 9; the only complete satyr play to survive to modern times. Sophocles (-496 to -406), The Trachiniae.
-422 Roman consuls: Lucius Manlius Capitolinus and Quintus Antonius Merenda and Lucius Papirius Mugillanus. Spartan Gen. Brasidas leads a handful of helots and mercenaries against the Athenian army under Cleon at the Battle of Amphipolis and captures the city, although both generals are KIA; the main obstacles to peace are now dead; Socrates shows bravery yet again before returning to Athens to talk youths' heads off?; Thucydides later harps on Brasidas' eloquence, so unusual for a Spartan, and Plato compares him to Achilles. Nicias is elected ruler of Athens. Plays: Aristophanes (-448 to -380), The Wasps.

-421 In Mar. the Peace of Nicias between Athens and Sparta is signed, pledging to defend each other for 50 years; too bad it doesn't work out. The number of Roman quaestors is raised to four, and the position is opened to plebeians. Architecture: The Ionian-style Erechtheum (Erechtheion), dedicated to the god Erechtheus on the N side of the Acropolis of Athens is begun (finished -405), featuring the Caryatid Porch (Porch of the Maidens), becoming the first known portal framed in stone instead of wood; it was supposed to have a W wing, but rival priests claim turf rights and stop it. Roman consuls: Gnaeus (Numerius) Fabius Vibulanus and Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus. Plays: Aristophanes (-448 to -380), The Peace.




-420 The 90th Olympiad. Roman consuls: Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus and Lucius Furius Medullinus and Marcus Manlius Vulso and Aqulus Sempronius Aratinus. In July after Boeotia refuses to accept the Peace of Nicias and leaves the Peloponnesian League, along with Elis, Mantinea, Corinth, and Argos, they form the Quadruple Alliance, which Corinth soon leaves; in July Alcibiades engineers an anti-Spartan alliance with the remaining three members of the Quadruple Alliance (Argos, Mantinea, Elis), and they all go to war with Sparta. Pericles' has-it-all (looks, brains, charm, family) nephew Alcibiades (-450 to -404) is elected ruler of Athens. Cumae is conquered by the Oscans using the gastraphetes (Gr. "belly bow"), a winched crossbow machine capable of throwing two arrows at the same time, invented by Pythagorean engineer Zopyrus of Tarentum; they go on to eradicate its Greek identity - easy cumae, easy osco? Architecture: About this time an Etruscan tomb is built near modern-day Tarquinia (discovered 1985) that shows the earliest images of hell and redemption, incl. the Blue Demon, showing a shocking rev. in 200-y.-o. Etruscan thought, probably caused by the threat of extinction by the Romans, creating a new theology that promises bliss to the worthy warriors and torment to the unworthy ones? Art: About this time Thracian sculptor Paionios (Paeonius) of Mende in Chalkidiki sculpts the Nike (Gr. "Winged Victory") of Paeonius; it is excavated in 1875 C.E. Science: About this time Abdera, Thrace-born Greek philosopher Democritus of Abdera (-460 to -370) pioneers the concept of atomic structure by contrasting the Intellect and the Senses: "Apparently there is color, apparently sweetness, apparently bitterness, actually there are only atoms and the void"; "Poor Intellect, do you hope to defeat us, while from us you borrow your evidence? Your victory is in fact your defeat." Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), The Suppliant Women (The Suppliants). Deaths: Greek philosopher (first humanist?) Protagoras of Abdera (b. -420): "Man is the measure of all things: of things which are, that they are, and of things which are not, that they are not."
-419 Roman consuls: Agrippa Menenius Lanatus and Publius Lucretius Tricipitinus and Spurius Nautius Rutilus and Gaius Servilius Axilla. The Argive War (ends -418) begins when Alcibiades puts the Argives up to attacking Epidaurus, and Lacedaemon's whole army marches toward the frontier city of Leuctra as a diversion. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), Andromache. Sophocles (-496 to -406), Electra.
-418 In summer while the Argives are attacking the Epidaurians, the Lacedaemonians and some allies under the command of Agis invade Argolis, but are intercepted and stopped by Agis II of Sparta, and gets their gens. Thrasyllus and Alciphron to sign a 4-mo. truce; too bad, as Agis II returns the Argives capture Orchomenus, and the Spartans get pissed-off that he didn't capture Argos, and appoint a 10-man council to decide whether he can lead a new attack, which they soon do after receiving a plea from the Spartans in Tegea; in Aug. after Athenian gen. Alcibiades leads a Quadruple Alliance force to help Argos, they are all decisively beaten by the Spartans under Agis II at the First Battle of Mantinea, ending the Argive War (begun -419) and restoring Spartan hegemony; the Athenians are turned back at Chalcidice. Roman consuls: Quintus Servilius Priscus Fidenas (dictator) and Lucius Sergius Fidenas and Marcus Papirius Mugillanus and Gaius Servilius Axilla.
-417 Athenian demagogue Hyperbolus (d. -411) is ostracized after the vote was supposed to decide between Nicias and Alcibiades, but they combine forces against him, causing the whole system to be junked - genius? Roman consuls: Titus Lucretius Tricipitinus Agrippa Menenius Lanatus and Spurius Veturius Crassus Cicurinus and Gaius Servilius Axilla.
-416 The 91st Olympiad. Selinus of Sicily calls for Athenian assistance in his war against Segesa, causing Alcibiades to propose an expedition to crush Sicily, Syracuse, and Carthage, which the assembly approves over Nicias' objections, with the soundbyte: "We shall not trouble you with specious pretenses... Since you know as well as we do that right, as the world goes, is only in question between equals in power, while the strong do what they can and the weak suffer what they must", after which the Athenians massacre the male pop. of Milos (Melos) and sell their wives and children into slavery for daring to remain neutral. Roman consuls: Aulus Sempronius Atratinus and Marcus Papirius Mugillanus and Quintus Fabius Vibulanus. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), Heracles.
-415 Roman consuls: Publius Cornelius Cossus and Gaius Valerius Potitus Volusus and Numerius (Marcus) Fabius Vibulanus and Quintus Quinctius Cincinnatus. The Sicilian Expedition led by Alcibiades, Nicias, and Lamachus arrives in Sicily, but Alcibiades is accused of mutilating the Herms (sacred pillars) a nd profaning the Eleusinian mysteries, and ordered to return to Athens, where he doesn't like the justice he's getting and ends up going over to the Spartans; Athens attacks Sicily, and wins a V in Syracuse (defended by Hermocrates) in Nov.; Athenian orator Andocides (-440 to -390) is implicated in the Herms affair and turns informer to save his life, accepting exile instead (until -403). The Carthaginians recapture Messina from Athens. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), The Trojan Women.
-414 Roman consuls: Gnaeus Cornelius Cossus and Lucius Valerius Potitus and Quintus Fabius Vibulanus and Publius Postumius Albinus Regillensis. Athenian efforts to conquer Syracuse bog down when a small Spartan force under Gen. Gylippus comes to their aid and takes the heights of Epipolae, preventing an Athenian circumvallation. The Spartans invade Argos, and an Athenian fleet supporting them raids the coast of Laconia. Plays: Aristophanes (-448 to -380), The Birds. Euripides (-480 to -406), Ion; Electra; Iphigenia in Tauris (Iphigenia among the Taurins), set in the Chersonesus Taurica (Crim Tartary) peninsula N of the Hellespont, inhabited by the savage Tauri; Agamemnon offends Artemis, causing her to detain the Greek fleet sailing for Troy at Aulis, and the seer Calchas tells him to sacrifice his daughter Iphigenia, but Artemis relents and substitutes a hind on the altar, carrying her away in a cloud to Tauris, making her a priestess required to sacrifice all strangers, but when her brother Orestes arrives, she flees with him, carrying a sacred wooden Artemis statue, which Sparta later claims to have; she is finally transformed into the goddess Hecate.

-413 Roman consuls: Aulus (Marcus) Cornelius Cossus and Lucius Furius Medullinus. Nicias is elected ruler of Athens, and sends reinforcements under Gen. Demosthenes to Sicily, while Syracuse receives aid from Sparta, Corinth, and Boeotia; the Athenians assaulting the heights of Epipolae begin to crack, and just as they are about to board an armada of 73 vessels to retreat, a lunar eclipse on the night of Aug. 27 causes soothsayers to counsel Nicias to hold firm, which he does, and the assinine Athenians are massacred and their fleet destroyed in Sept. in the Battle of Assinarus (Syracuse), with 50K captured or KIA, incl. gens. Demosthenes and Nicias; the POWs are put to work in the mines; Alcibiades gets the Spartans to capture the Athenian fortress of Decelea (Dekeleia) (Tatoi) in N Attica, bringing Athenian agricultural to a virtual standstill. Darius II quells a revolt in Lydia in W Asia Minor; Tissaphernes (d. -395) becomes Persian satrap of coastal Asia Minor. Perdikkas II dies, and his son (by a slave woman) Archelaus I (-413 to -399) murders his uncle, cousin, and half-brother to become king of Macedonia (until -399), moving the court to Pella, building up its infantry, and encouraging Hellenization, inviting Euripides and other Greek artists; meanwhle the Athenian defeat at Syracuse that destroys most of their fleet puts him in a position to set the price of Macedonian timber, and after he supplies them all they want they become his friends and shower him with honors.
-412 The 92nd Olympiad. Roman consuls: Quintus Fabius Ambustus Vibulanus and Gaius Furius Pacilus. The Sicilian defeat causes the popular party in Athens to be thrown out, and Theramenes (-455 to -404) to be elected ruler of Athens; the College of Ten Deliberators (probouloi) replaces many of the functions of the Areopagus Council; a 5% harbor tariff replaces tribute among the Delian League allies; the Athenians use their last 1K talents to rebuild their lost fleet, but have to recruit green sailors; Rhodes breaks with Athens and its Delian League. Donald Trump, er, Alcibiades negotiates the Treaty of Miletus between the Spartans and Persians, which recognizes the Persians' right to subjugate the Ionian cities in return for money to build a Peloponnesian fleet to use to harass Athenian grain shipments from Egypt and the Black Sea; the Spartans then turn on Alcibiades, causing him to flee to the court of Persian satrap Tissaphernes. Ephesus revolts against Athens and sides with Sparta in the Peloponnesian War. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), Helen. Births: Greek Cynic philosopher Diogenes of Sinope (the Cynic) (d. -323) (b. -404?) in Sinope, Pontus; founder of the Cynic School of Philosophy; his father Icesias is a banker who is convicted of debasing coinage, causing Diogenes to have to leave Sinope for Athens, where he gets Cynic philosopher Antisthenes to take him in and begins living like a dog in a tub (large ceramic jar) in the marketplace, masturbating in public, hence the name cynic (canine) (like a dog), carrying a lamp in daytime to look for an honest man; sabotages the lectures of Plato, criticizing and embarrassing him and Alexander the Great; is captured by pirates on a voyage to Aegina, sold as a slave in Crete to Xeniades of Corinth, and set free and made tutor of his children; teacher of Zeno of Citium - he's not on the pedophile list?
-411 Roman consuls: Marcus Papirius Mugillanus and Spurius (Gaius) Nautius Rutilus. In July after Alcibiades promises Persian support, the oligarchy of the Four Hundred led by Antiphon, Peisander, Theramenes, and Phrynicus overthrows the Athenian democracy; the Athenian fleet at Samos refuses to recognize the new govt.; the Peloponnesians attack Euboea, causing the oligarchy to send a small fleet, which is defeated, and the oligarchs attempt to hand Athens over to Sparta, causing them to be overthrown by Theramenes (-455 to -404), who establishes the Constitution of the Five Thousand; Alcibiades is returned to favor in Athens, and in Sept. leads the Athenians in a V over the Spartans in the naval Battle of Cynossema in the Thracian Chersonese (Galipoli Peninsula). Plays: Aristophanes (-448 to -380), Thesmophoriazusae (Gr. "Women Celebrating the Festival of the Thesmophoria) (The Poet and the Women); another satire of Euripides; Lysistrata; the women try to end the Peloponnesian Wars by denying the men sex. Births: Greek statesman-gen. Timoleon of Corinth (d. -337); son of Timodemus.


-410 Roman consuls: Manius Aemilius Mamercinus and Gaius Valerius Potitus Volusus. Darius II quells a revolt in Media, but loses Egypt. The Athenians under Alcibiades decisively win the naval Battle of Cyzicus against the Spartan navy and supporting Persian army, but the new demoagogue Cleophon (d. -404) muffs peace overtures; meanwhile, democracy is restored in good ole Athens, and Thrasybulus (Thrasybolus) (d. -389) and Thrasyllus (Thrasyllos) (d. -406) are elected rulers (strategoi). Nicocles dies, and his son Evagoras (d. -374), who had been exiled by the Phoenicians sneaks back in with 50 followers to become king of Salamis in Cyprus (until -374), going on to cultivate the friendship of Athens and Persia and extend his control to all of Cyprus. In this decade Greek physician-historian Ctesias of Cnidus (the Cnidian) (-400) of the Cnidian School of Medicine (rival to Hippocrates) flourishes, becoming physician to Achaemenid king Artaxerxes II and accompanying him on his 401 B.C.E. expedition against his brother Cyrus the Younger, going on to write Persica (23 vols.) (a reply to Herodotus founded in the Persian royal archives) and Indica, the first full monograph on NW India, giving the Persian view, describing a land full of fantastic monsters incl. elephants and talking parrots, containing the first Western description of a unicorn, a white beast with blue eyes, purple head, and multicolored horn, which cures epilepsy, along with a description of Indian medicine, along with a statement that Indians disdain death; he also writes a treatise on medicine (lost), On the Tributes of Asia (lost), and Periodos (Periegesis) (Periplous) (3 vols.), a geographical treatise on Asia incl. Egypt, the Black Sea region, and Italy. Art: Late in this cent. the Etruscan bronze Mars of Todi statue is sculpted. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), Phoenissae (The Phoenician Women).
-409 An Athenian expedition under Thrasyllus captures Colophon in Lydia, and raids the Ionian countryside, but is defeated outside Ephesus by a combined force from Ephesus, Syracuse and Persia. Sparta recovers Pylos, which falls into obscurity until -369. Alcibiades recovers Byzantium from the Spartans under Clearchus (d. -401), and clears the Bosphorus for Athenian shipping. Seeing his chance with the mutual exhaustion of Athens and Syracuse, the Carthaginians under Hannibal Mago (d. -406) invade Sicily to avenge his grandfather Hamilcar, defeating the Sicilian Greeks, then capturing the cities of Selinus (modern-day Selinunte) and Himera, torturing and killing 3K POWs as revenge for his grandfather's defeat in the Battle of Himera in -480 before returning to Carthage with spoils; "Himera... was conquered by force and the barbarians gave themselves to a long ruthless massacre of all those who remained there... Hannibal plundered the sacred places and, snatching away the people who took refuge there, set them on fire and razed the city to the ground, which had been inhabited for 240 years..." (Diodorus Siculus); in 2008-11 12K+ untouched graves are unearthed in Himera. The city of Rhodes on the island of Rhodes, designed by Greek urban planner ("the Father of European Urban Planning") Hippodamus of Miletus (-498 to -408) is built, based on the Hippodamian (Grid) Plan, becoming its 4th major town after Camirus (Kamiros), Lindus (Lindos), and Ialysus (Isalyssos). Roman consuls: Gnaeus Cornelius Cossus and Lucius Furius Medullinus. Plays: Sophocles (-496 to -406), Philoctetes; about the son of Poeas, Hercules' armor bearer and friend, who slays Priam's son Paris at Troy with his poison arrows after being retrieved from the island of Lemnos by Odysseus and healed of a snake wound to the foot by Machaon.
-408 The 93rd Olympiad. Roman consuls: Publius Cornelius Rutilus Cossus (dictator) and Gaius Julius Iullus and Publius Cornelius Cossus and Gaius Servilius Ahala. The Carthaginians destroy the city of Himera in N Sicily. Alcibiades returns to Athens in triumph after a 7-year absence, leading the religious procession to Eleusis to atone for his impiety in -415, and getting a promotion to CIC, after which he rejoins his fleet in Samos. Pleistoanax dies, and his son Pausanias (d. -395) (king in -445 to -426) becomes Agiad king of Sparta (until -395); both Sparta and Athens court Darius II Persia, who decides to back Sparta, while his wife Parysatis talks him into appointing his younger son Cyrus the Younger (d. -401) (brother of Artaxerxes III) as satrap of all Asia Minor in place of Tissaphernes, who is reduced to satrap of Caria in the SW; Cyrus is sent with funds to Sardis to raise Persian support for Sparta; in the fall Spartan adm. Lysander arrives in Ephesus and begins rebuilding the Spartan fleet with help from Cyrus; too bad, Cyrus uses the opportunity to build his own personal mercenary army with rebellious idea in mind; a Panhellenic gathering is held in Olympia, at which Nihilist philosopher Gorgias (-483 to -378) speaks against the Spartan-Persian alliance. Inventions: A building material inventory in Greece mentions the wheelbarrow ("1-wheeler"). Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), The Phoenician Women; Orestes; after they are both performed he gets pissed-off and leaves Athens for Magnesia, followed by the court of Archelaus I of Macedonia in Pella at his invitation. Births: Greek astronomer-mathematician Eudoxus of Cnidus (d. -355) (-390 to -337?); student of Plato. Syracuse tyrant Dion (d. -354); son of Hipparinus; brother-in-law of Dionysius I. Deaths: Greek architect Hippodamus of Miletus (b. -498).
-407 Thrasybulus recaptures Abdera and Thasos on the coast of Thrace; meanwhile Alcibiades attempts to lure the Spartans out of Ephesus to do battle, but adm. Lysander doesn't bite; too bad, Alcibiades goes out searching for supplies, leaving behind his boyhood friend Antiochus in command of the Athenian fleet blockading the Spartan fleet in Ephesus, but the green Greek disobeys orders and tries to draw the Spartans led by new navarch (navy CIC) Lysander into battle with a decoy force, and loses the notable naval Battle of Notium (Ephesus) to them and a Persian force, causing Alcibiades to be stripped of command for being a bozo, causing him to leave Athens permanently, returning to his own land in the Thracian Chersonese. Exiled moderate dem. leader Hermocrates of Syracuse is KIA trying to force his way back into Syracuse, and the Carthaginians decide to conquer the Greek cities of Sicily. Roman consuls: Lucius Furius Medullinus and Gaius Valerius Potitus Volusus and Umerius (Gnaeus) Fabius Vibulanus and Gaius Servilius Ahala. Births: Greek philosopher Speusippus (d. -339) in Athens; Plato's nephew by sister Potone, and his successor at the Academy.

-406 Carthage invades Sicily and attacks Acragas (Akragas), but plague breaks out in their camp, killing Hannibal Mago, after which Himilco (d. -396) becomes CIC (until -397) and finishes capturing the city, followed by Gela, which is sacked and destroyed, then Camarina, whose survivors flee to Syracuse; too bad, the soldiers carry the plague back to Carthage after Hannibal Mago is killed by it. Conon and Cleophon are elected rulers of Athens; Callicratidas replaces Lysander as head of the Spartan fleet (navarch), which sieges Methymna on Lesbos (known for its excellent wine) to interrupt the Athenian grain supply; Lysander is made cmdr. in his place; the Athenians then lose the naval Battle of Mytilene to Sparta, after which the Spartans siege Mytilene until the Athenians raise another fleet under Conon and seven other strategoi and use new tactics to win the naval Battle of Arginusae near Canae E of Lesbos Island against Sparta under Callicratidas, after which at the instigation of Theremenes the Athenians put six of the eight gens. (incl. the son of Pericles) to death for not rescuing drowning sailors; a peace overture by Sparta is rejected by Cleophon, and Persian satrap Cyrus the Younger orders the Spartans to put Lysander in charge of another fleet in the Hellespont. Jerusalem is fully rebuilt in all its ancient glory (Jehovah's Witnesses). Roman consuls: Publius Cornelius Rutilus Cossus and Gnaeus Cornelius Cossus and Numerius (Gnaeus) Fabius Ambustus and Lucius Valerius Potitus. Plays: Euripides (-480 to -406), Iphigenia at Aulis; The Bacchants (Bacchae). Deaths: Greek dramatist Sophocles (b. -496) in Athens; leaves the play Oedipus at Colonus (his birthplace), which is produced by his grandson Sophocles in -401; same chars. Oedipus' son-brother King Polyneices of Argos, Creon's son Haemon, and King Thesus of Athens; old blind Oedipus comes to Colonus to be with the Furies (Eumenides) and his daughters when he dies, and is absolved by Zeus for his crimes first. Greek tragedian Euripides (b. -480) in Macedonia; leaves 92 plays (23 tetralogies), of which 17 tragedies and one satyr play ("Cyclops") survive to modern times: "Whom the gods would destroy, they first make mad."
-405 Roman consuls: Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus and Quintus Quinctius Cincinnatus and Gaius Julius Iullus and Aulus Manlius Vulso Capitolinus and Lucius Furius Medullinus and Marius Aemilius Mamercinus (Mamercus). The Romans seige the pesky Etruscan military fort of Veii just 10 mi. from Rome, the richest city of the Etruscan League. I'll be right here, soldier? The Athenian fleet under Alcibiades follows the Spartan fleet under Lysander to the Hellespont, then attempts to warn the Athenian fleet under Conon at the mouth of the Aegospotami (Aegospotamos) River in Thrace (where it flows into the Hellespont) against a surprise attack, but are ignored, and the Athenian fleet is destroyed in Sept. in the naval Battle of Aegospotami in the Sea of Marmara, causing Conon to flee to Cyprus, all but ending the Peloponnesian War; Lysander then sails across the Aegean, replacing pro-Athenian democracies on allied islands with decarchies (oligarchies of ten) under a Spartan overseer (harmost), after which Spartan king Pausanias sieges Athens while Lysander's fleet blockades Piraeus, closing their grain route through the Hellespont to starve them out, causing Theramenes to lead an embassy for 3 mo. to negotiate terms of capitulation. Former govt. clerk Dionysius I (the Elder) (-430 to -367) becomes tyrant of Syracuse, and signs a treaty with plague-weakened Carthaginians under Hamilco leaving Carthage in control of most of W and S Sicily, then fortifies Syracuse with a wall, fortifies Epipolae, removes and/or enslaves Greek oligarchs from Naxos, Catana and Leontini, and confiscates their land to give it to his Sicilian and Italian mercenaries, and enfranchises the serfs to build up his army, with plans of ousting the Carthaginians completely. Euripides' plays "The Bacchae" and "Iphigenia at Aulis" are posth. performed at the Dionysia festival, and win first prize. Architecture: The Erechtheum in Athens (begun -421) is finished. Plays: Aristophanes (-448 to -380), The Frogs; satirizes the late Euripides again; given an unprecedented 2nd performance plus a civic crown; the earliest literary mention of an inn, at which a group of men devour 16 loaves of bread, 20 meatballs, garlic, fish, and cheese, and then walk out without paying; the chorus of the frogs is "Brek-ek-ek-ex, ko-ax, ko-ax", which later becomes a cheer of Yale U. students.



-404 The 94th Olympiad. On Apr. 25 after pesky never-say-die Cleophon is tried and executed, the Peloponnesian War (begun -431) ends with the surrender of plague-stricken Athens, which has been starved into submission over the winter; Theramenes secures peace terms, allowing Athens to keep its independence while giving up all foreign possessions (which become subjects of the Persian Empire) and its bedraggled fleet, and becoming an ally of Sparta; the Long Walls (built -457) are torn down and burned to the accompaniment of Spartan flutes; the Spartans are now the rulers of Greece, having to wear shades their future is so bright?; the Athenian oligarchs, led by Critias and Theramenes and supported by the Spartans and Lysander set up a Commission of Thirty to devise a new constitution, but instead they seize power as the Thirty Tyrants (until -400), executing several citizens and suspending rights; Critias has Theramenes condemned to drink hemlock for treason; Alcibiades flees to Phrygia in NW Asia Minor under protection of Persian satrap Pharnabazus (d. -373), seeking help for Athens, then being assassinated by orders of Pharnabazus after the Spartans learn about it and tell him to; 3K of the richest citizens are enfranchised in name only, and many more are exiled or flee to Argos and Thebes; in the fall Thrasybulus leads some exiles to Phyle and then to the Piraeus; Lysander conquers Samos for Sparta; in 1997 an Athenian graveyard for soldiers killed in the Pelopponesian War is unearthed. Persian king (since -423) Darius II Ochus Nothus dies of illness in Babylon, and is succeeded by his eldest son Artaxerxes II Mnemon (-445 to -358) as king of Persia (until -358); his younger brother Cyrus the Younger (d. -401) is accused by Tissaphernes, satrap of Caria of plotting to kill him, but after their mother Parysatis intervenes he is pardoned. Amyrtaeus (Amyrtaios) (Amenirdisu) of Sais (d. -399), a relative of the 26th Egyptian Dynasty royal family revolts against the Persians, ending the First Persian Occupation (begun -525), and becomes the one and only ruler of the Egyptian 28th (XXVIII) Dynasty (ends -398). Marcus Furius Camillus (-447 to -365) becomes Roman censor, beginning a long rise. Roman consuls: Gaius Valerius Potitus Volusus and Manius Sergius Fidenas and Publius Cornelius Maluginensis and Gnaeus Cornelius Cossus and Kaeso Fabius Ambustus and Spurius Nautius Rutilus. Deaths: Greek Athenian statesman Alcibiades (b. -450) in Mount Elaphus, Phrygia (assassinated). Persian king (-423 to -404) Darius II Ochus Nothus (b. ?) (d. -405?) in Babylon.
-403 Early in the year as Athens groans under the rule of the Spartan-imposed Thirty Tyrants (incl. Plato's uncle and cousin, both of whom are ex-friends of Socrates), a bunch of Spartan Quislings of a conservative and vengeful stamp (who order more than 1.5K executions before they are defeated) are defeated at the Battle of Munichia at Piraeus by Athenian exile forces under Thrasybulus, who kills Critias and restores democracy to Athens once again, electing the govt. of The Ten, while the Thirty, er, Twenty Nine flee to Eleusis and asks Sparta for help, and they send Lysander, but he is replaced by less hawkish king Pausanias, who narrowly defeats the Athenians at the naval Battle of Piraeus, with both sides taking large numbers of casualies, then arranges a settlement, incl. reunification of Athens and Piraeus, a gen. amnesty (excluding the oligarchic extremists after Athenian orator Lysias gives a speech) and the abolition of the Spartan decarchies in the former Athenian allies; Athenian orator Andocides is allowed to return, but his oligarchic tendencies cause him to be distrusted; the new Athenian regime adopts the 24-letter Ionian Alphabet, developed in the Anatolian city of Miletus, which incl. the lovely letters eta and omega, becoming the most common classical Greek alphabet by the middle of the cent. Dionysius I of Syracuse conquers Catana, then sieges Naxos. The state of Jin in Shanxi in NE China is partitioned among three landholding families, and the state of Chao (Zhao) (ends -222) in NE and C Shanxi and SW Hopeh is founded by Chao Chi, while Confucian marquis Wen of Wei (d. -387) becomes ruler of the state of Wei. Roman consuls: Manius Aemilius Mamercinus and Lucius Valerius Potitus and Appius Claudius Crassis Inregillensis and Marcus Quinctilius Varus and Lucius Julius Iullus and Marcus Furius. Deaths: Greek Athenian tyrant Critias (b. -460) (KIA).
-402 Dionysius I of Syracuse conquers Naxos, then takes on Leontini. Archelaus I of Macedonia establishes a pro-Macedonian oligarchy in Larissa, Thessaly. Roman consuls: Gaius Servilius Ahala and Quintus Servilius Fidenas and Lucius Verginius Tricostus Esquilinus and Quintus Sulpicius Camerinus Cornutus and Aulus Manlius Vulso Capitolinus and Marius Sergius Fidenas. Births: Greek Athenian statesman-gen. Phocion (Phokion) (the Good) (d. -318); known for his frugality, honesty, virtue, and wisdom, getting elected strategos a record 45x; too bad, he disagrees with everybody else in the assembly, causing him to get plotted against; "The chopper of my speeches." (Demosthenes)

-401 Cyrus the Younger, satrap of Anatolia and brother of Artaxerxes III rebels, and is KIA in the Battle of Cunaxa near Babylon despite having the help of Greek mercenaries, the Ten Thousand, who stage a heroic retreat (Katabasis) through Armenia (ends -399), crying "Thalatta! Thalatta!" (The sea! The sea!) on Mt. Theches (Mt. Madur) in Surmene on the NE coast of Trabzon (Turkey), which is immortalized by Greek soldier Xenophon (-431 to -354) in his Anabasis (Gr. "An Ascent") (7 vols.) (an expedition from a coastline to the interior of a country, as opposed to katabasis, from the interior to the coast), ("One of the great adventures in human history" - Will Durant), about the Greek expedition of the Ten Thousand against Artaxerxes II of the Persians and the long journey home after their sponsor Cyrus the Younger is KIA in Babylon; how Spartan gen. Clearchus, the leader of the Ten Thousand is treacherously murdered in a conference by Tissaphernes, leaving Xenophon as one of the last three leaders of the soldiers, bravely leading them N from N Mesopotamia through Corduene and Armenia to the Black Sea at Trebizond; upon encountering some barbarians (Celts?), he puzzles about their strange drink, with the soundbyte: "There were stores within of wheat and barley and vegetables, and wine made from barley in great big bowls; the grains of barley malt lay floating in the beverage up to the lip of the vessel, and reeds lay in them, some longer, some shorter, without joints; when you were thirsty you must take one of these into your mouth, and suck. The beverage without admixture of water was very strong, and of a delicious flavor to certain palates, but the taste must be acquired"; Cyrus the Younger uses a mercenary force of Peltasts from Greece or Thrace, who wear foxskin Phrygian caps, patterned tunics, fawnskin boots, long cloak (zeira) with a bright geometric pattern, and crescent-shaped wicker shields (peltes), going on to become the main type of Greek mercenary infantry in the 4th cent. B.C.E. Orontes I (d. -366) becomes Persian satrap of Armenia. Zhou Wei Li Wang dies, and his son Zhou An Wang (d. -376) becomes Dong Zhou king #20 of China (until -376); the Spring and Autumn Period (begun -771) ends, and the Warring States Period begins among the seven states in the Zhou (Chou) Dynasty in China (ends -221). Roman consuls: Lucius Valerius Potitus and Marcus Furius Camillus and Manius Aemilius Mamercinus and Gnaeus Cornelius Cossus and Kaeso Fabius Ambustus and Lucius Julius Iullus. Plays: Oedipus at Colonus by the late Sophocles debuts in Athens.